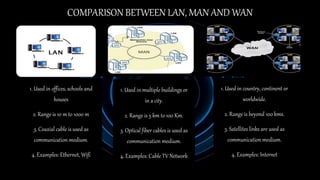
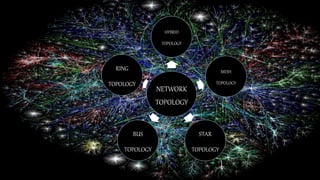
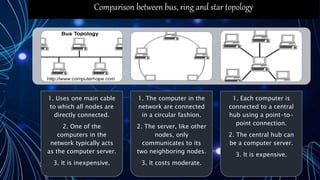
The document provides an overview of computer networking, defining it as a group of computers sharing resources through common communication protocols. It covers the history, applications, and different types of networks, including Local Area Networks (LAN), Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN), and Wide Area Networks (WAN), along with their characteristics and examples. The conclusion emphasizes the role of computer networks in data sharing and highlights the internet as a key example.