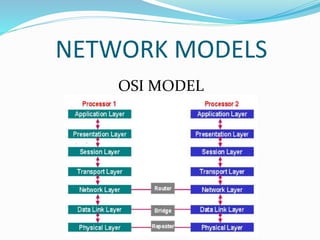
This document defines and describes various aspects of computer networks. It explains that a network is a collection of connected computing devices that communicate and share resources, and can transmit any combination of voice, video, and data. It also outlines requirements for networking like resource sharing and reliability. Additionally, it describes different types of networks, cables, networking devices, network models, IP addressing, classes of IP, subnetting, firewalls, types of firewalls, and wireless LAN topologies.