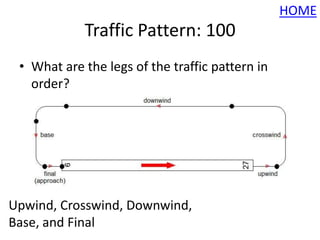
This document summarizes the rules and content of a semester 1 review game for aviation students. It provides the categories and point values that will be covered, as well as the rules of play which include only allowing one speaker at a time and a time limit for answering questions. The review covers topics like basics of flight, aircraft instruments, signs and markings, traffic patterns, communication and miscellaneous questions. It includes sample questions, answers and instructions that would be used in the review game.