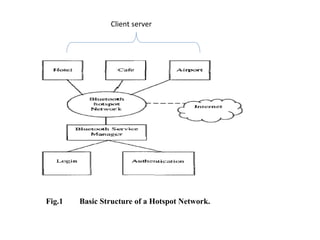
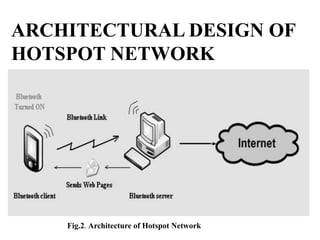
This document discusses Bluetooth hotspot technology. A Bluetooth hotspot allows multiple Bluetooth-enabled devices to access the internet through a single connection. It works on a client-server model, where the server connects to the internet and shares the connection with clients. Key technologies involved include Bluetooth, L2CAP for packet data transfer, RFCOMM for streaming data, and OBEX for object exchange. The document outlines the architecture and process of using a Bluetooth hotspot network, including how clients connect to the server and request web pages. The objectives are to provide low-cost wireless internet access to multiple devices and help bridge the digital divide.