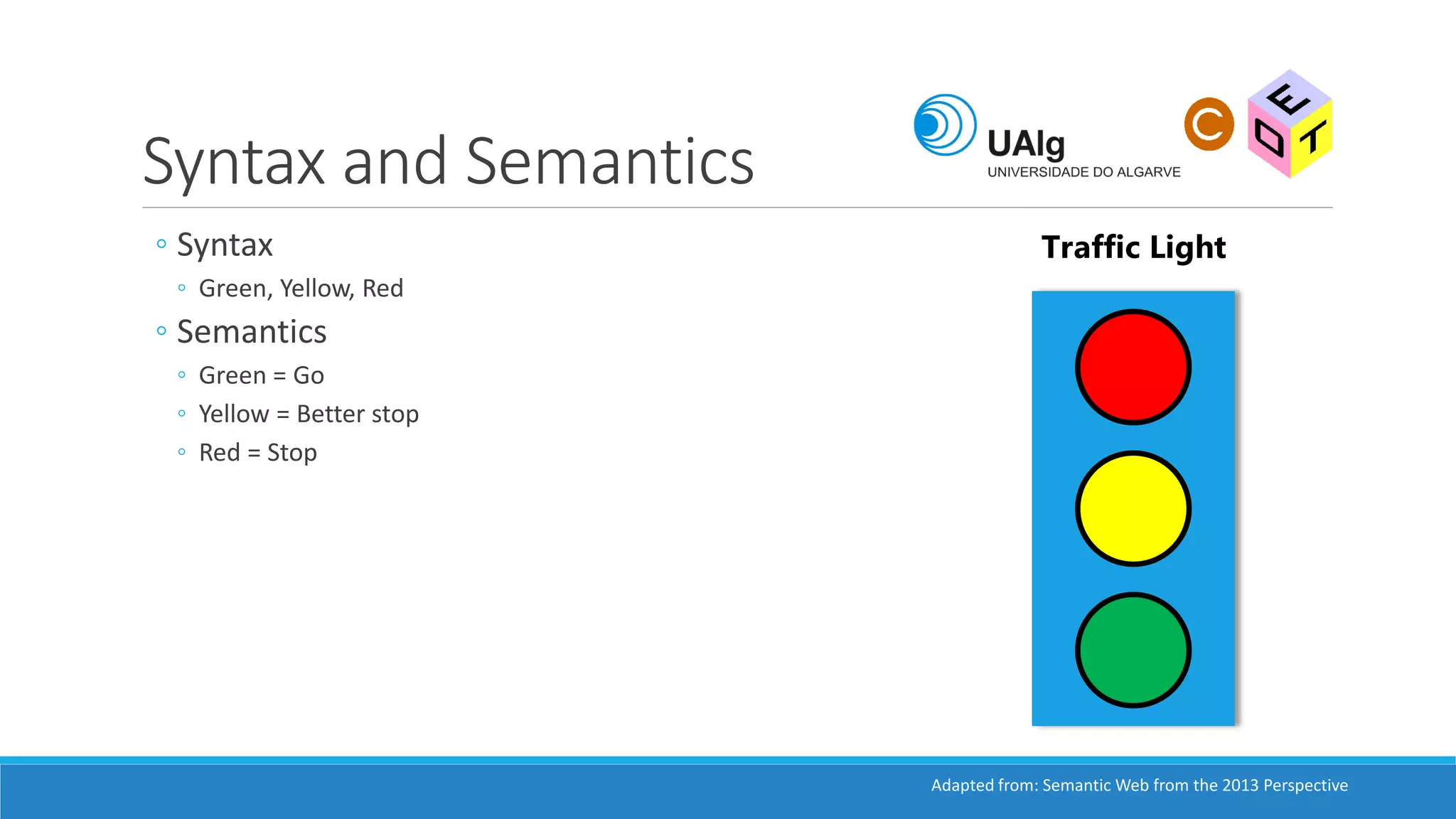
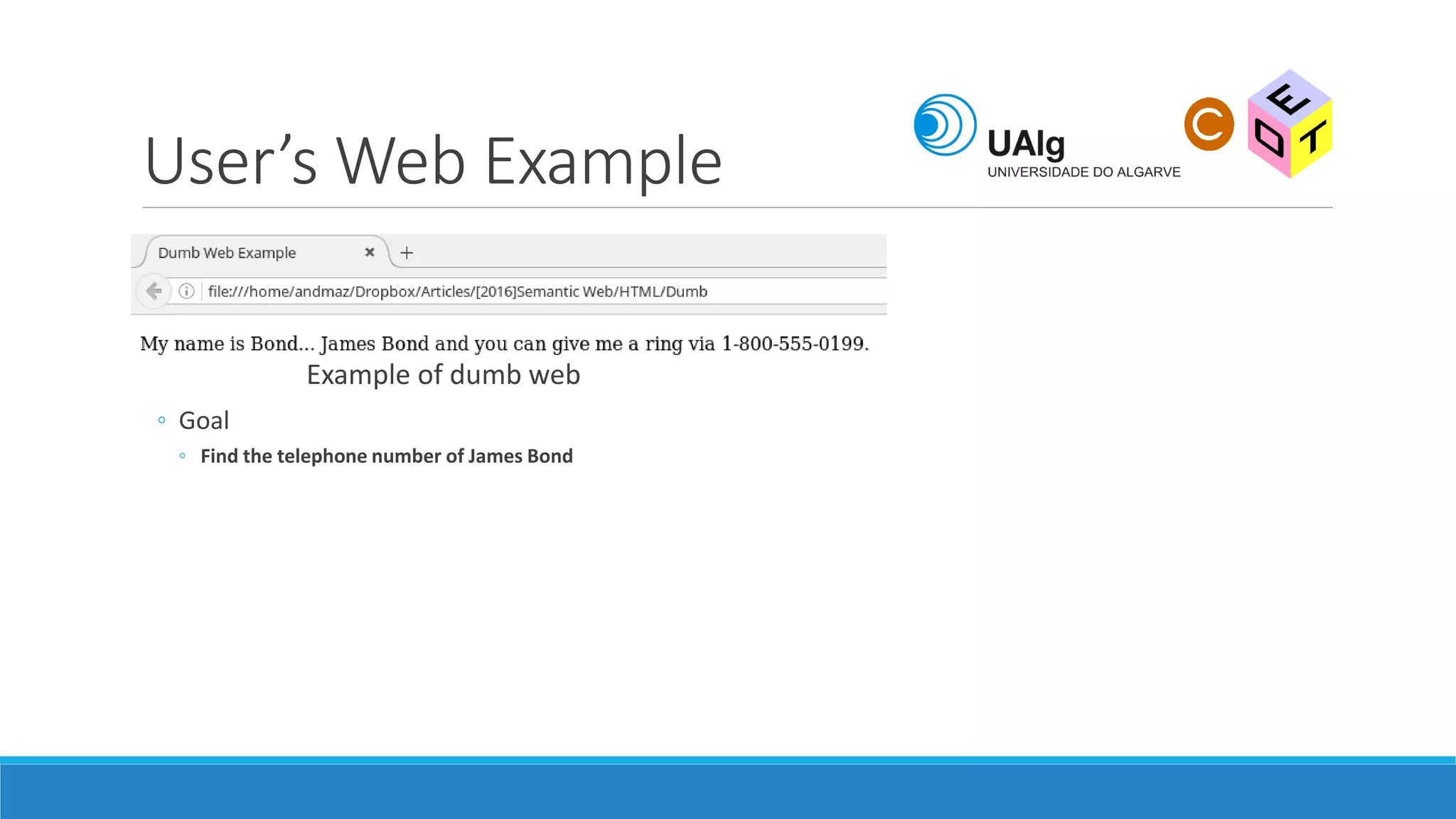
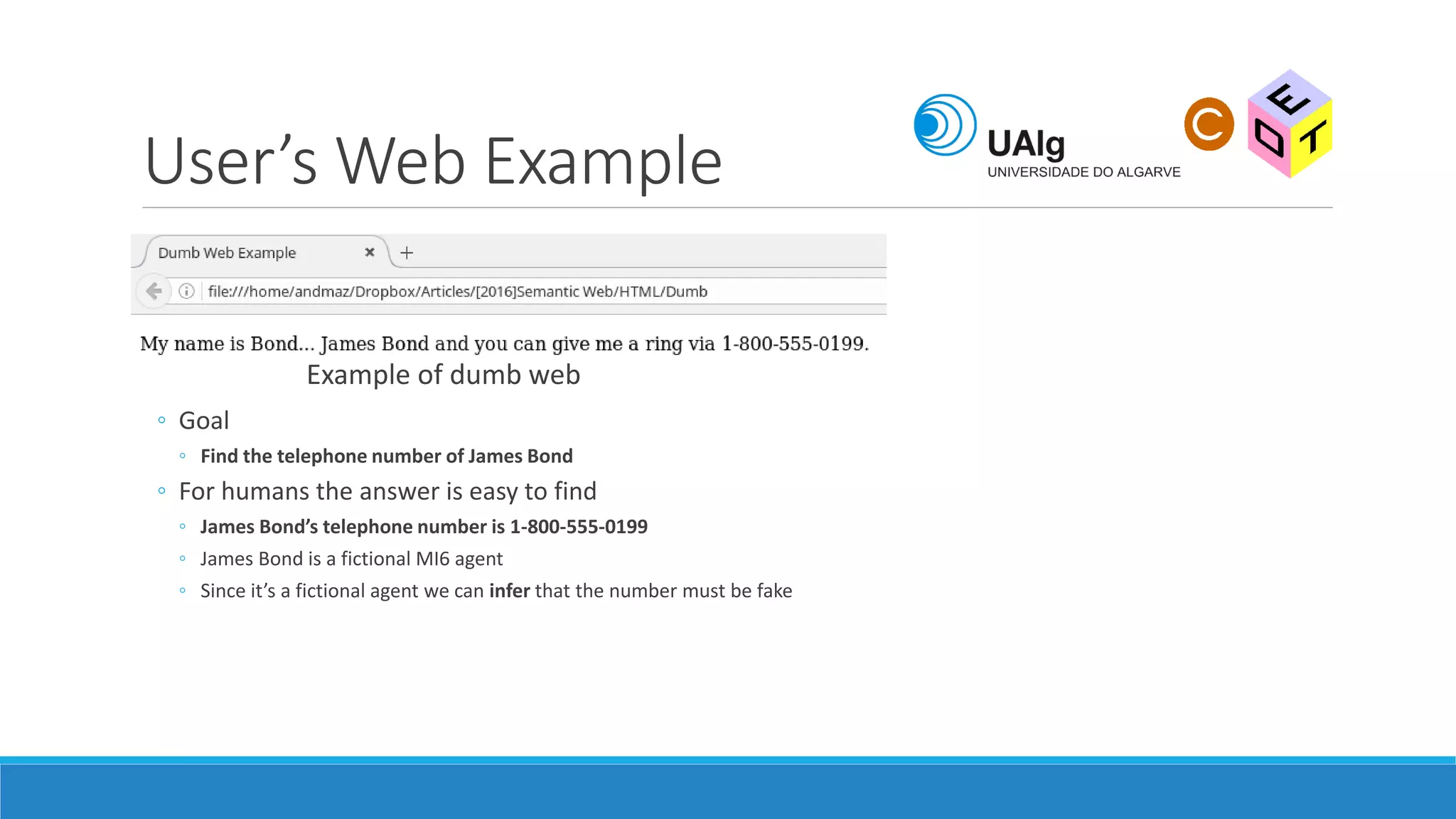
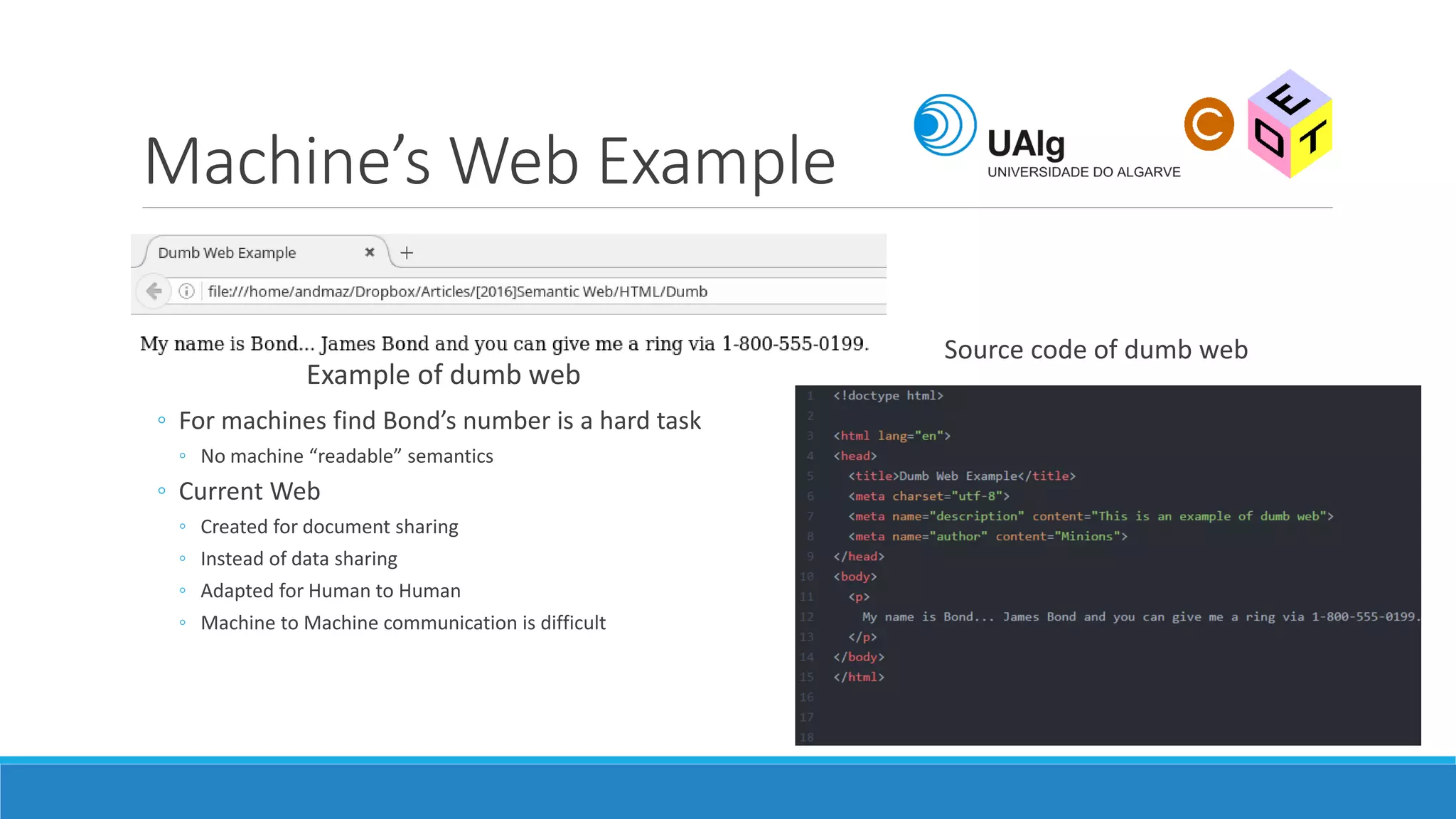
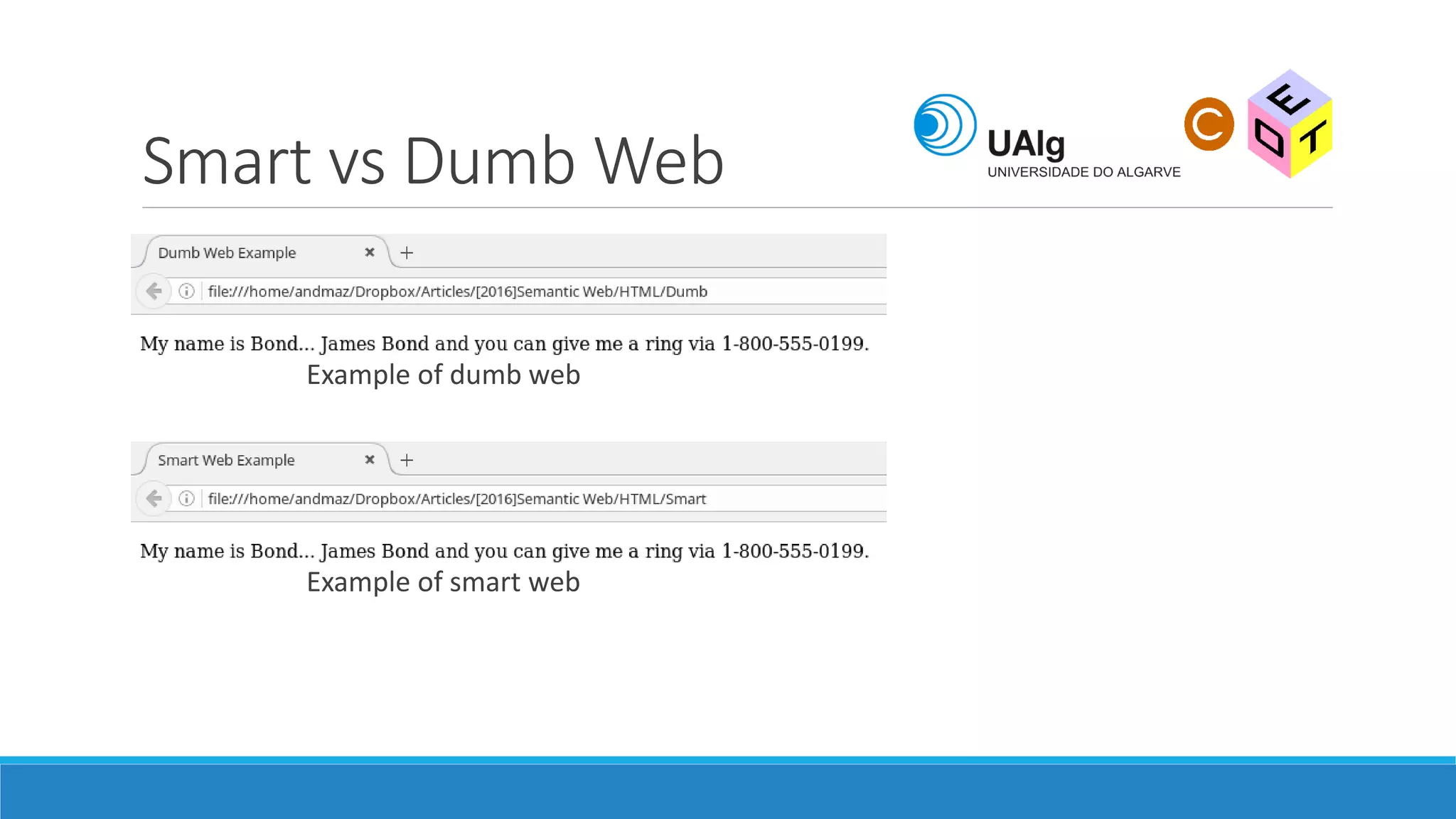
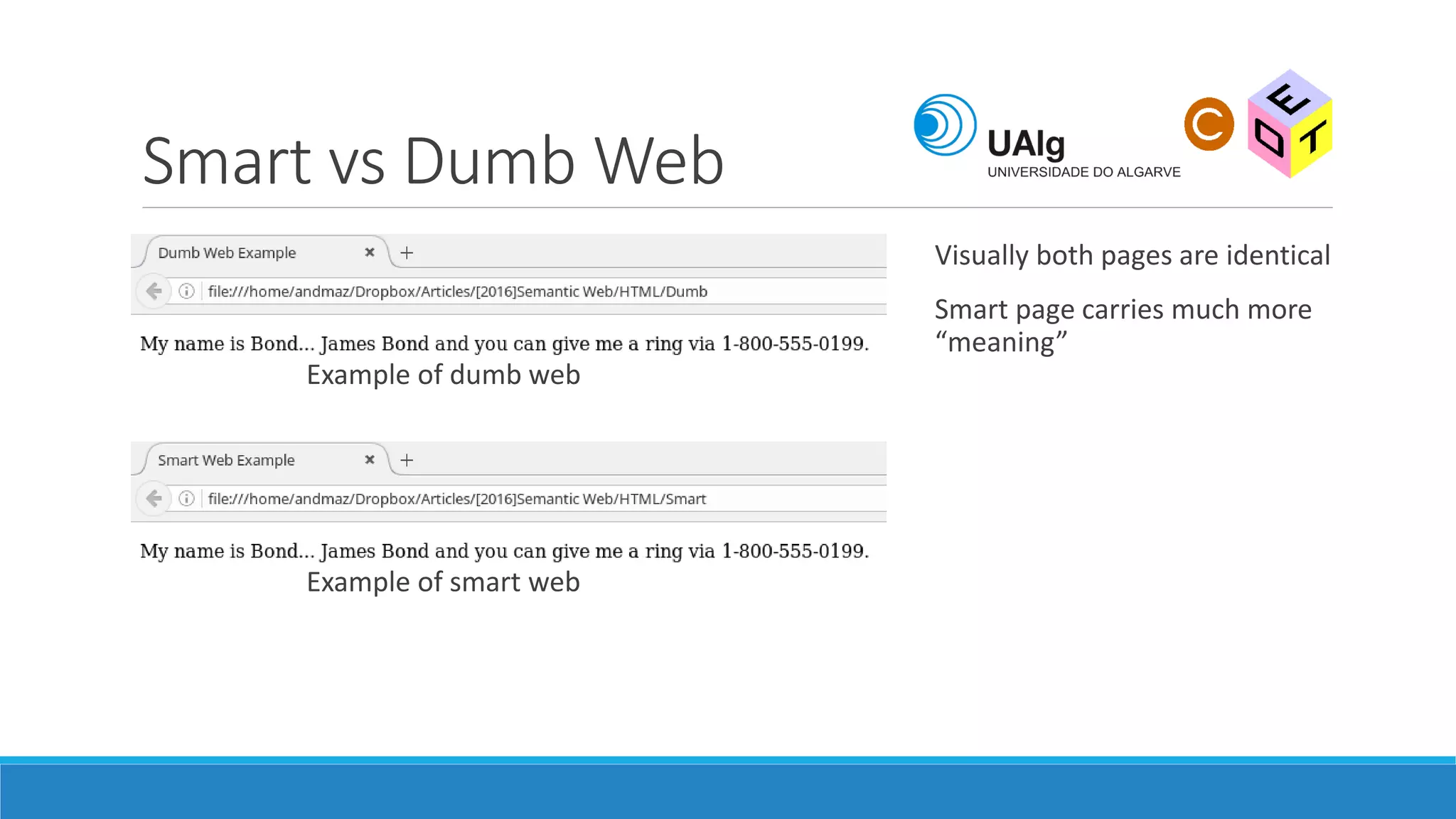
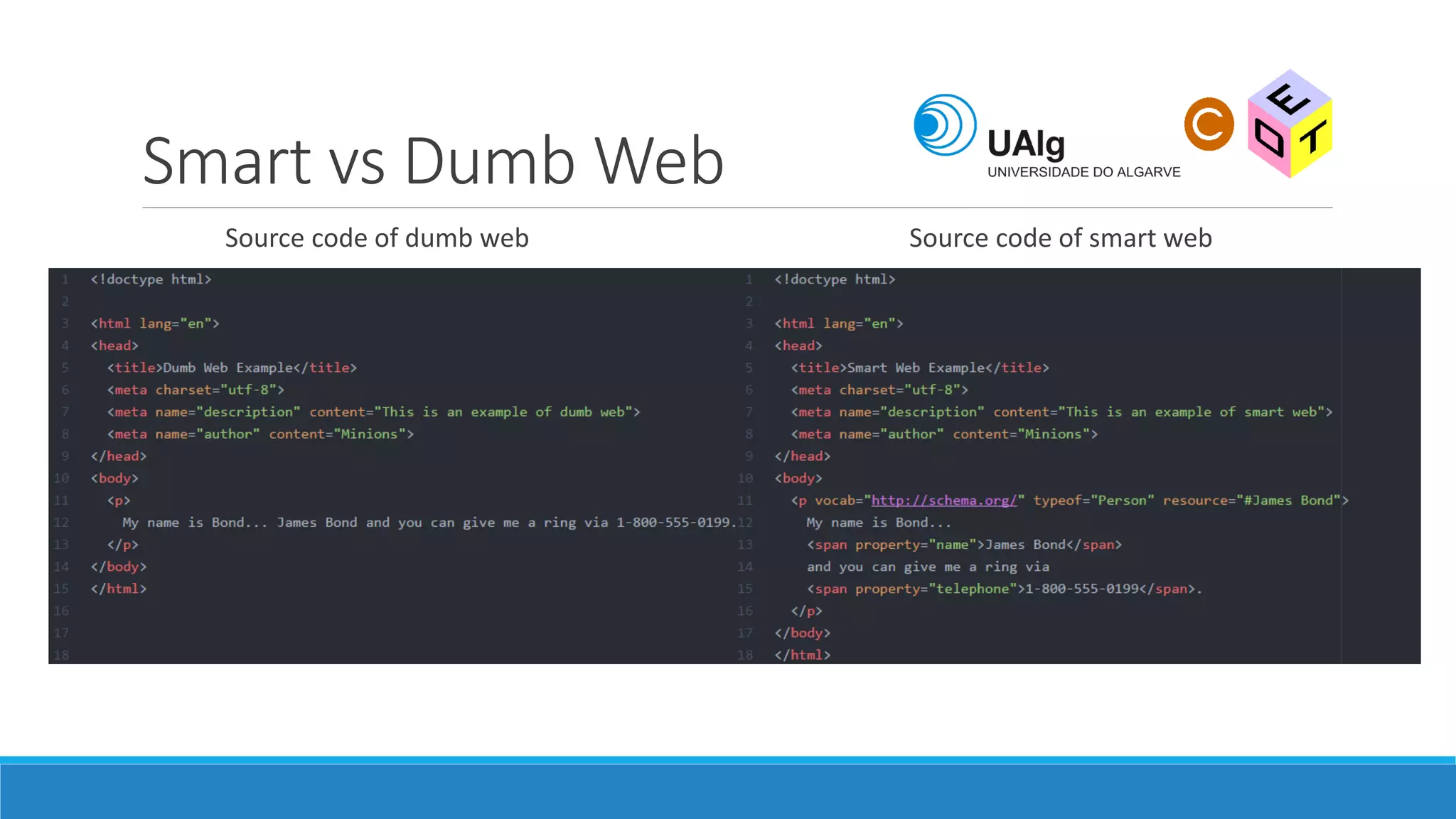
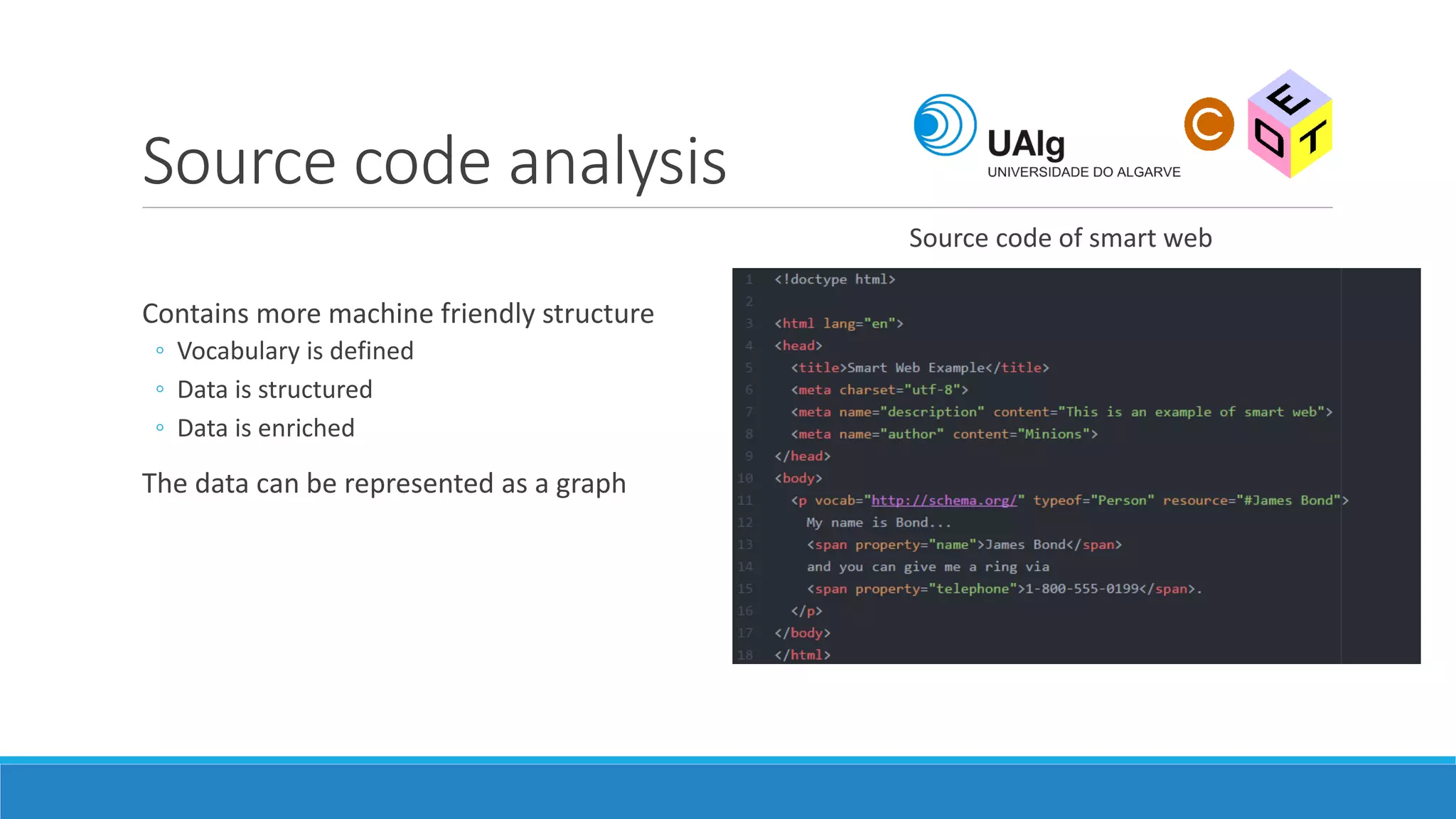
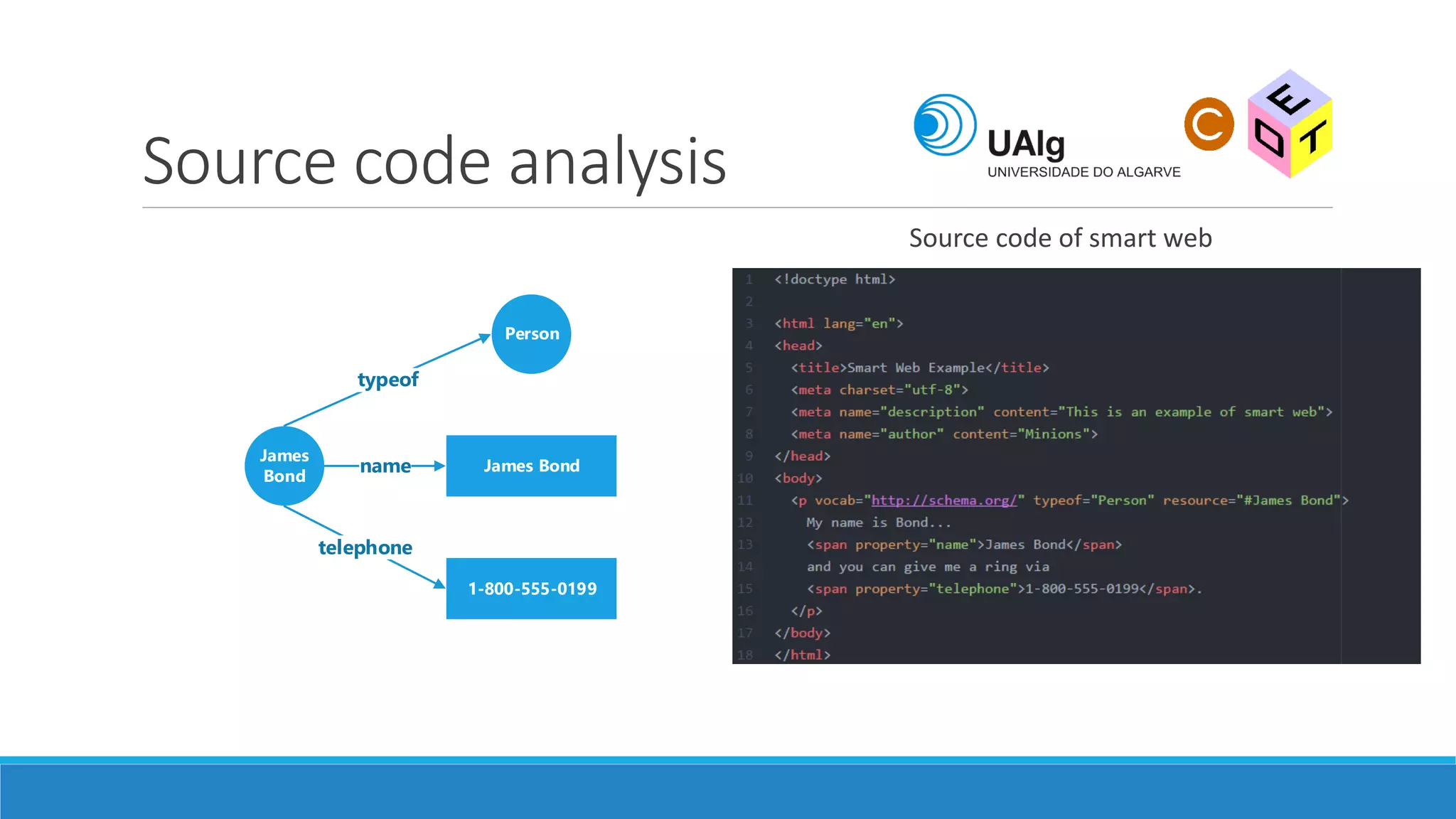
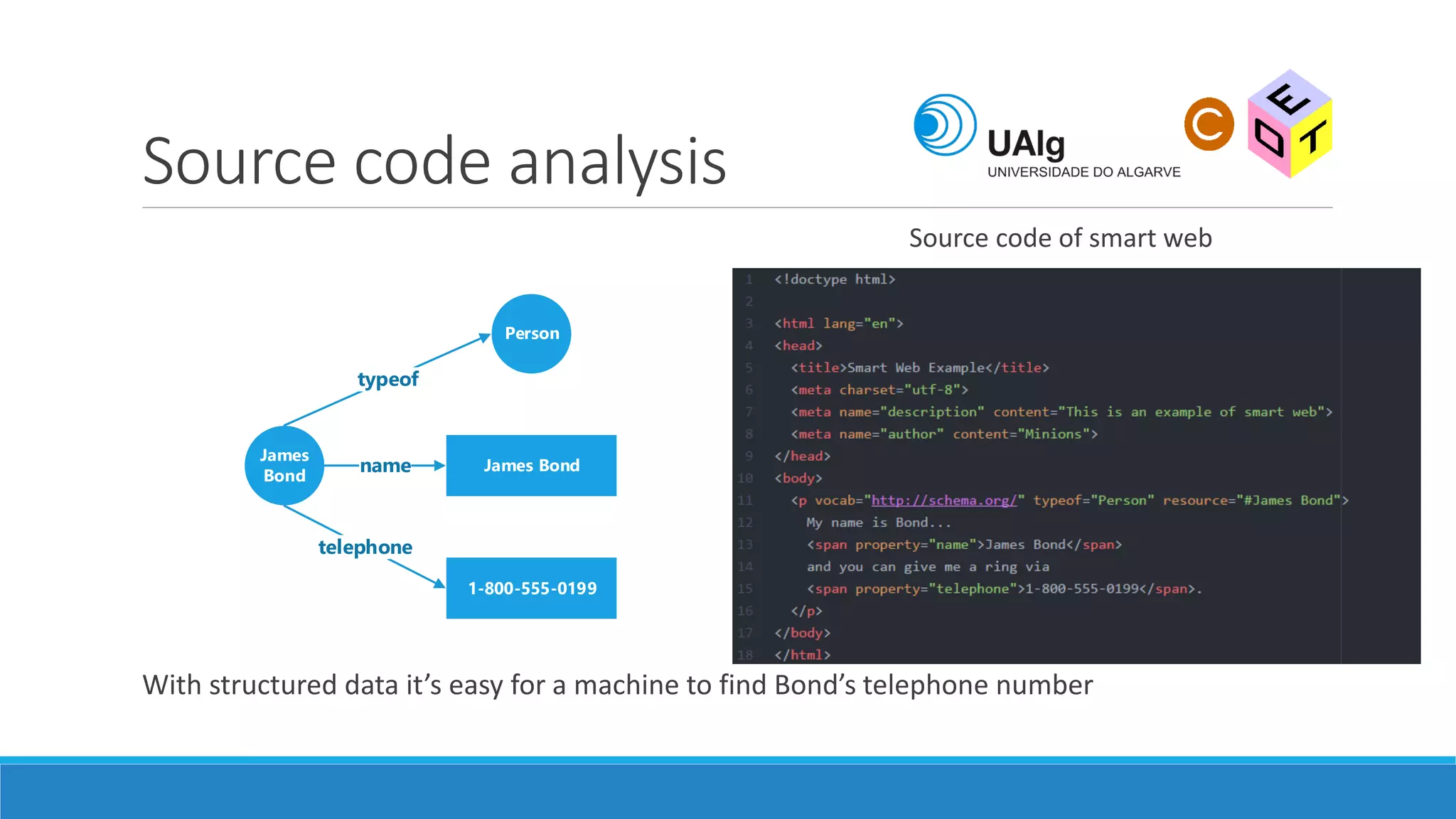
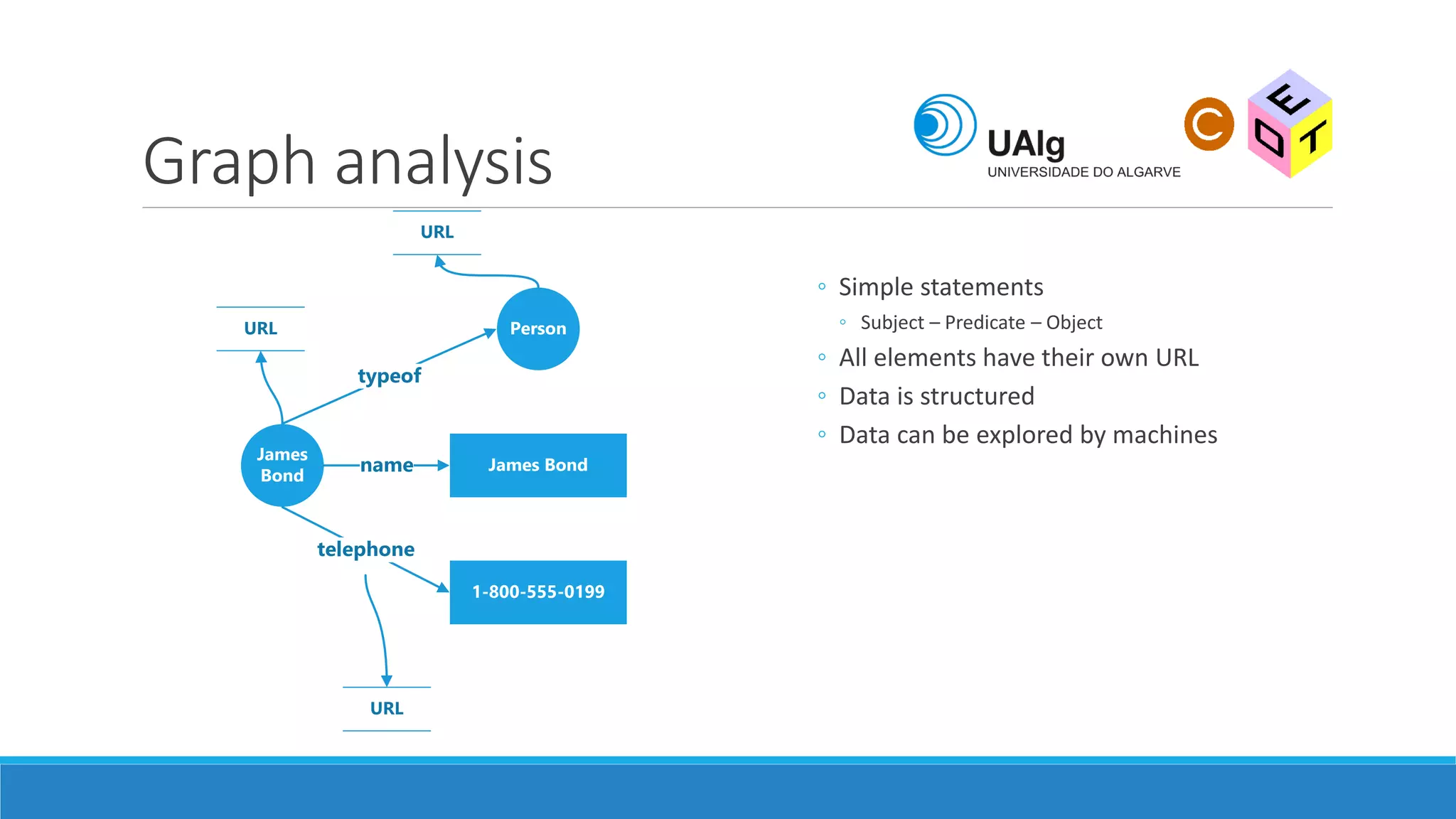
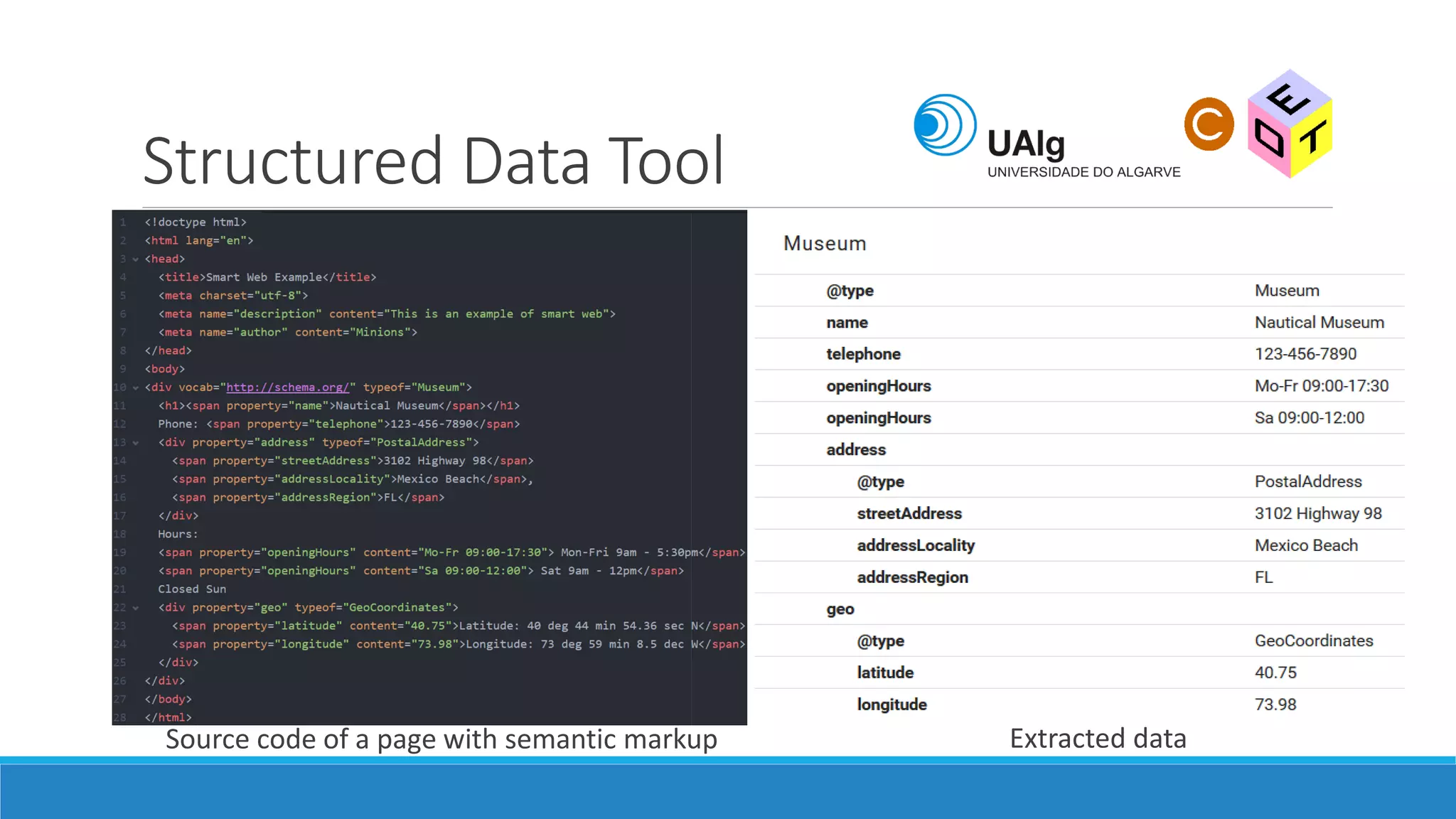
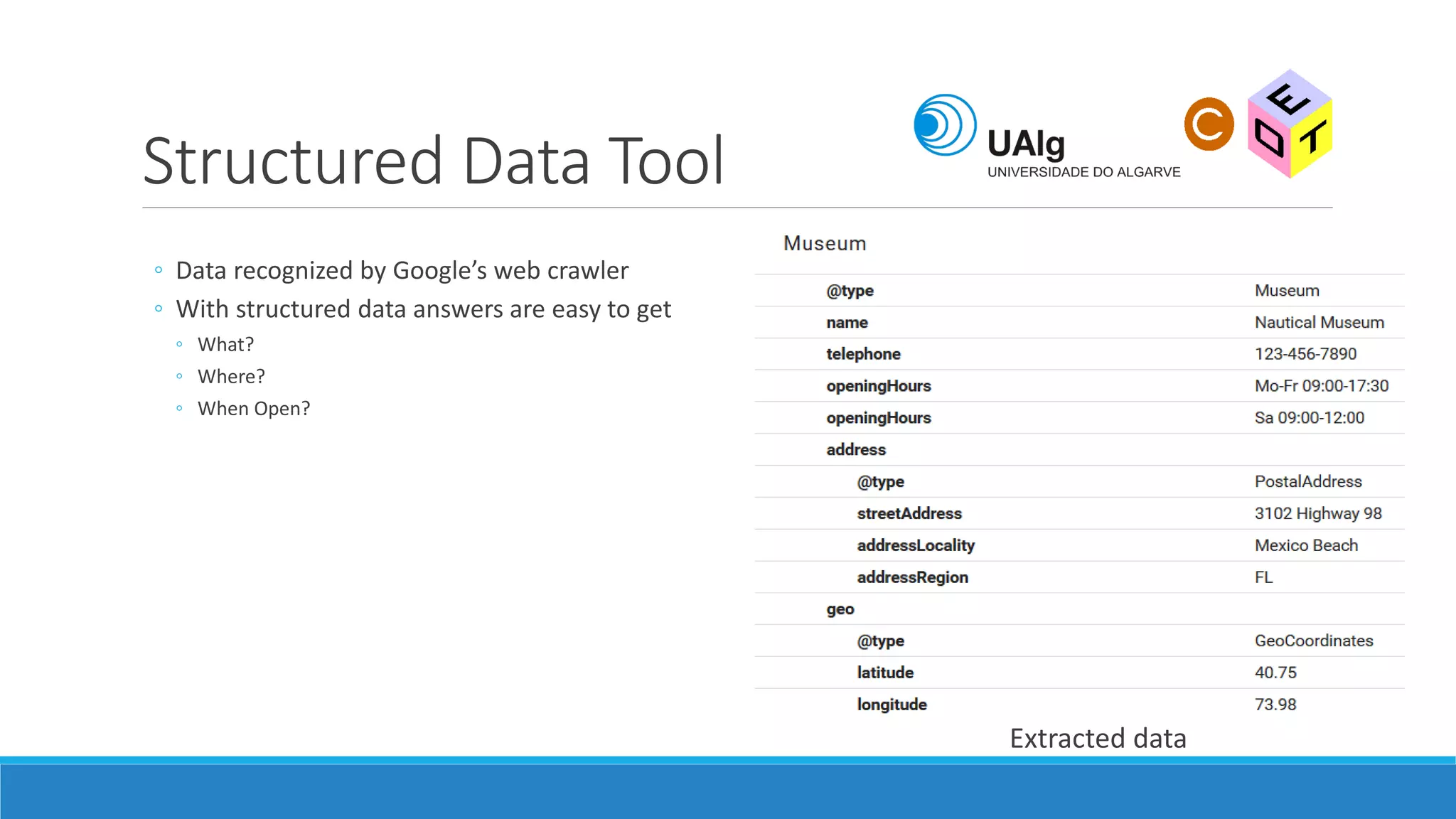
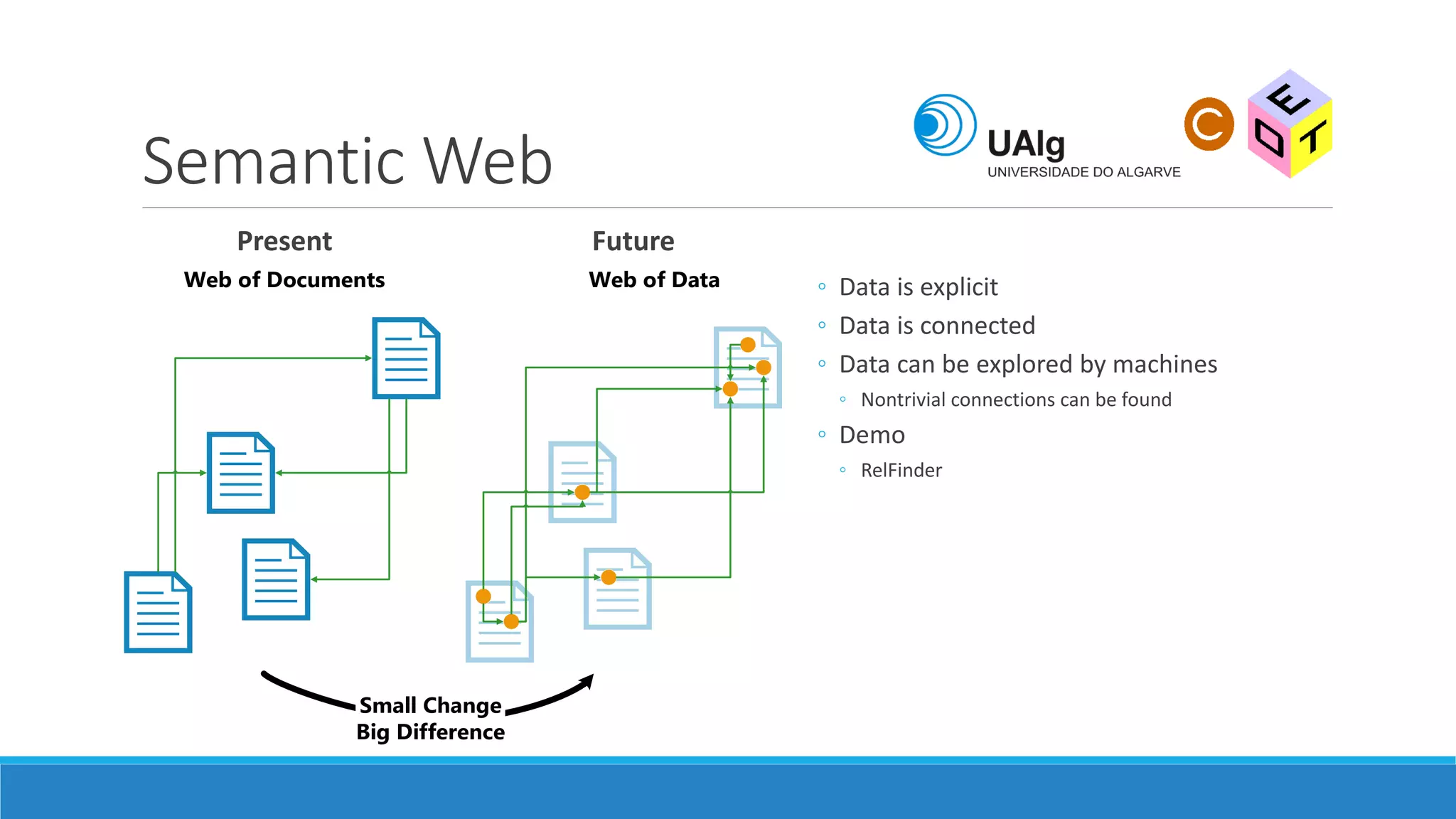
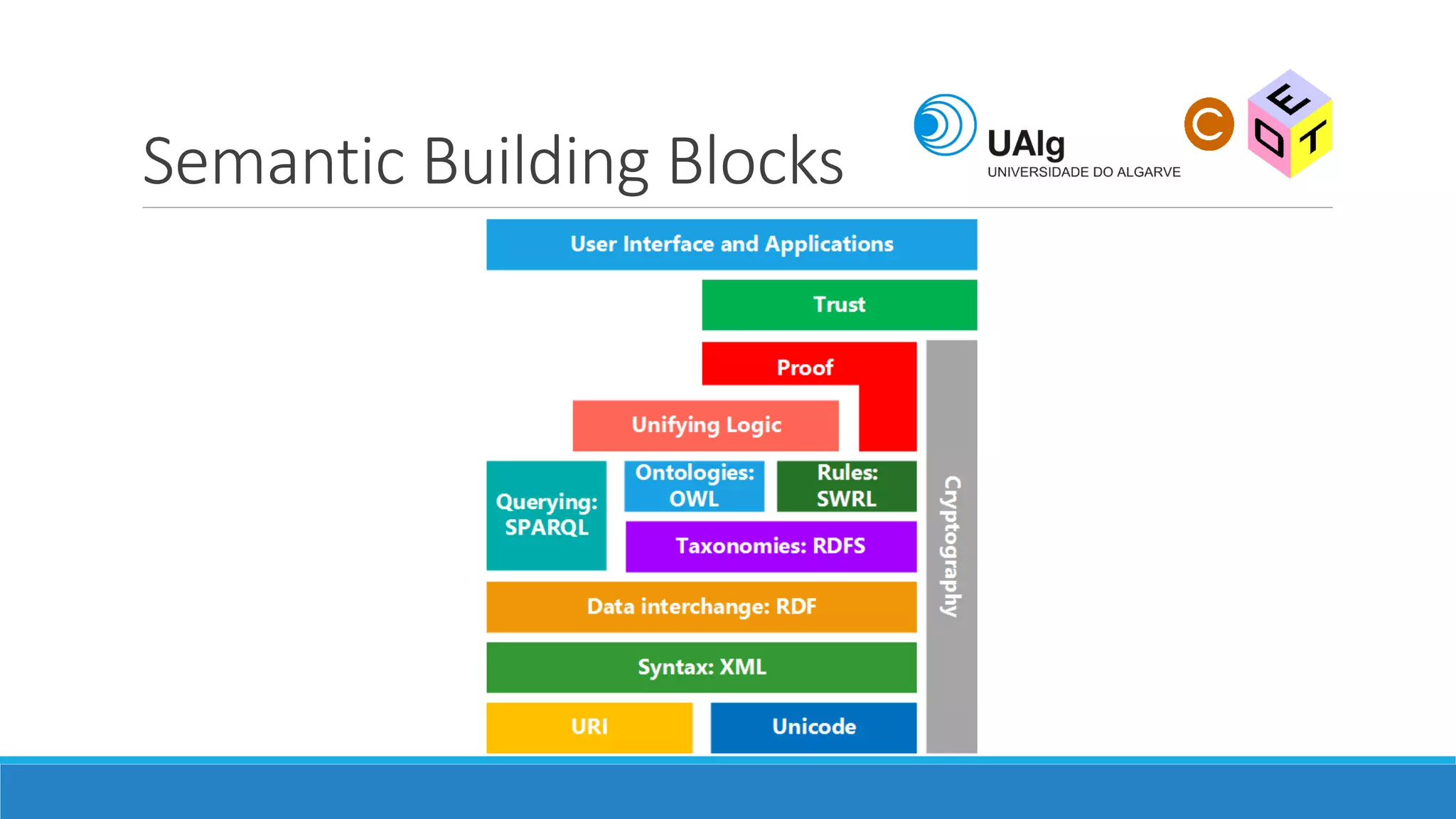
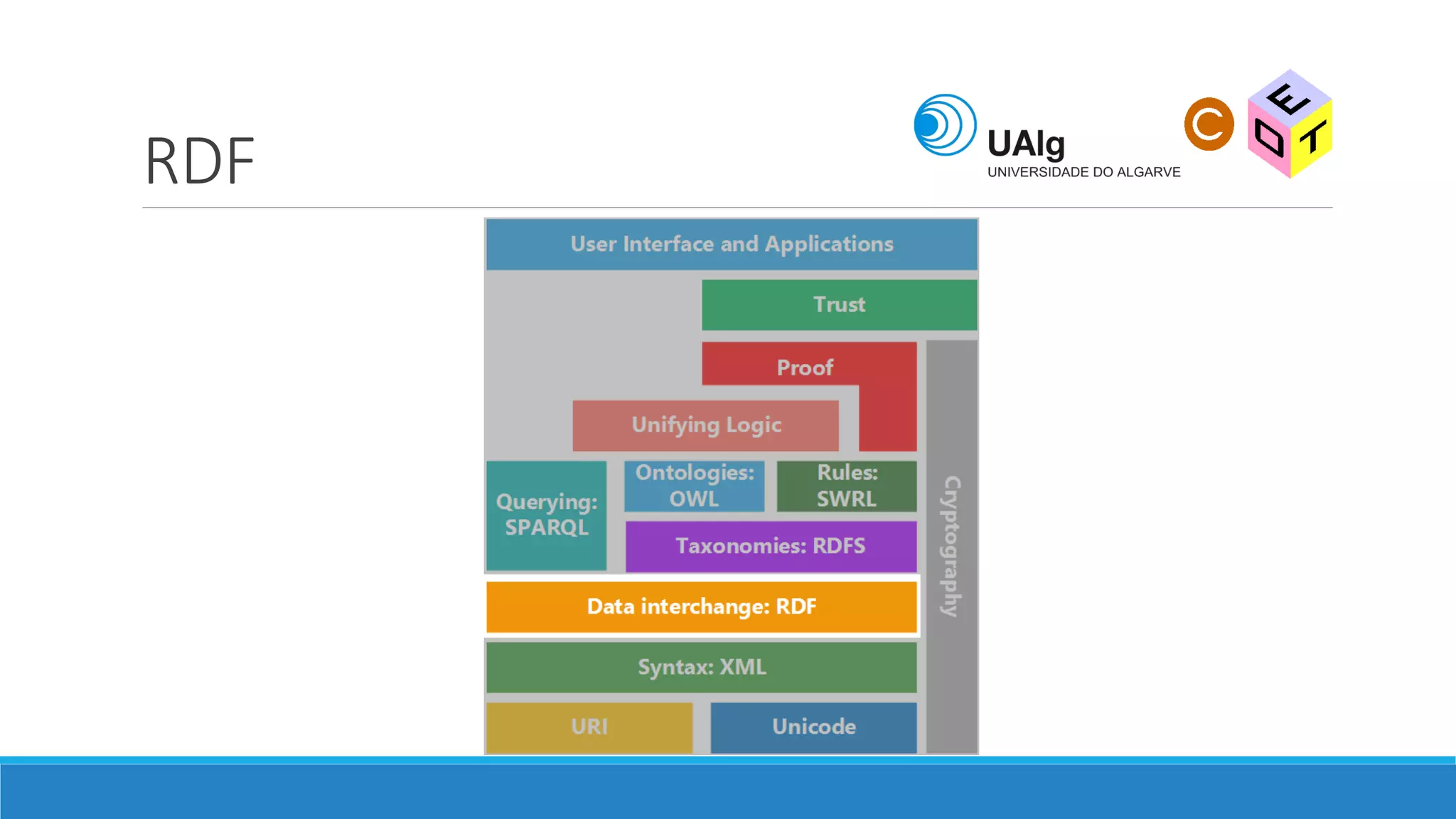
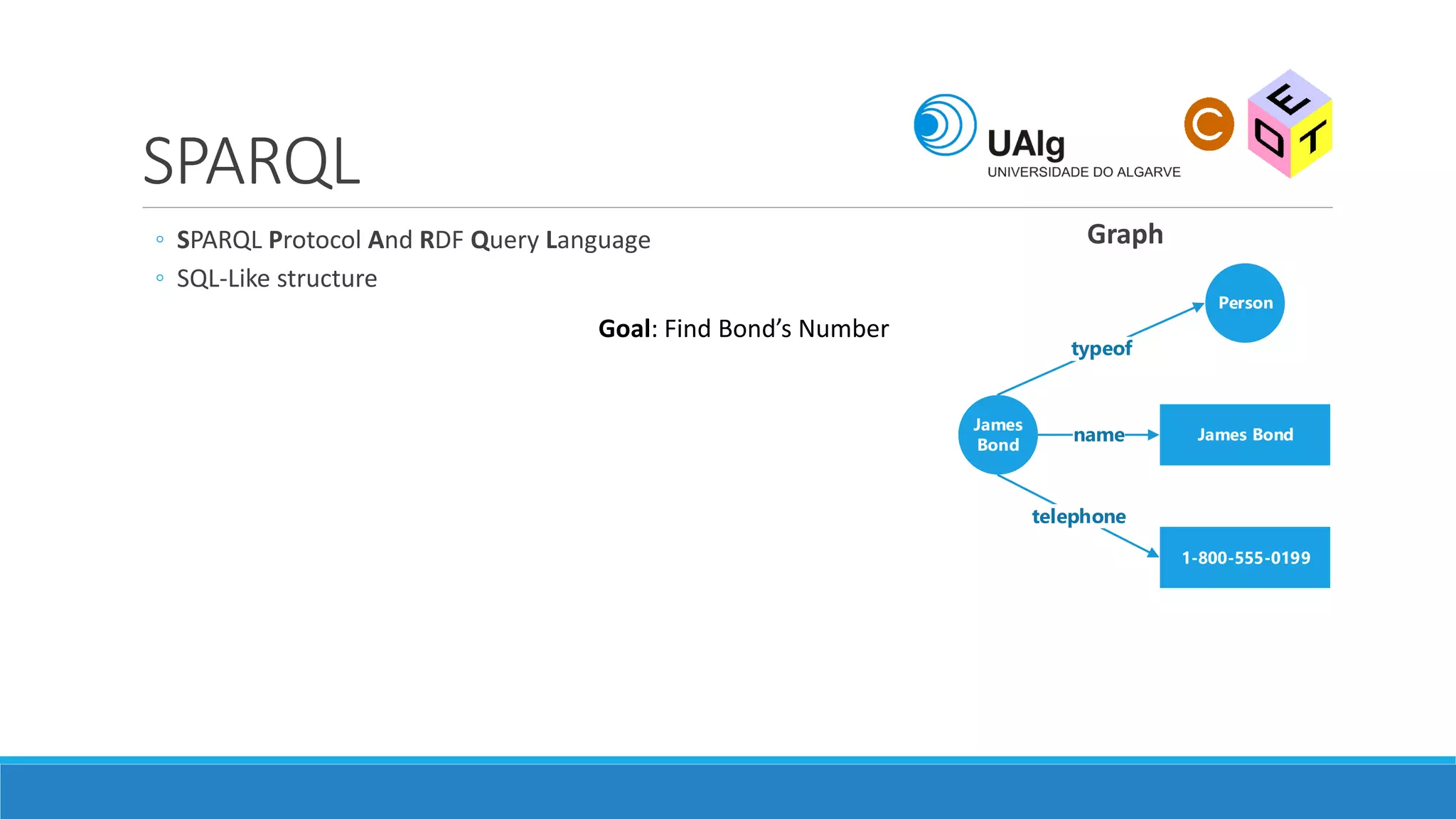
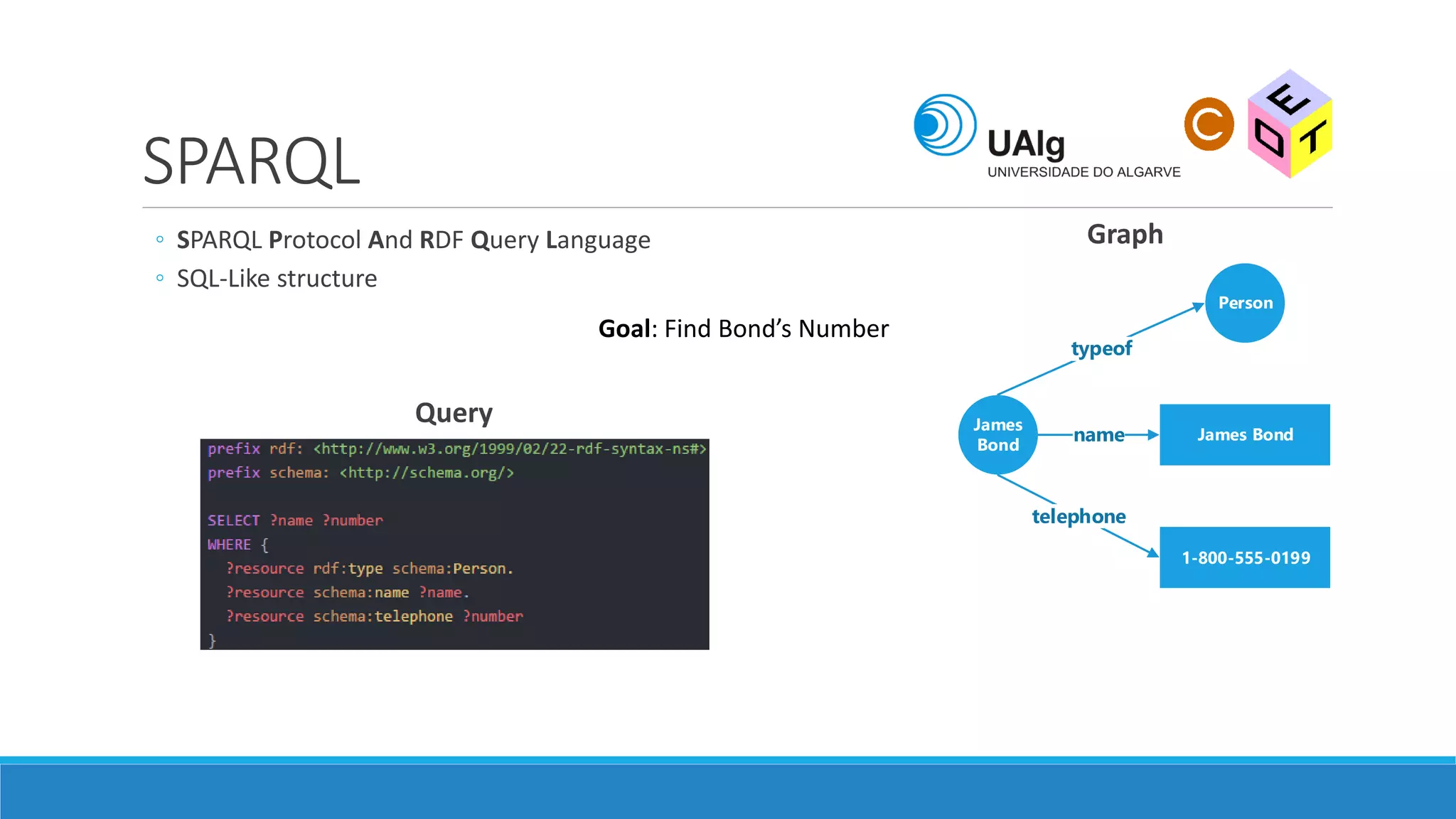
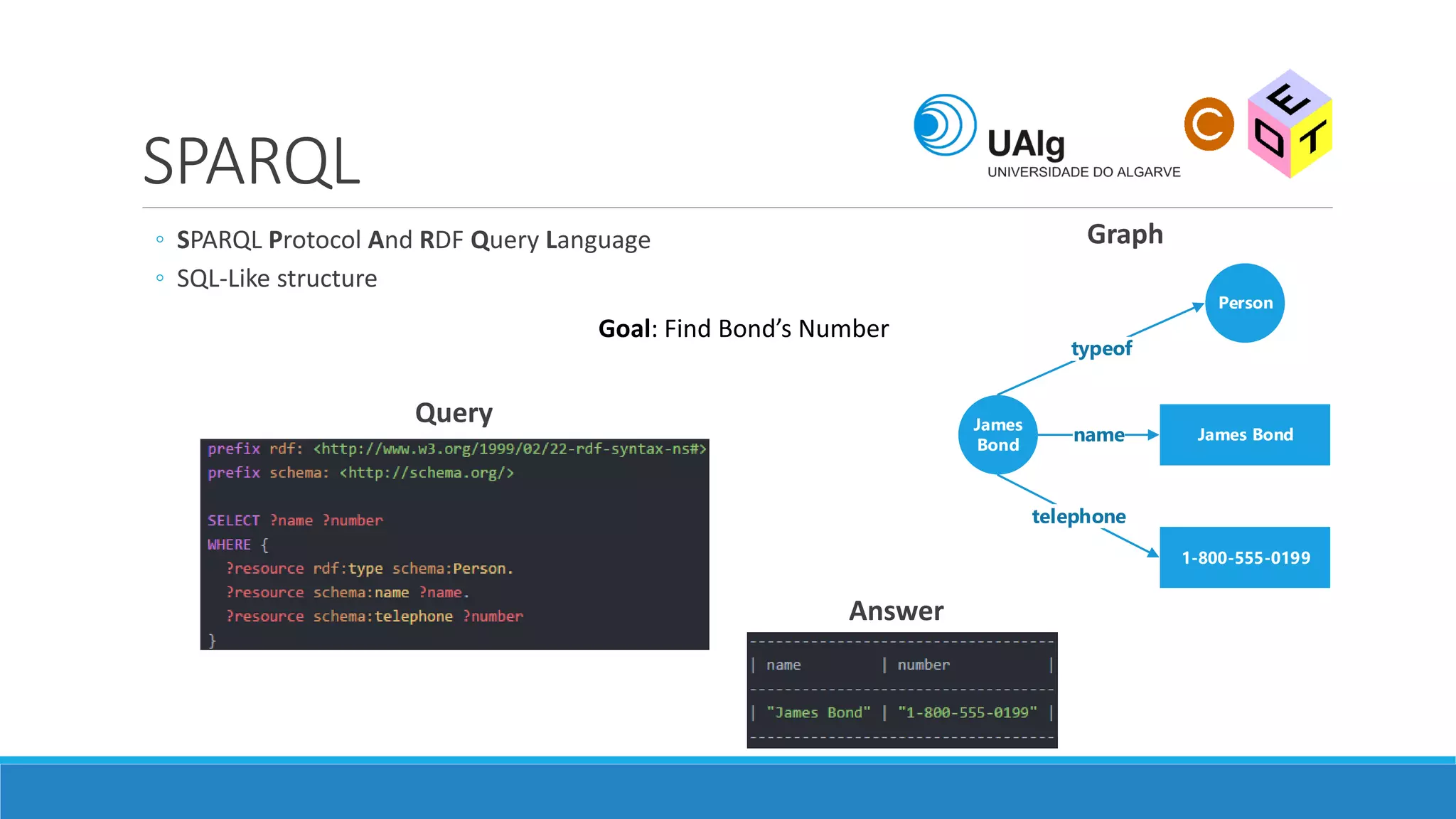
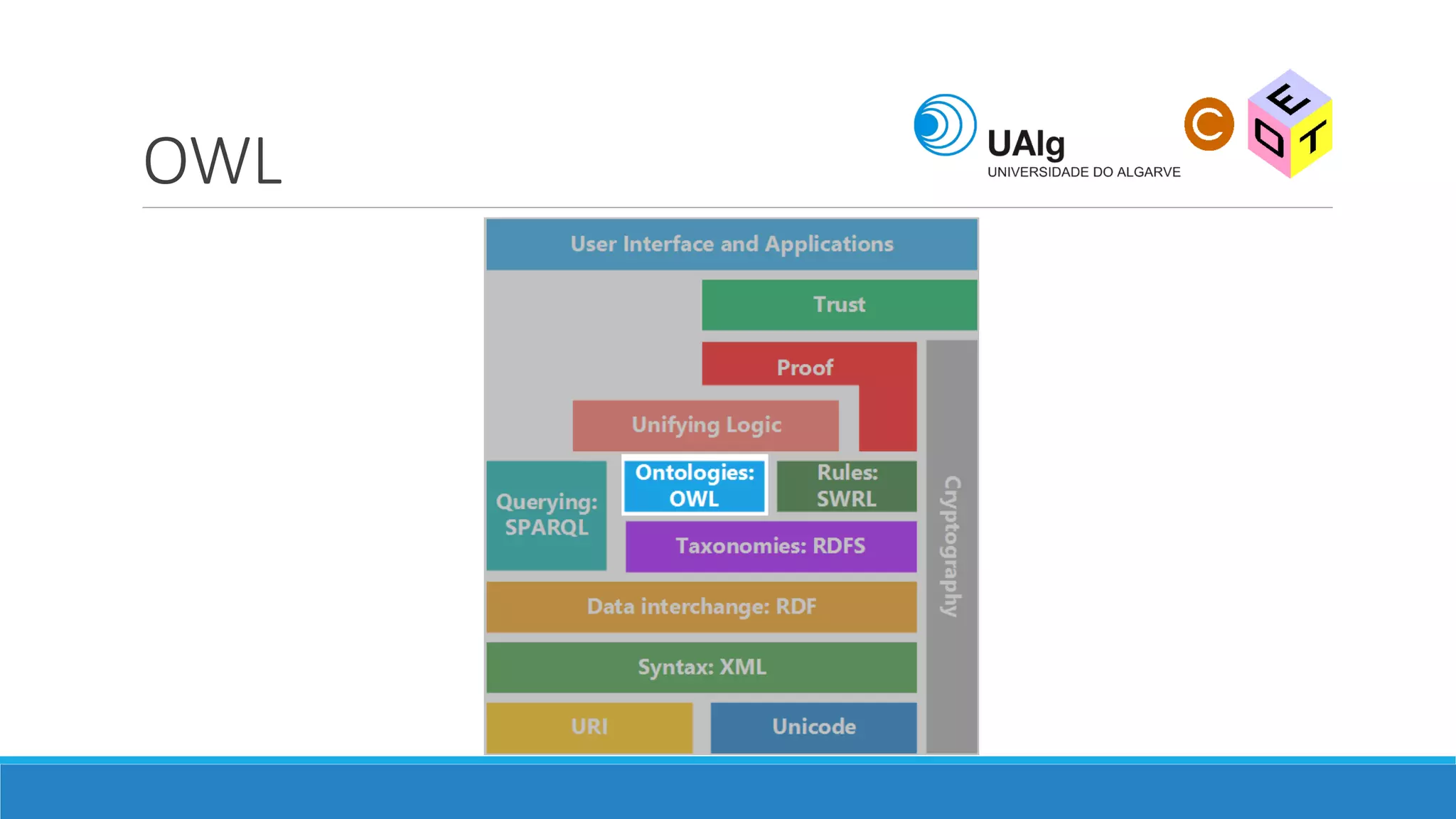
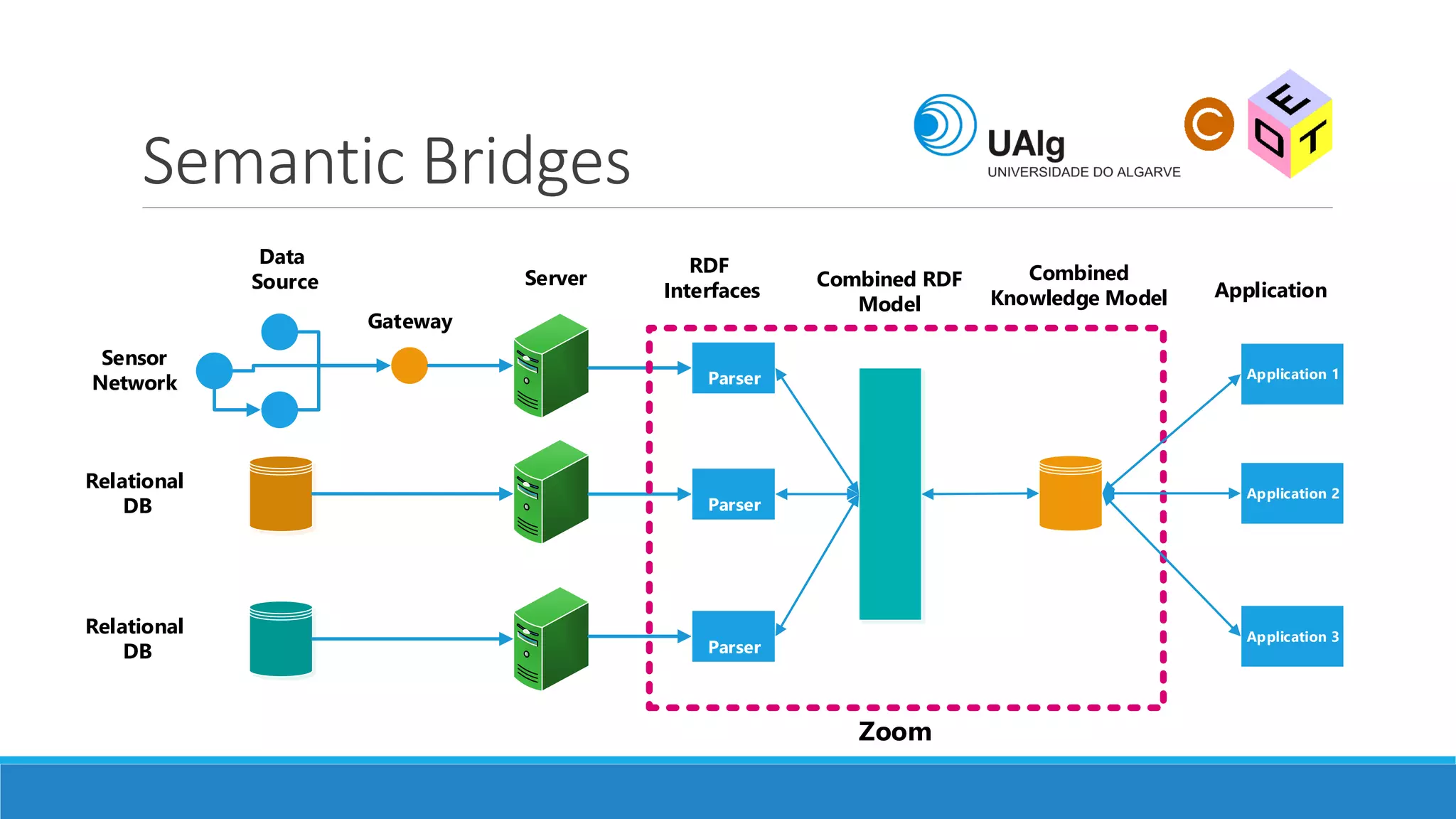
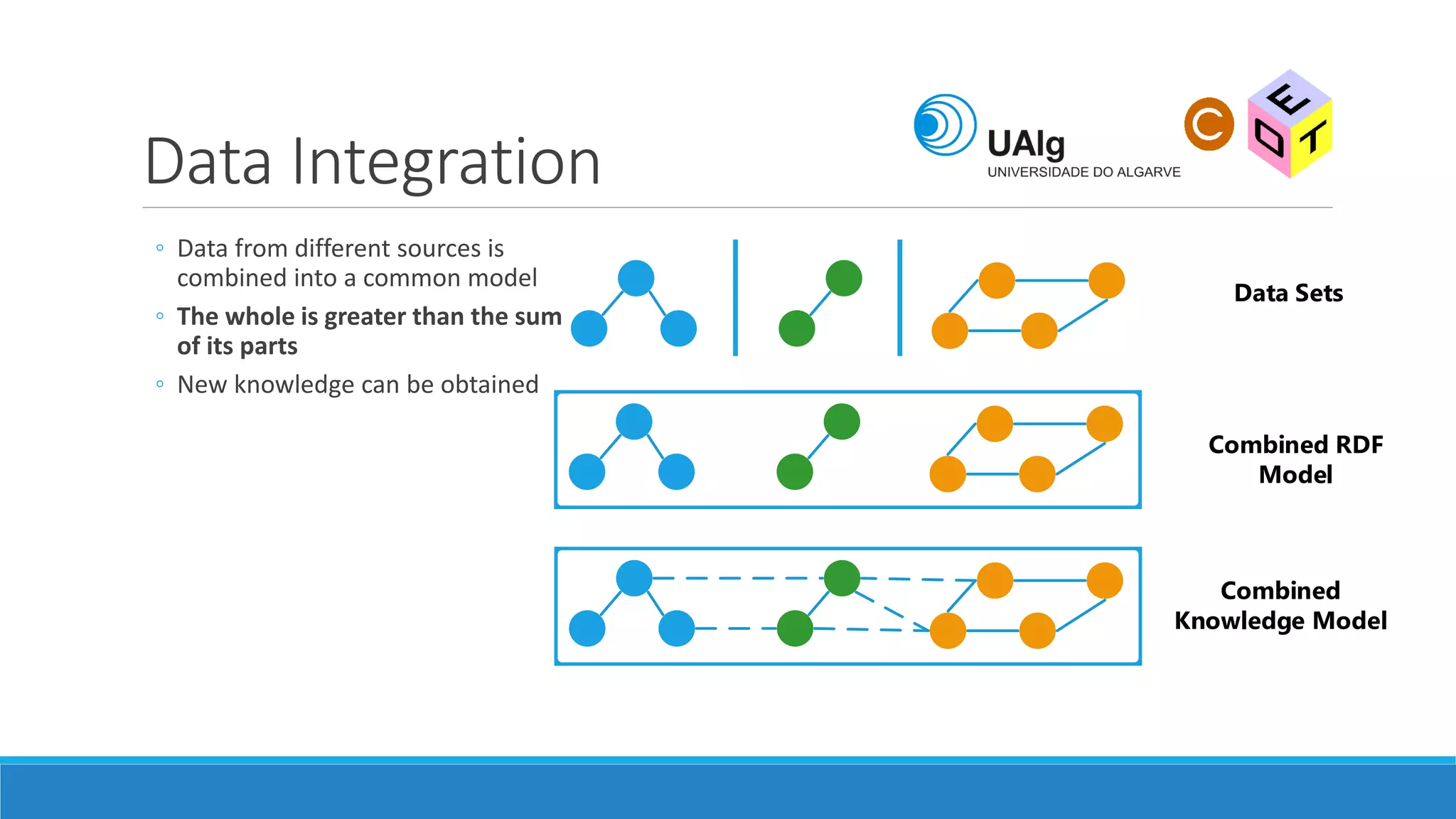
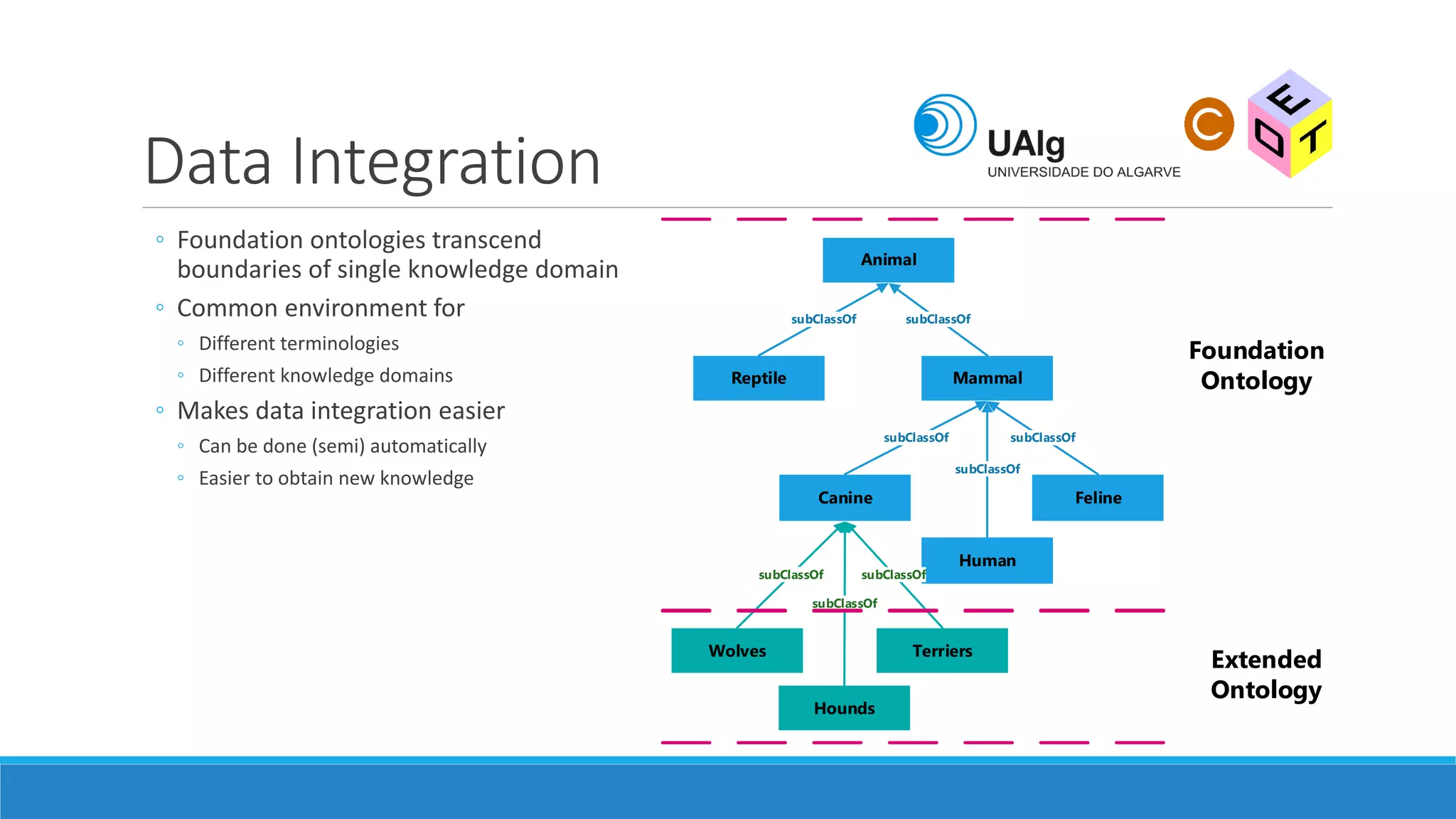
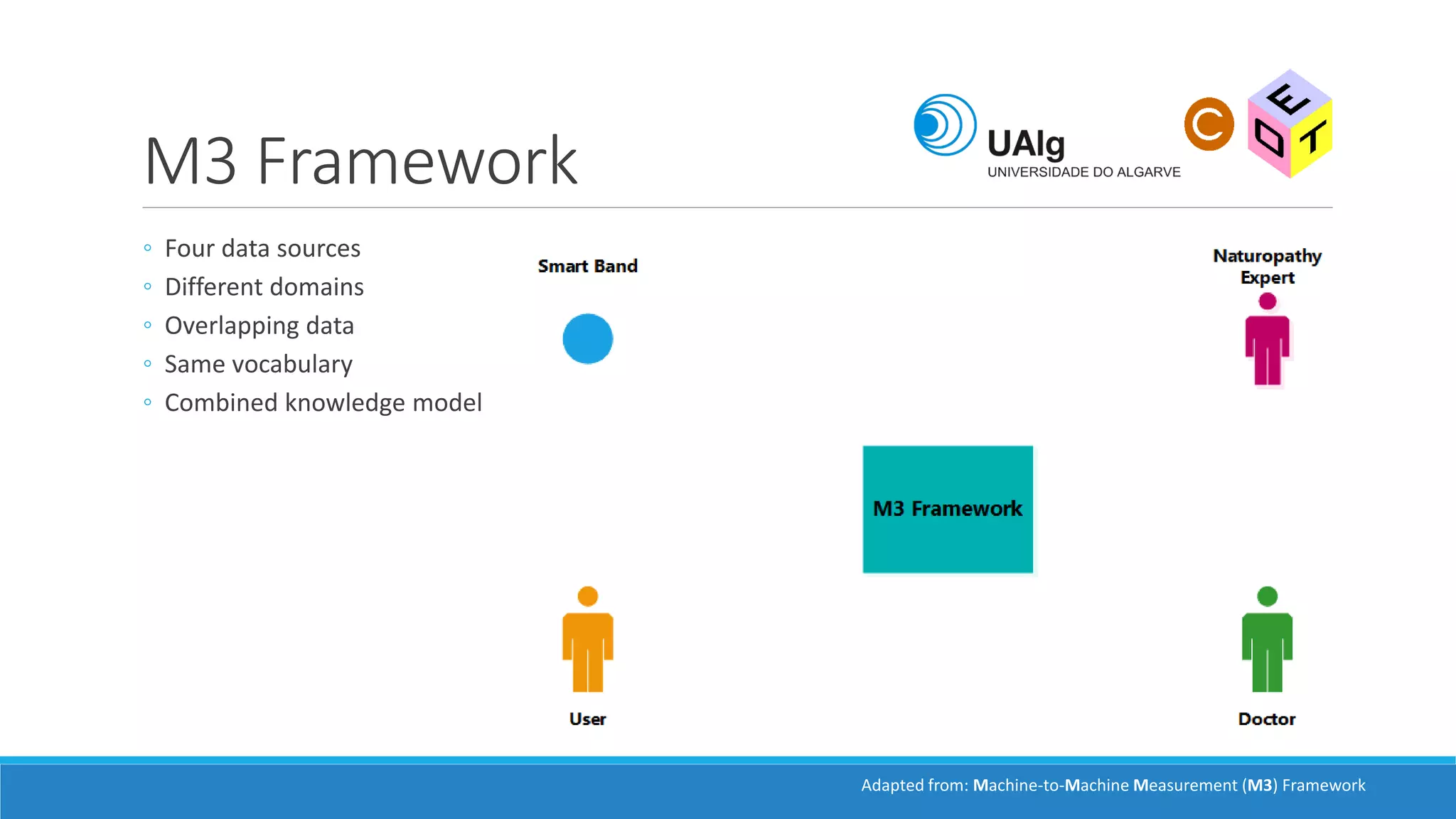
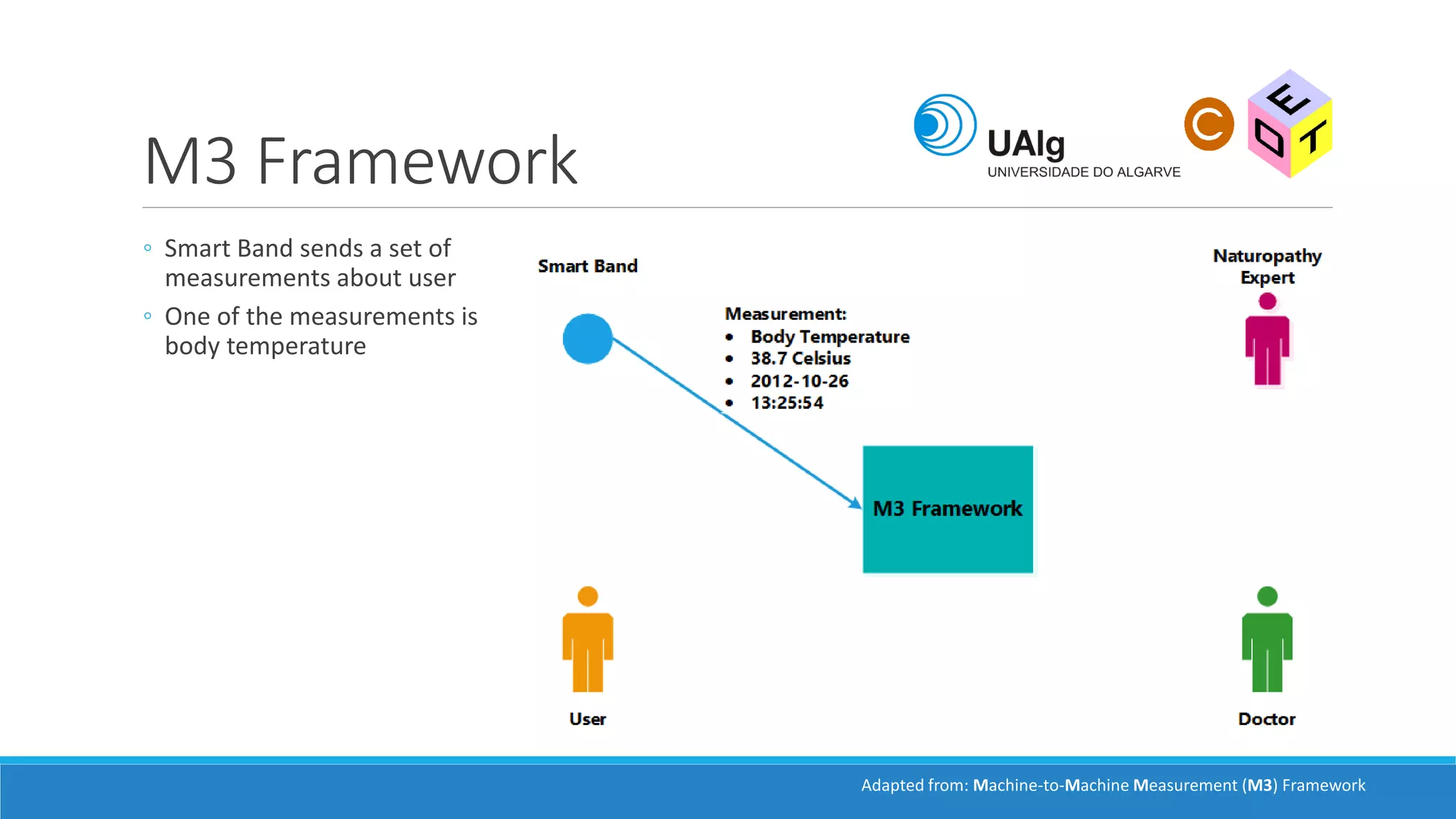
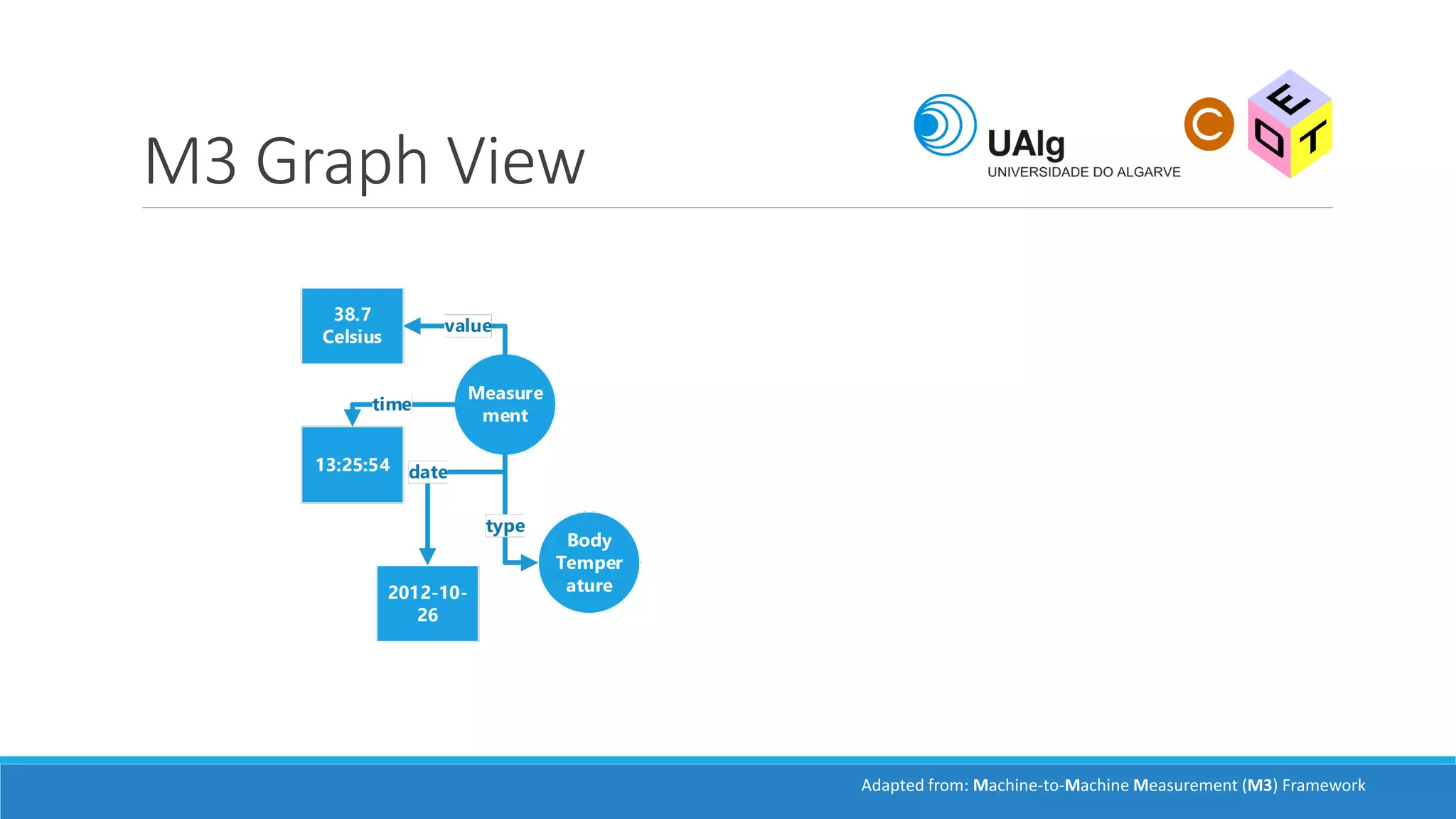
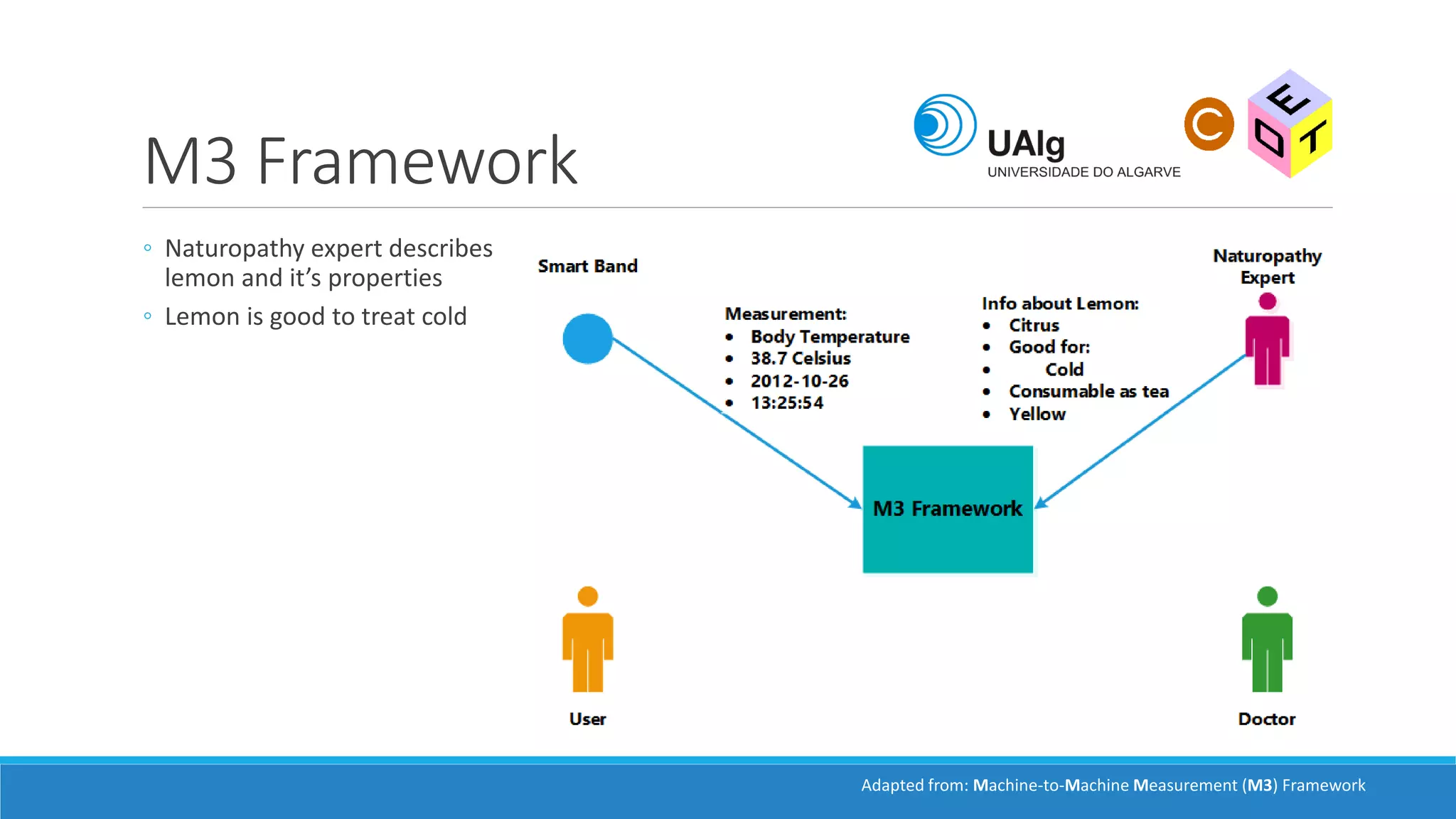
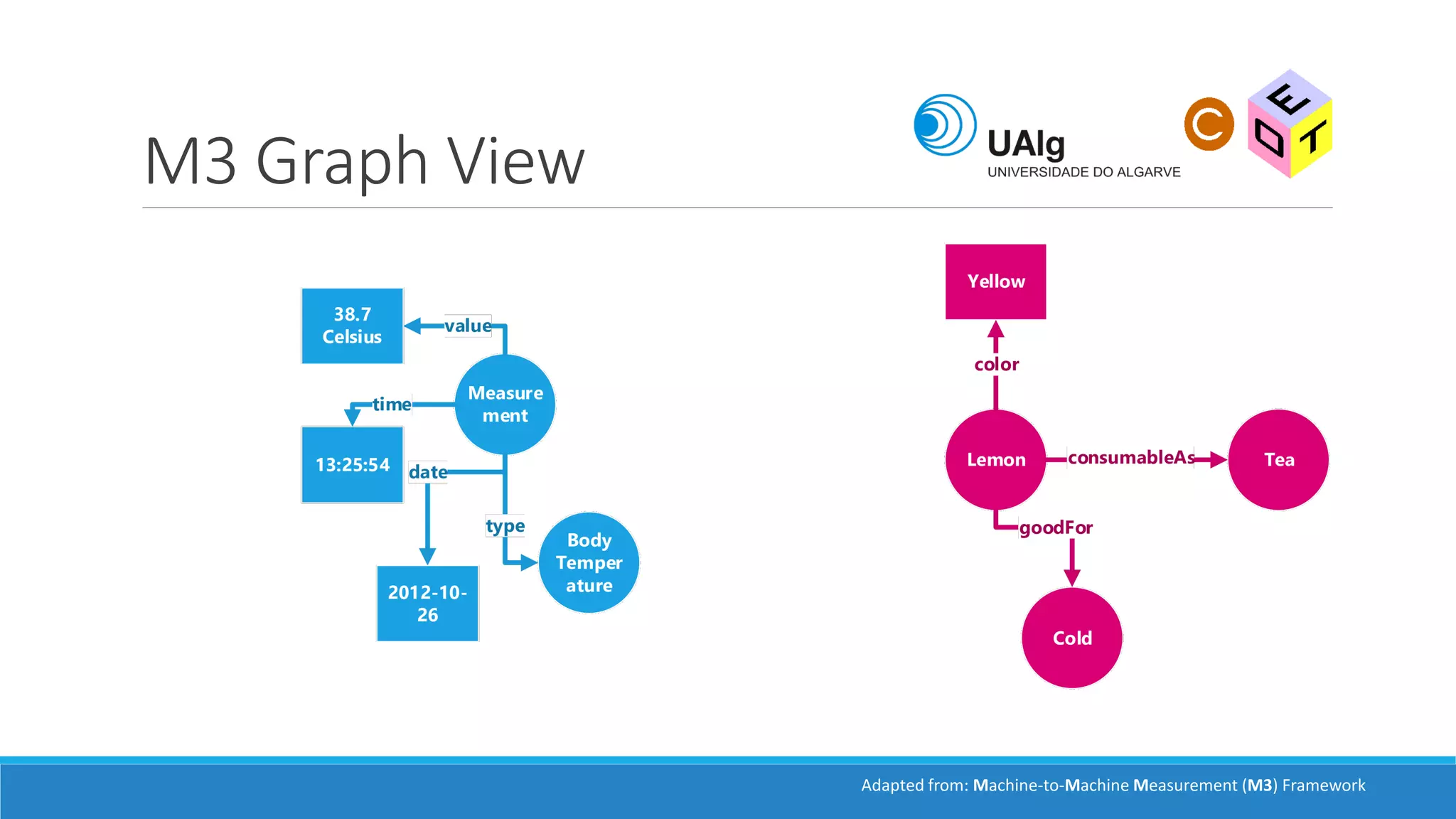
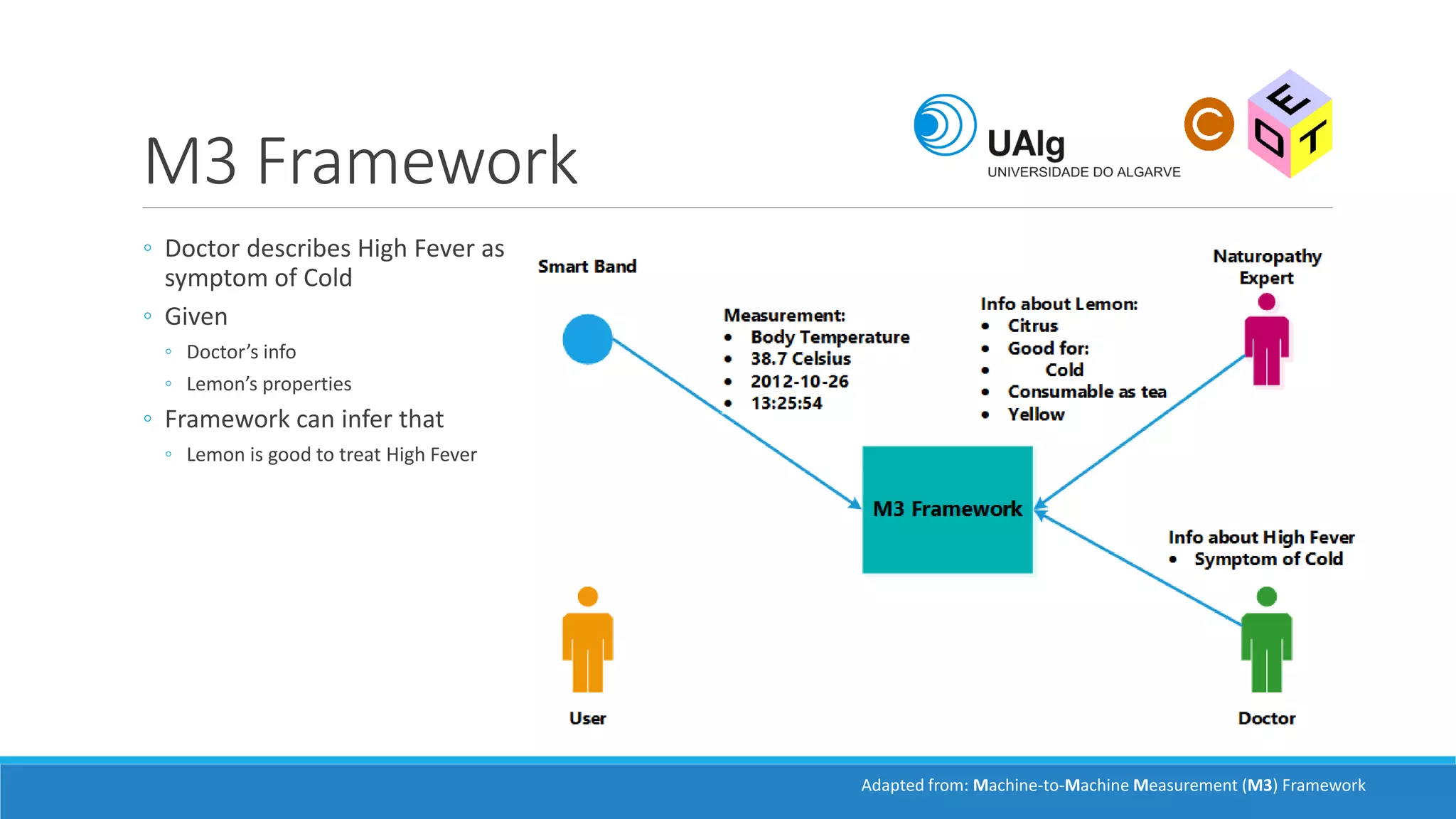
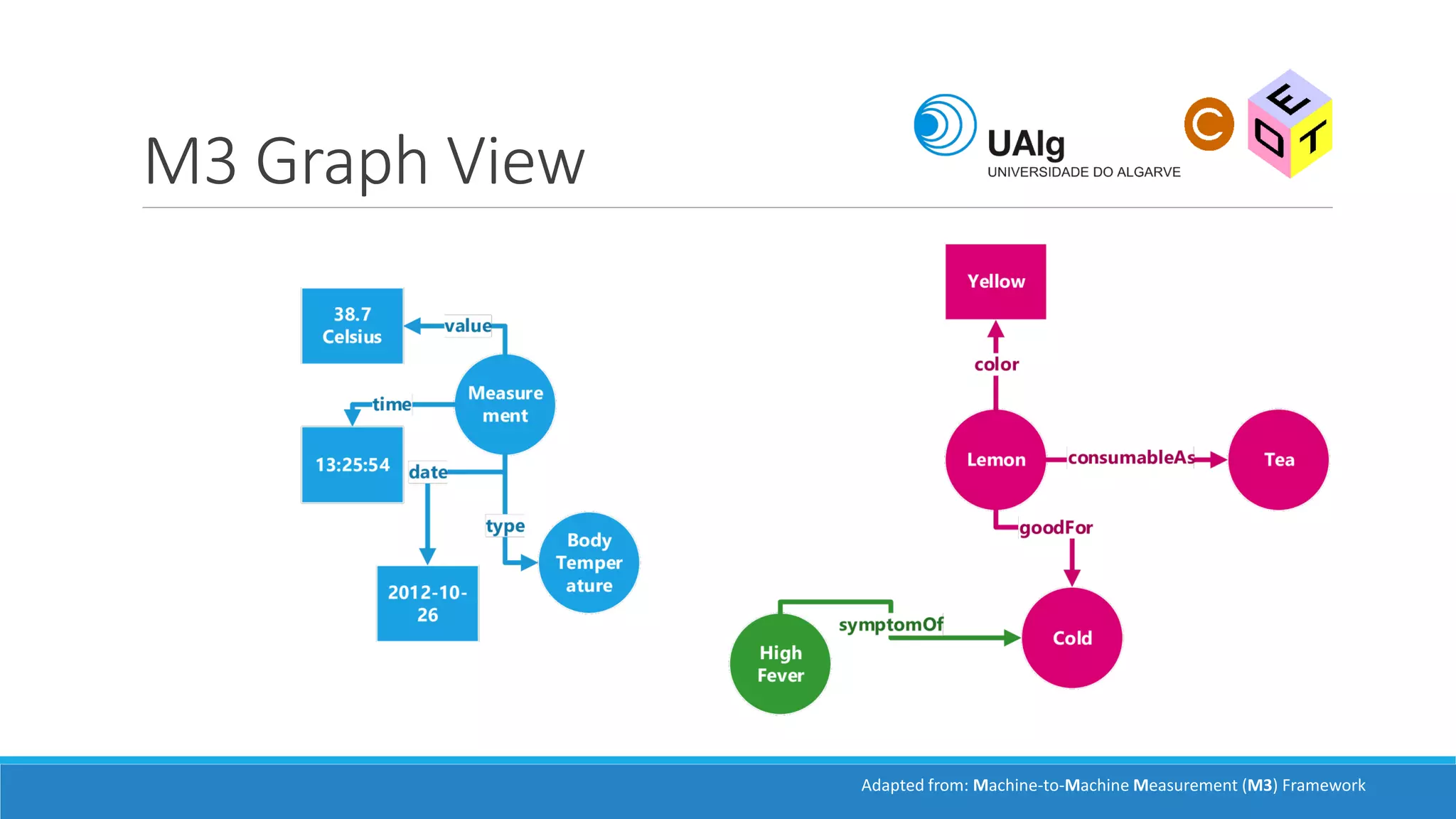
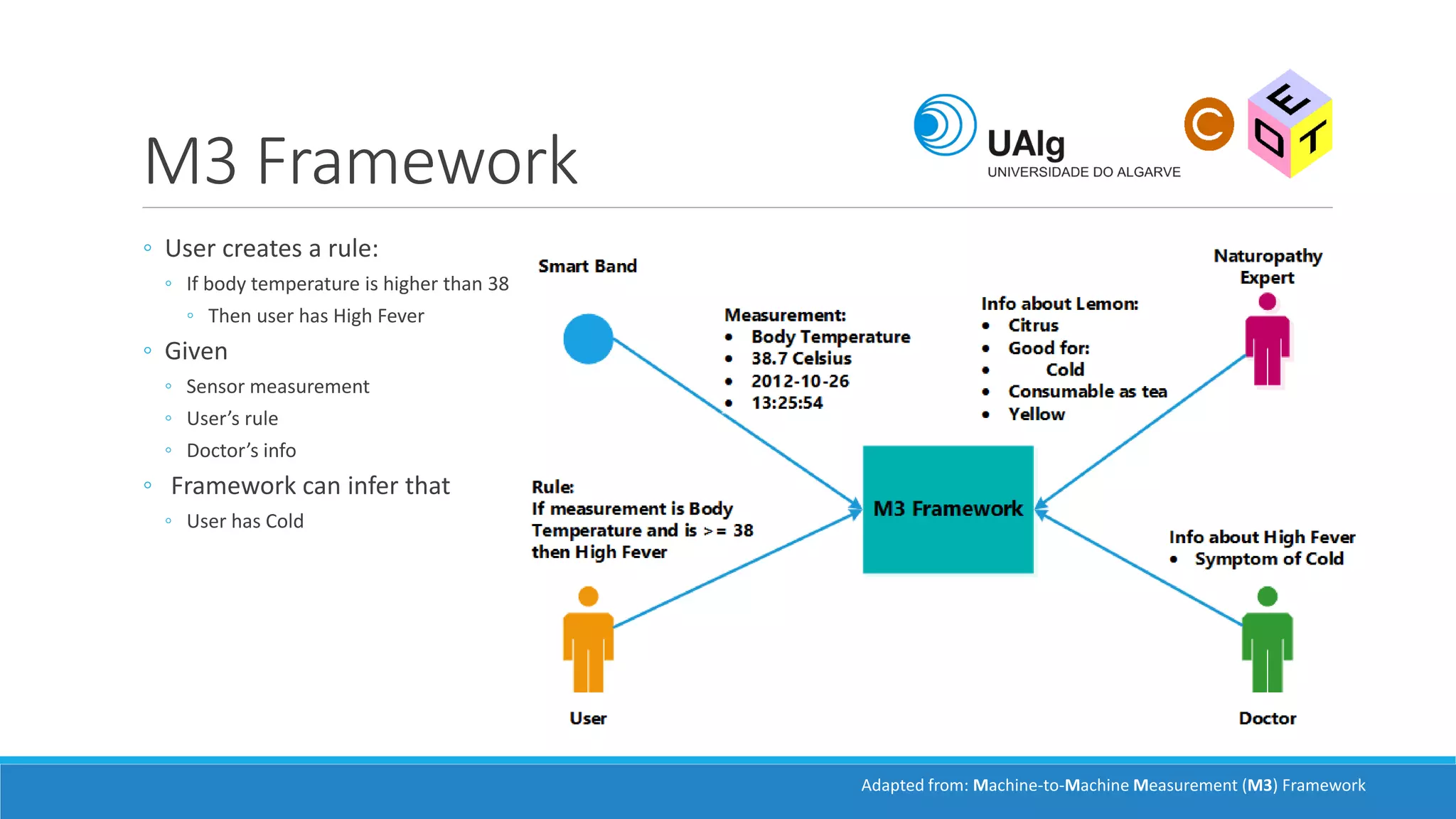
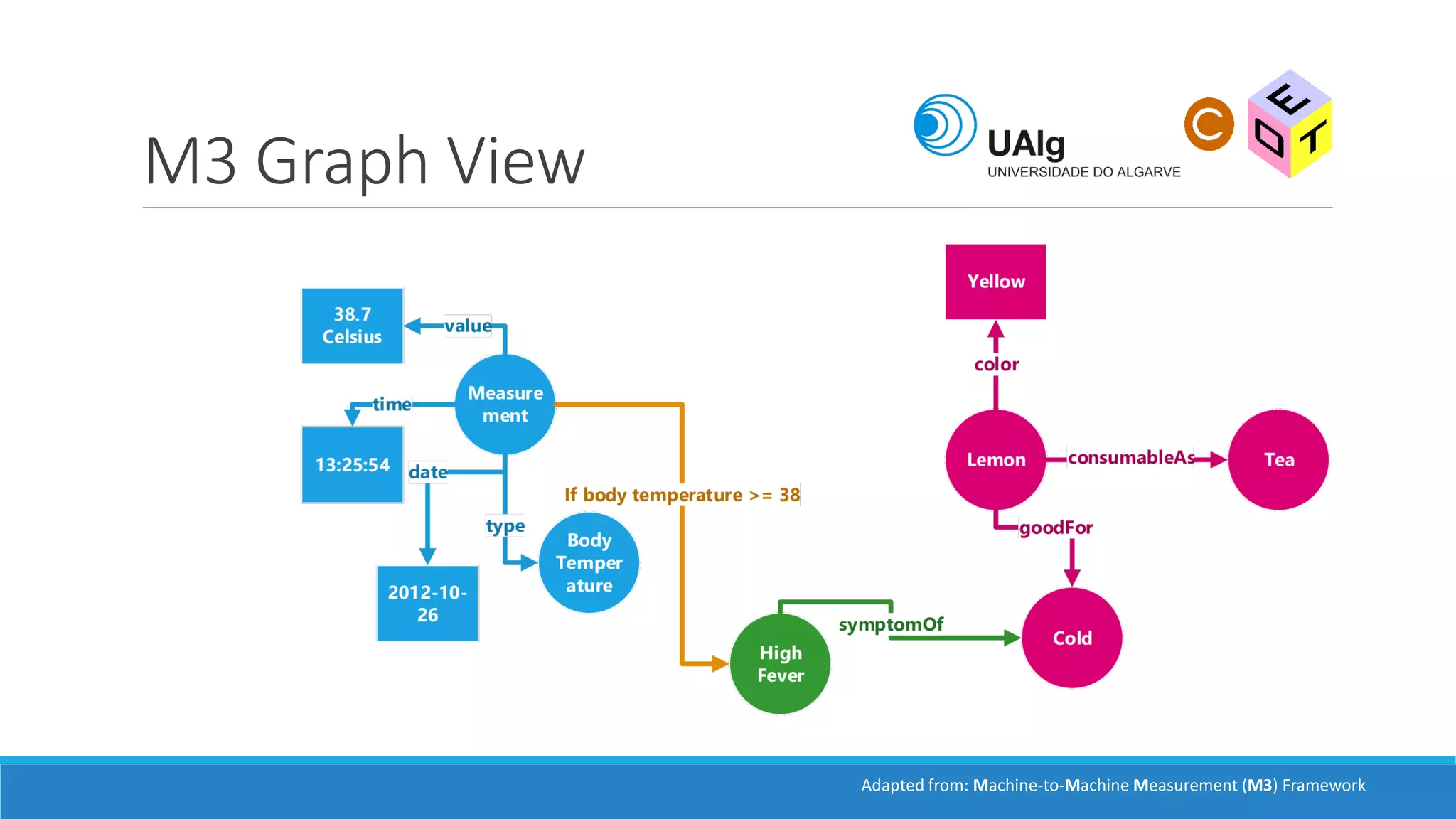
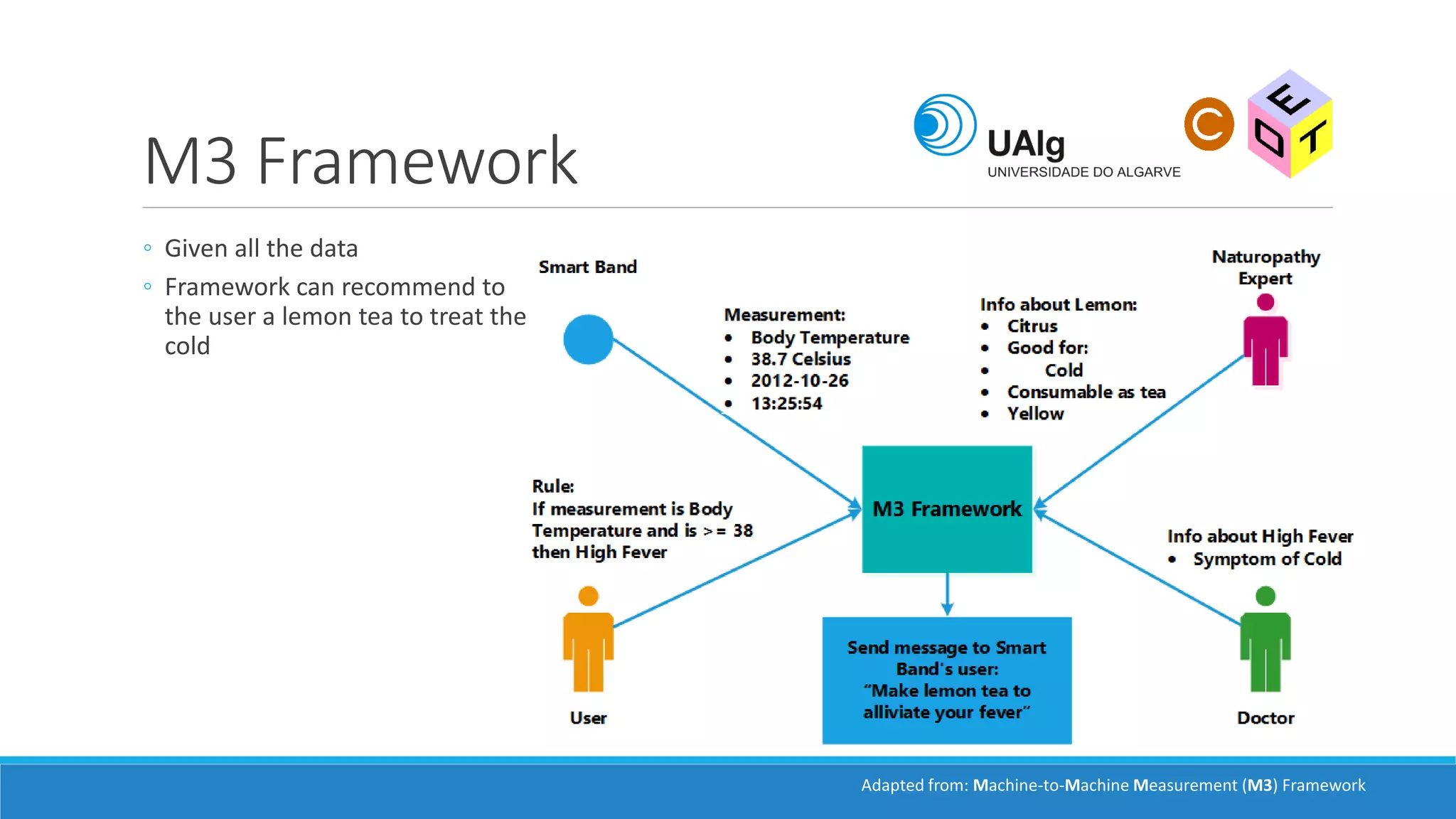
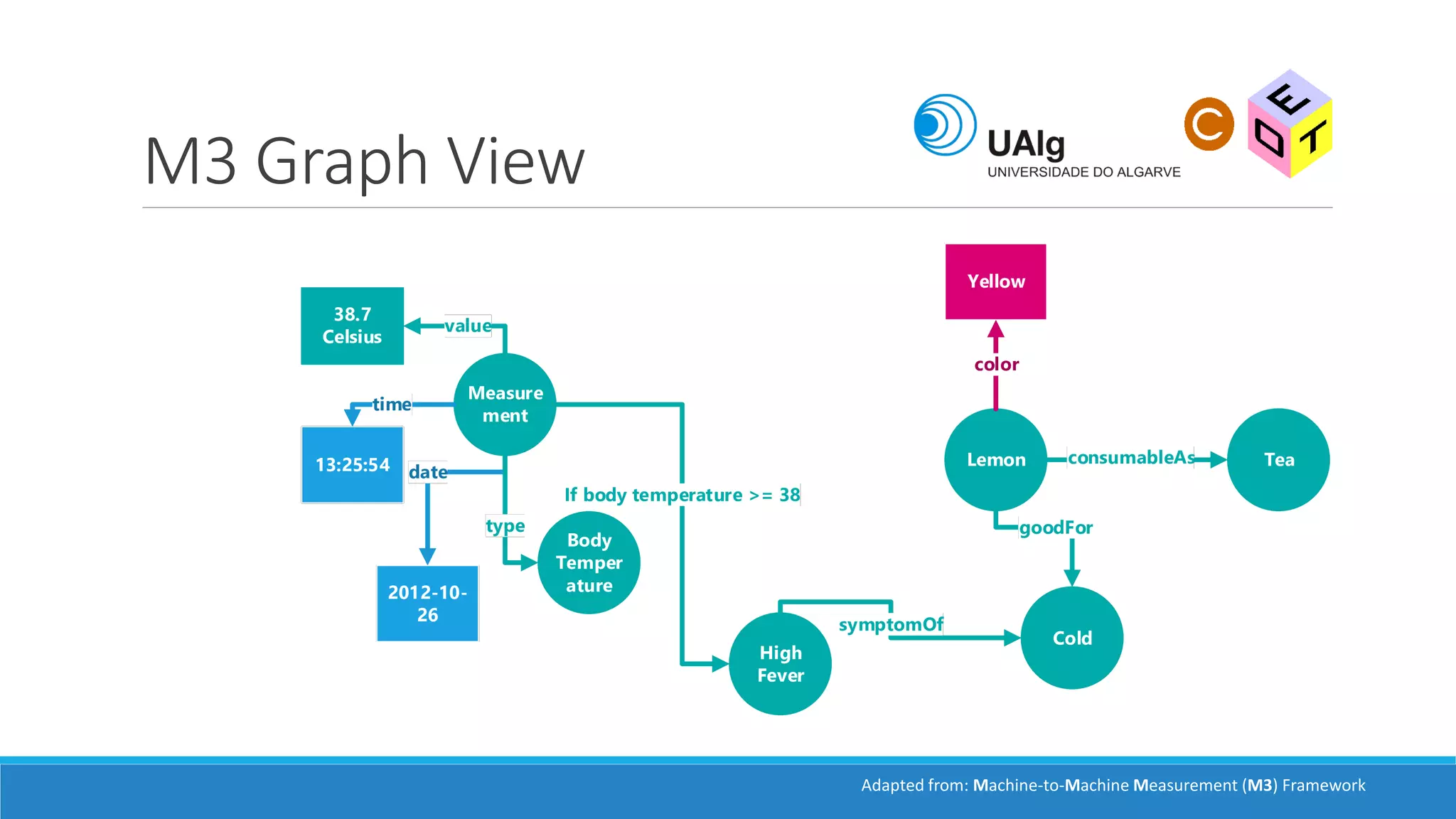
The document presents an overview of the Semantic Web, emphasizing its purpose of enhancing data sharing and search processes by using machine-readable semantics. It contrasts the 'dumb web,' primarily designed for human interaction, with the 'smart web,' which enables easier machine communication through structured data and linked data models. Key concepts discussed include RDF, OWL, and data integration frameworks that facilitate more efficient access and organization of information across various domains.
![Semantic Web
PRESENTED BY: ANDRÉ MAZAYEV
ANDRE.MAZ.90[ AT]GMAIL[DOT]COM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticweb-160908121036/75/Semantic-web-An-overview-1-2048.jpg)