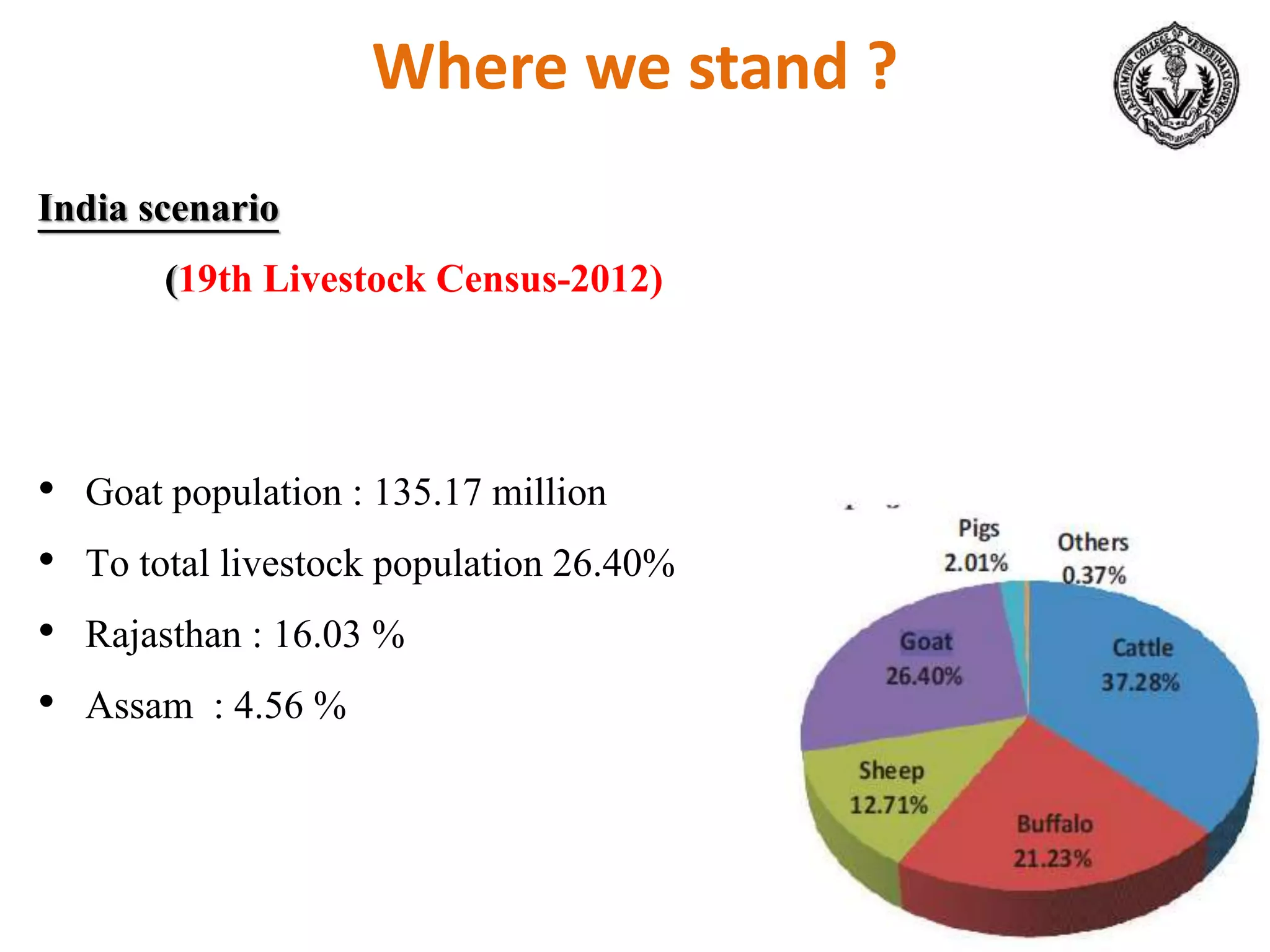
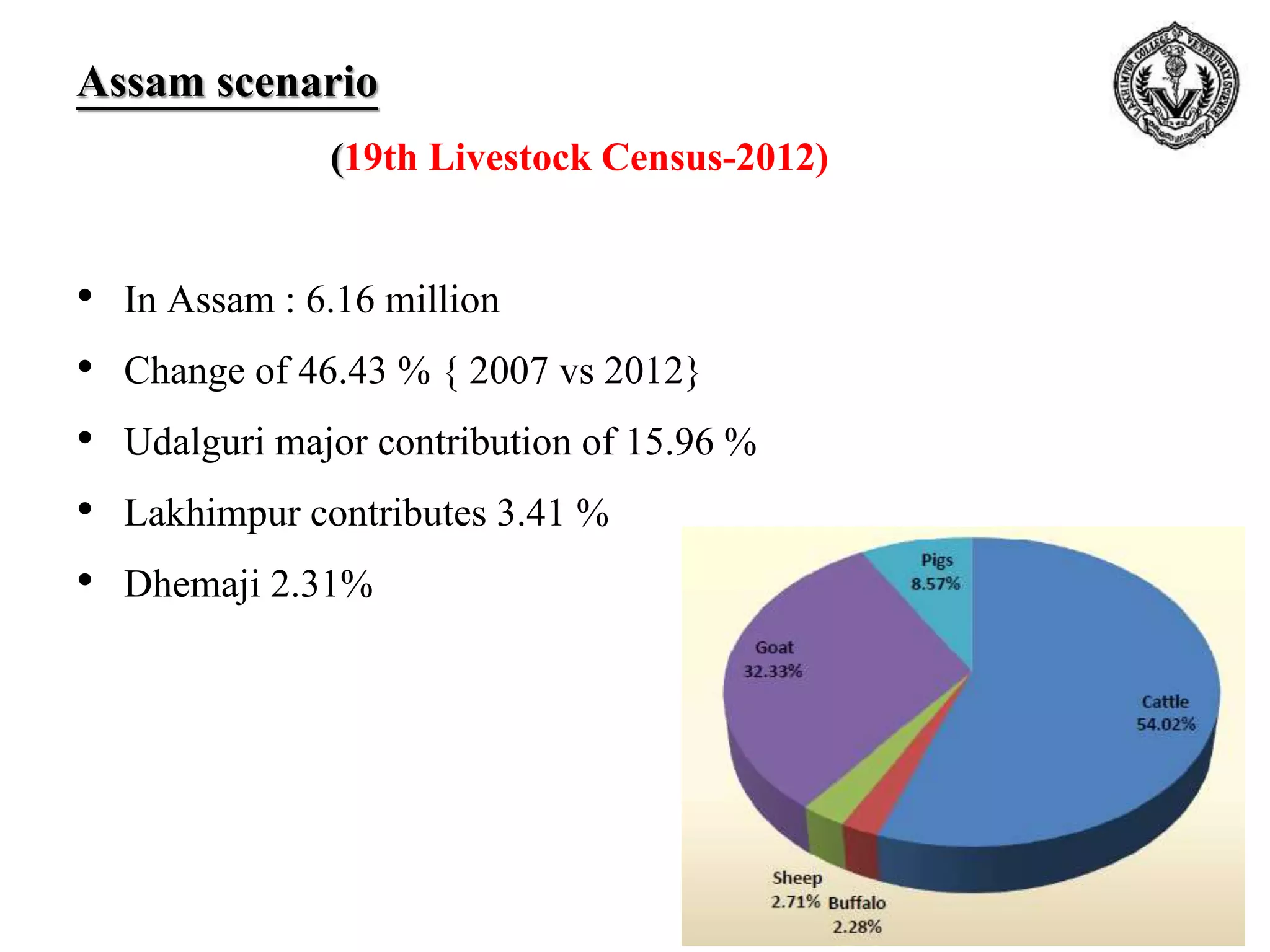
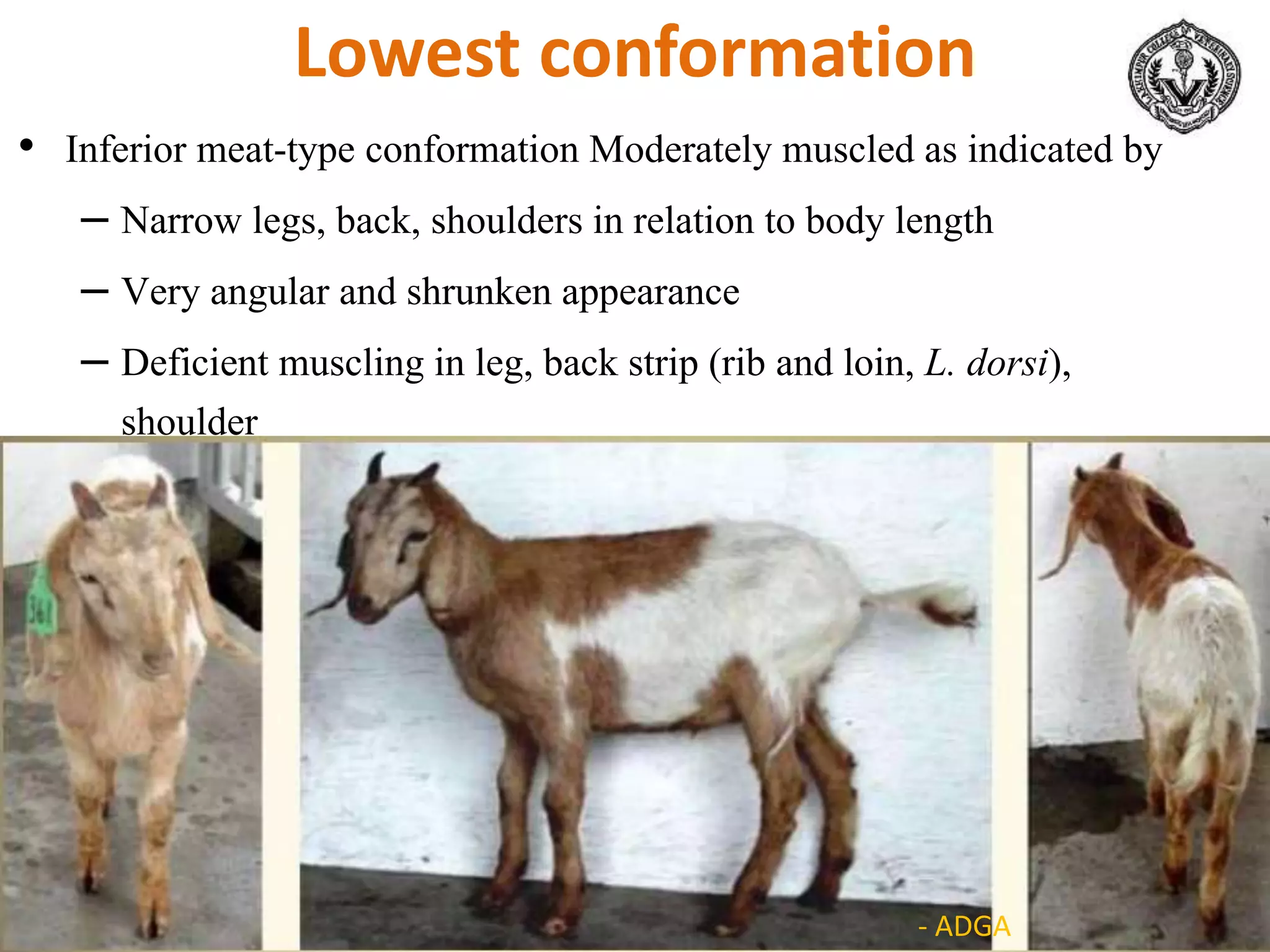
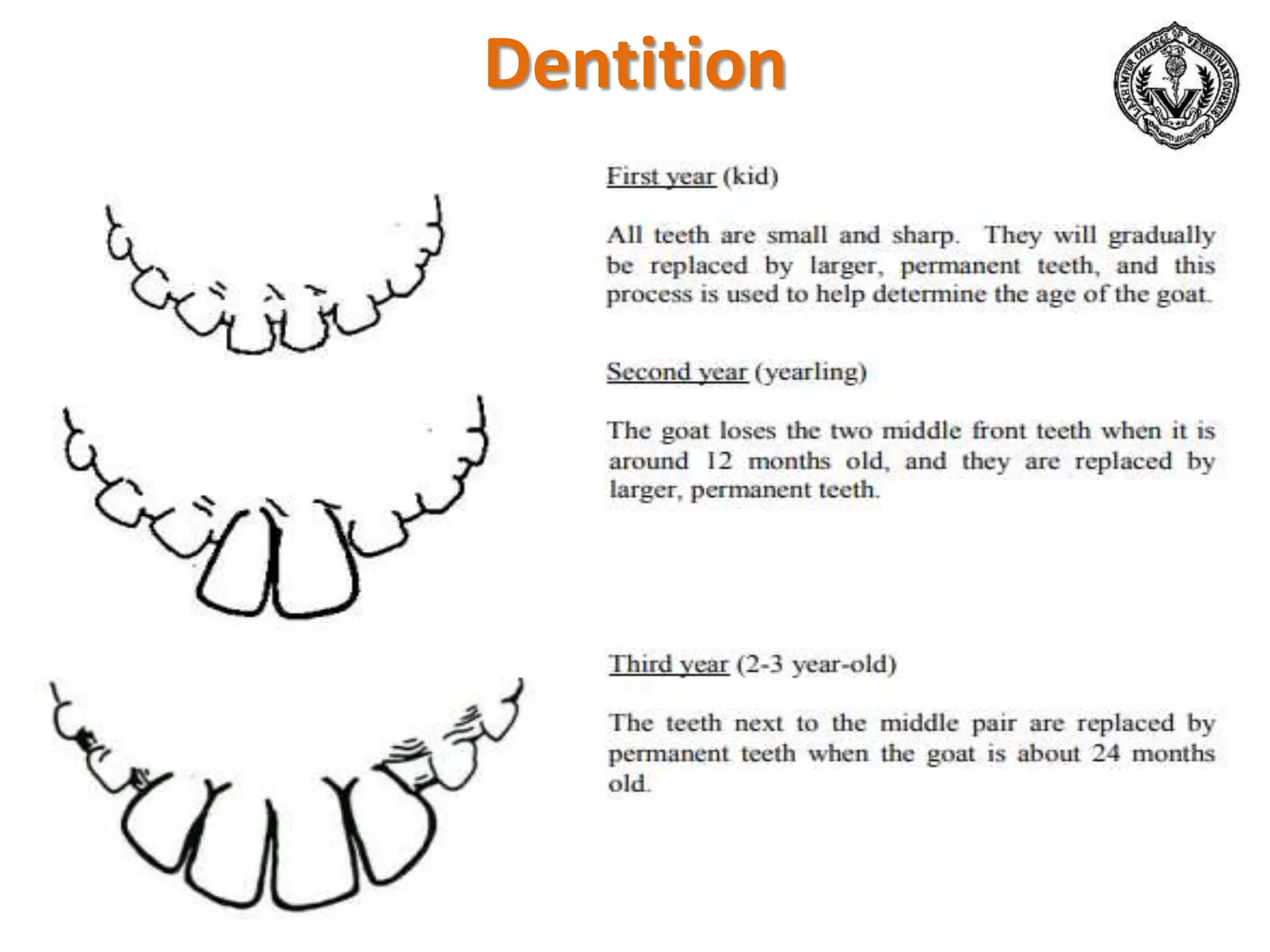
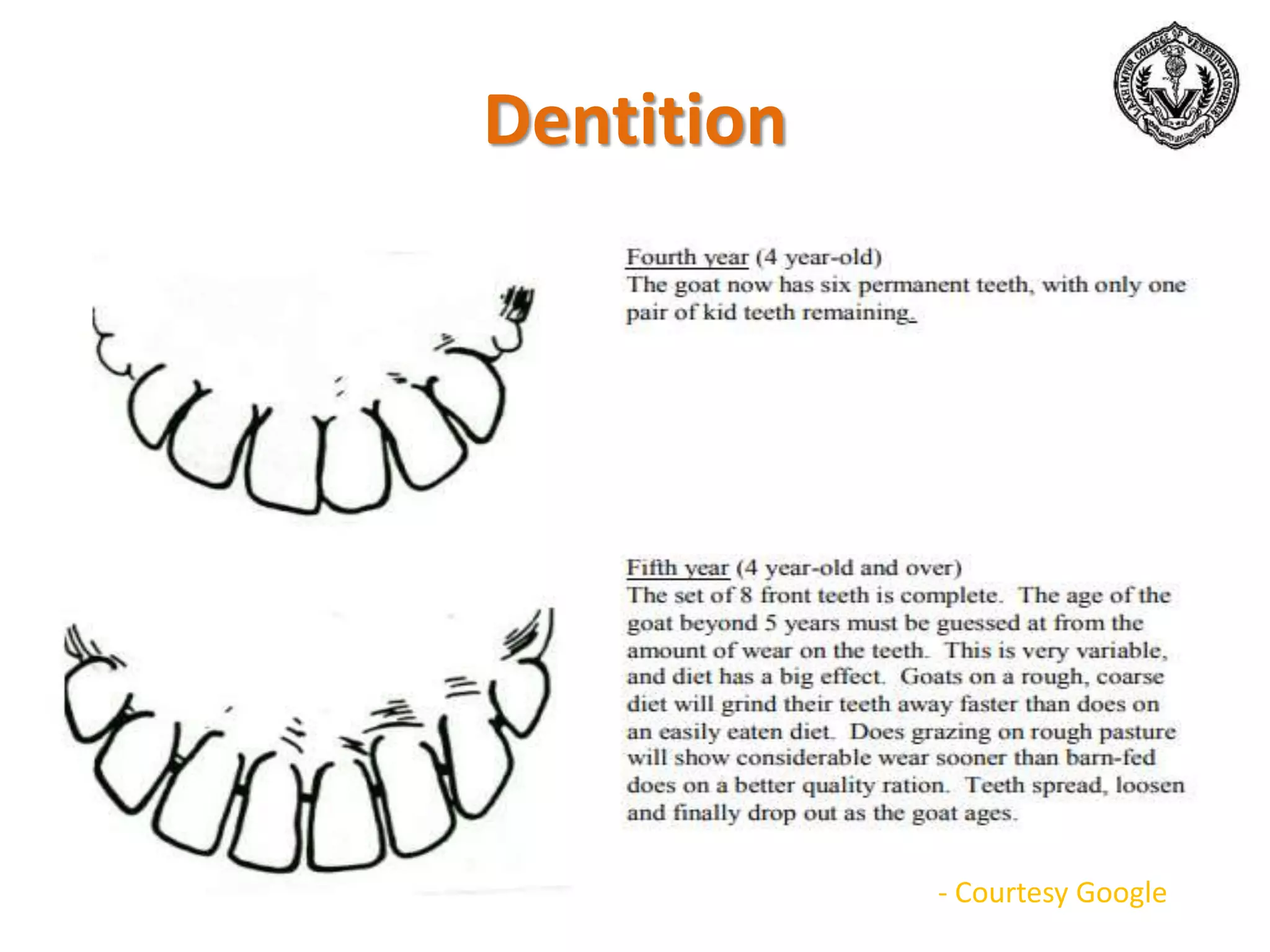
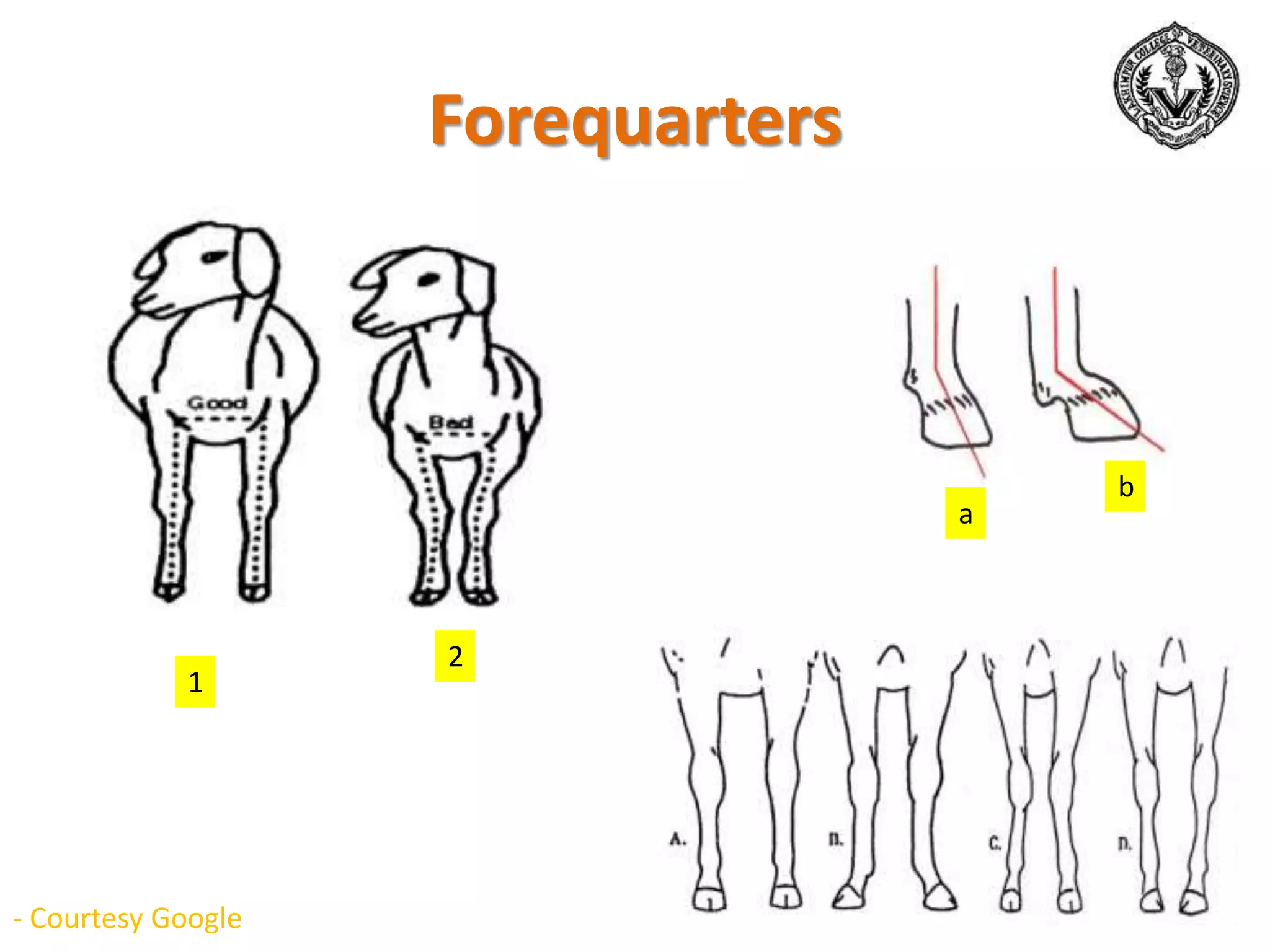
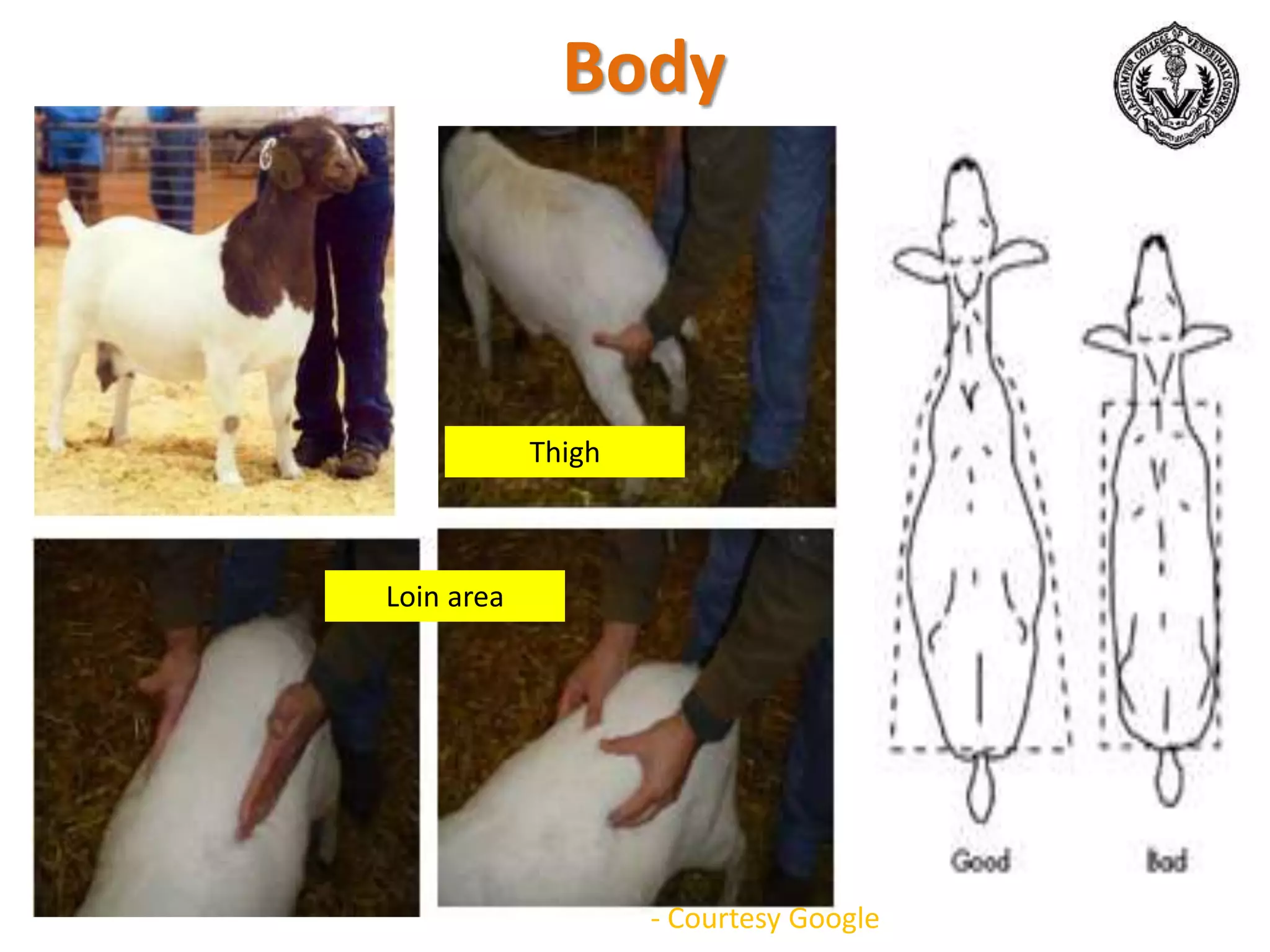
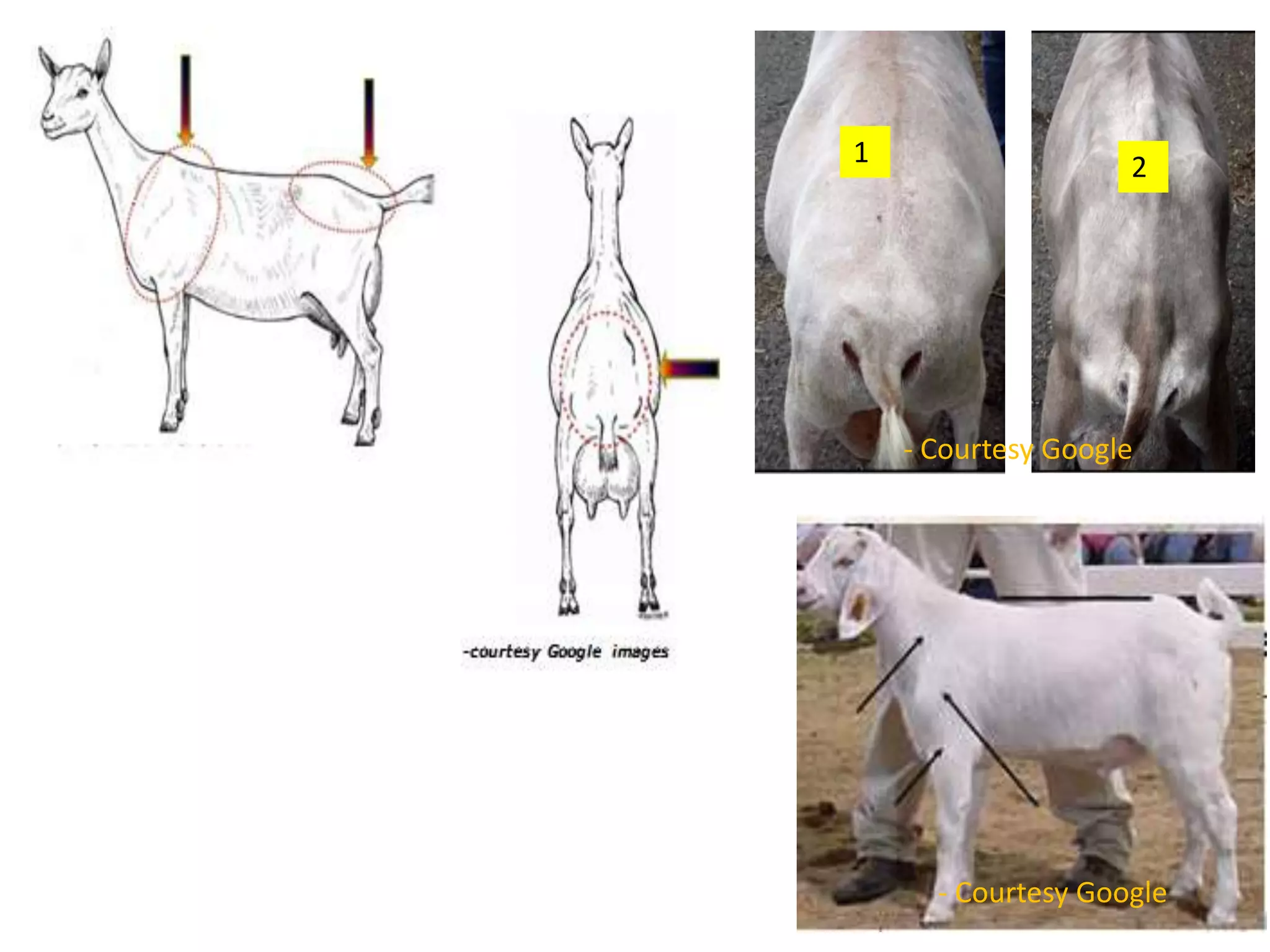
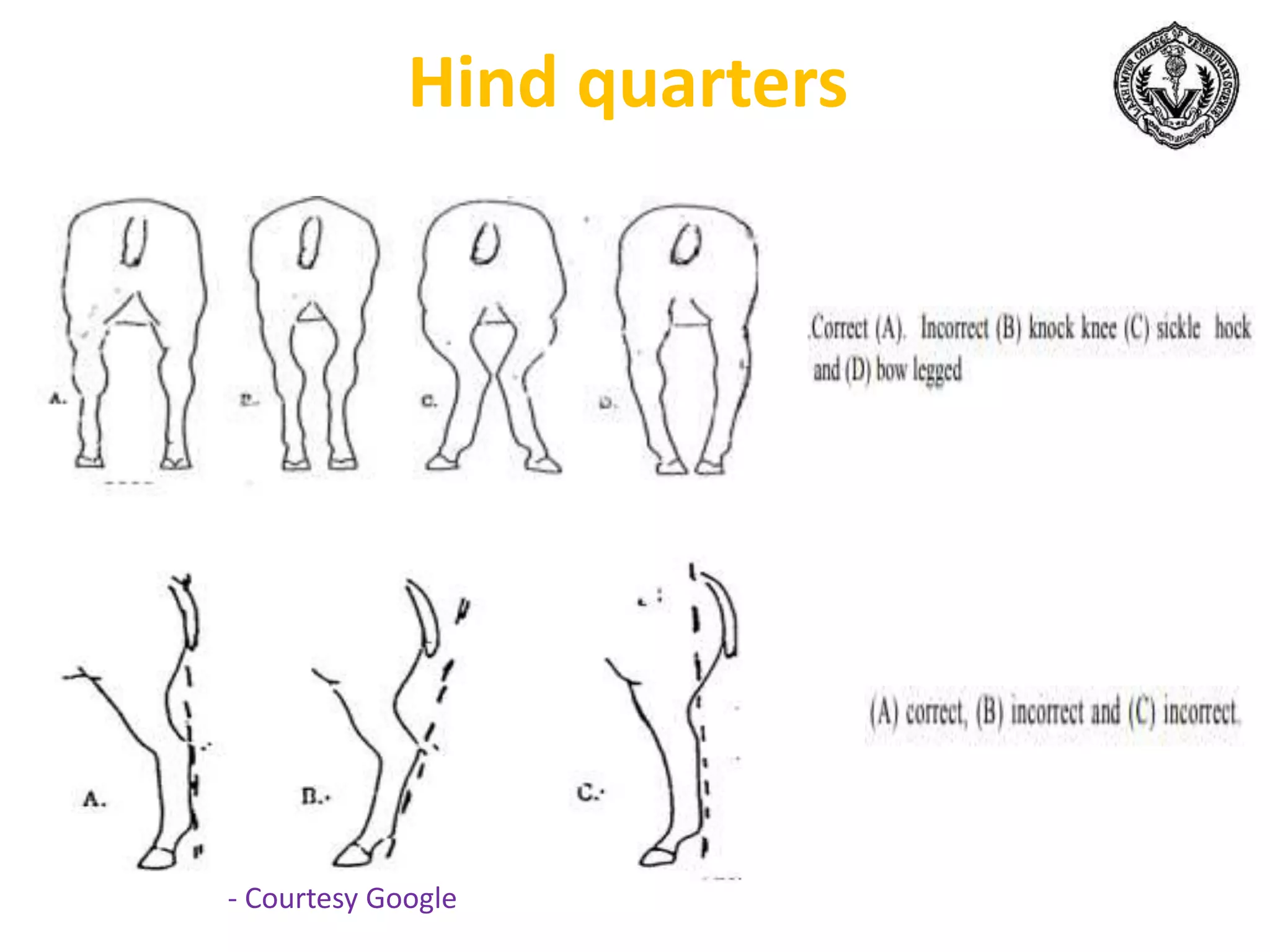
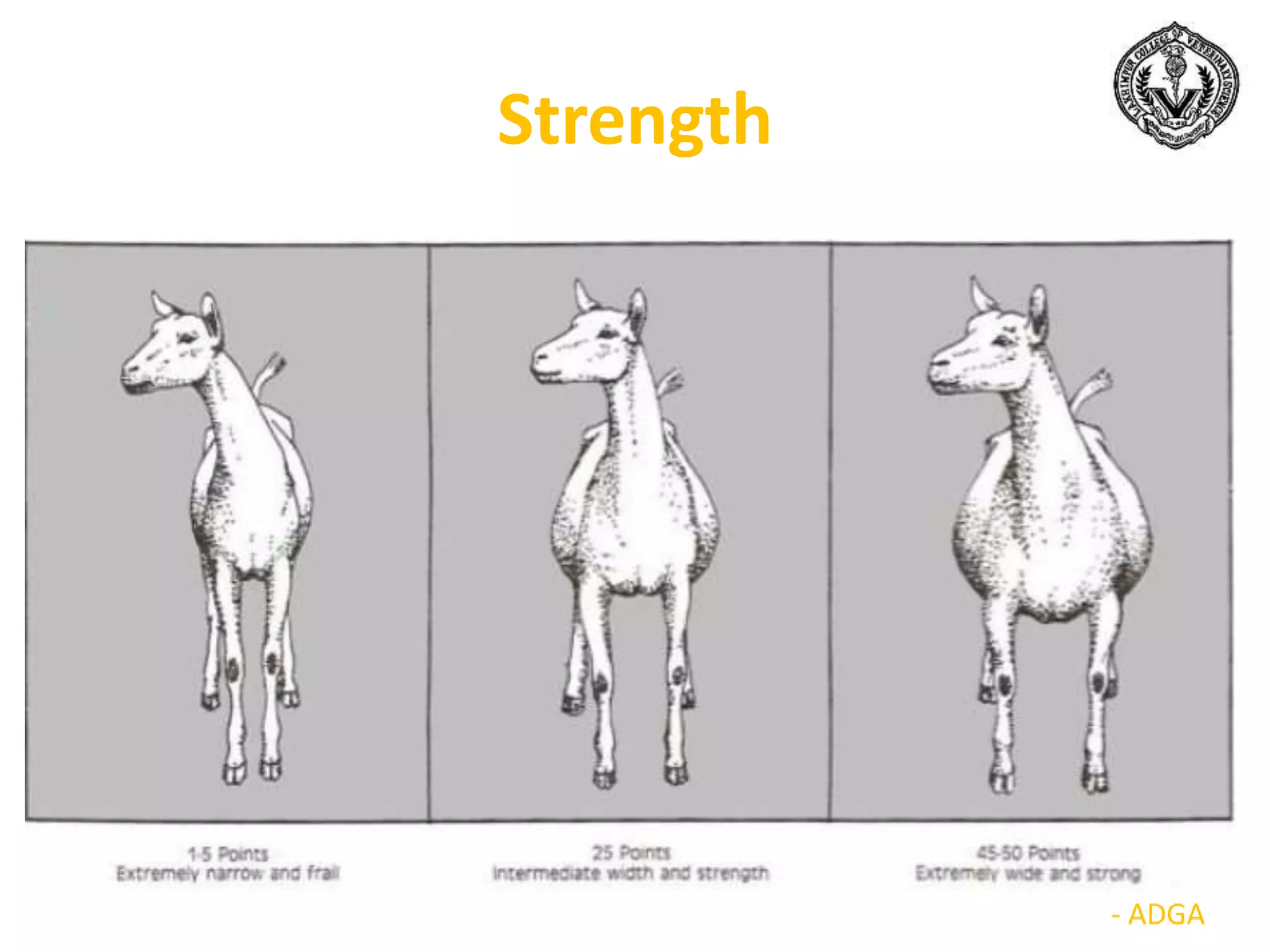
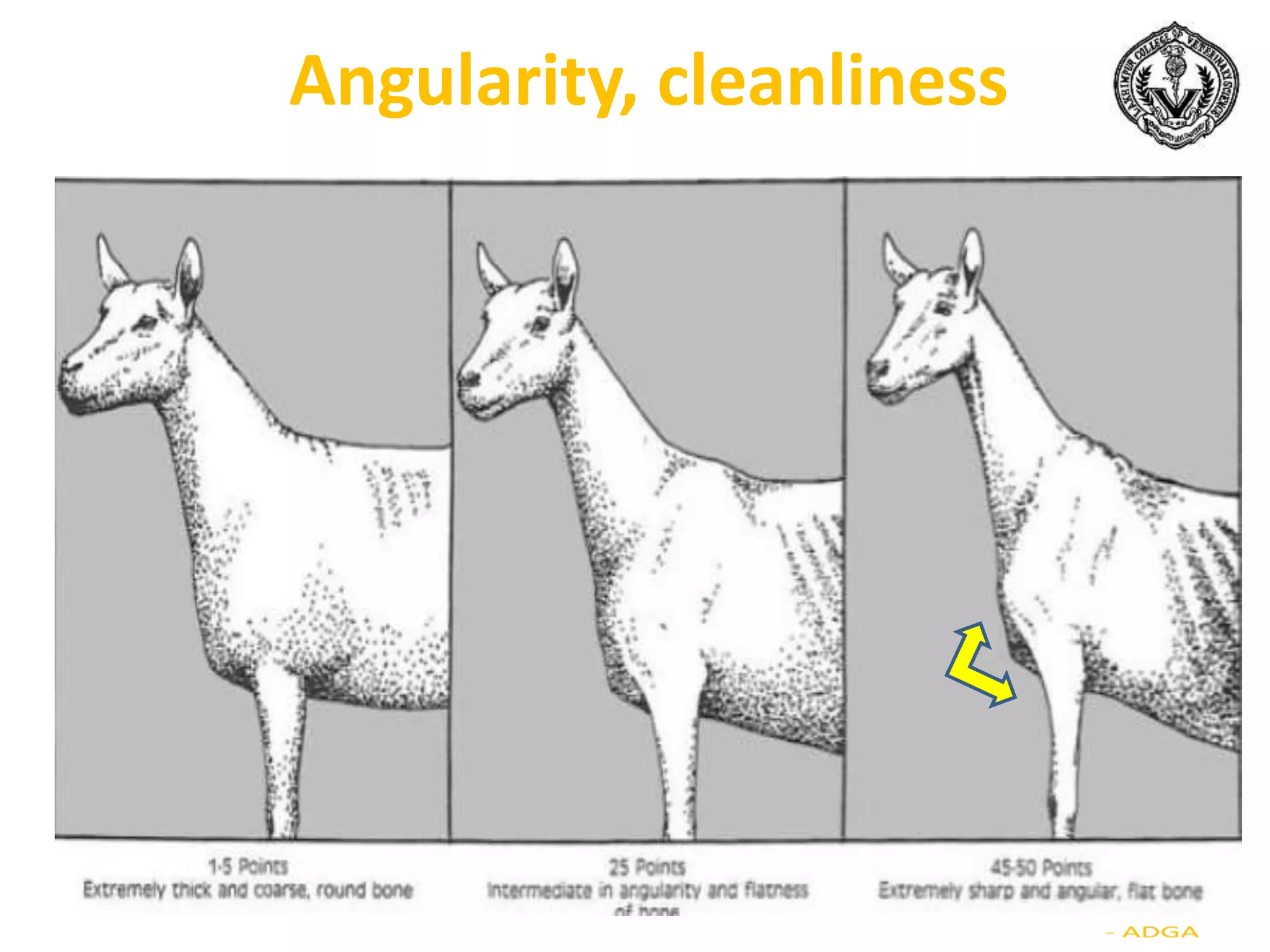
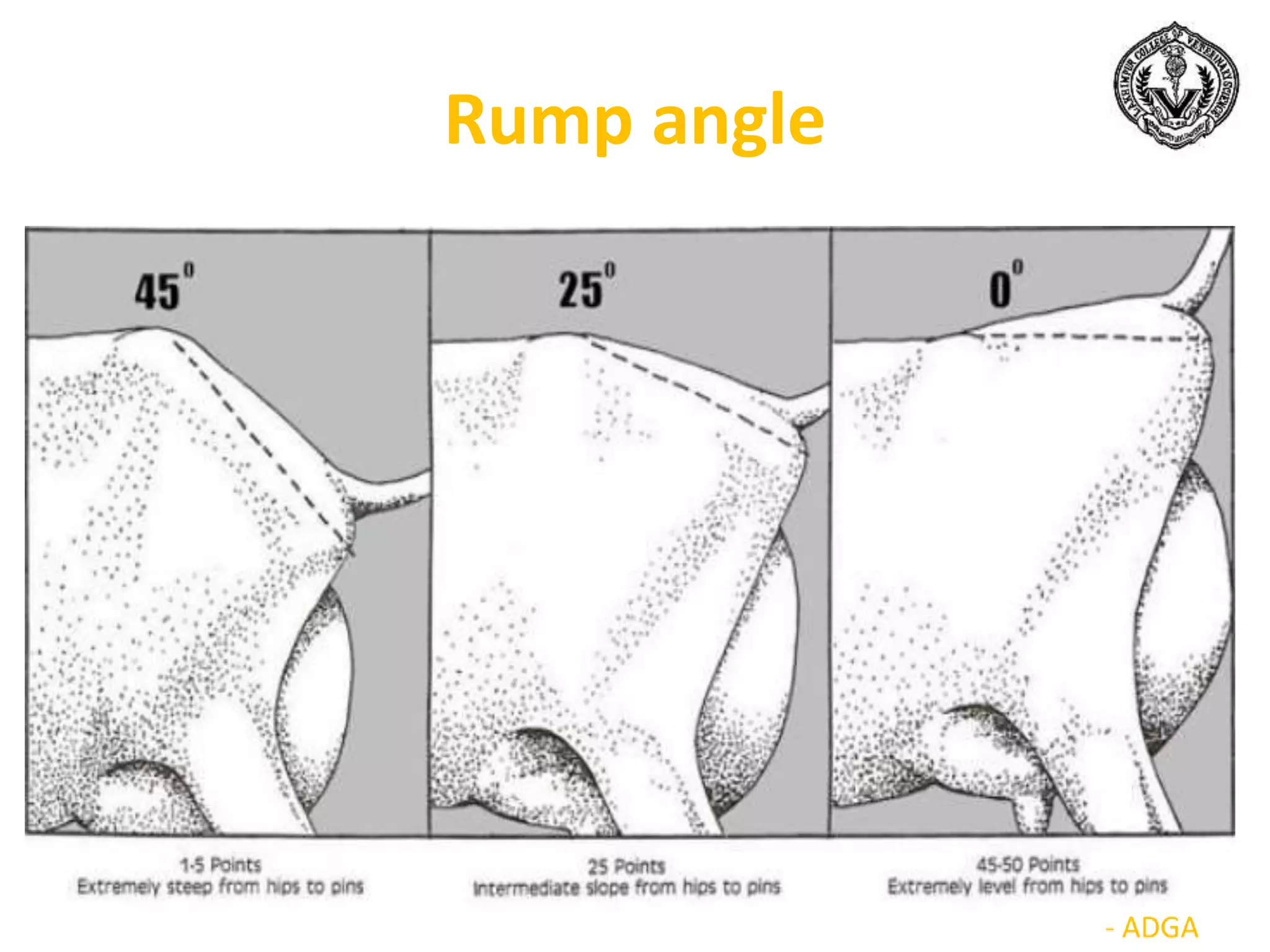
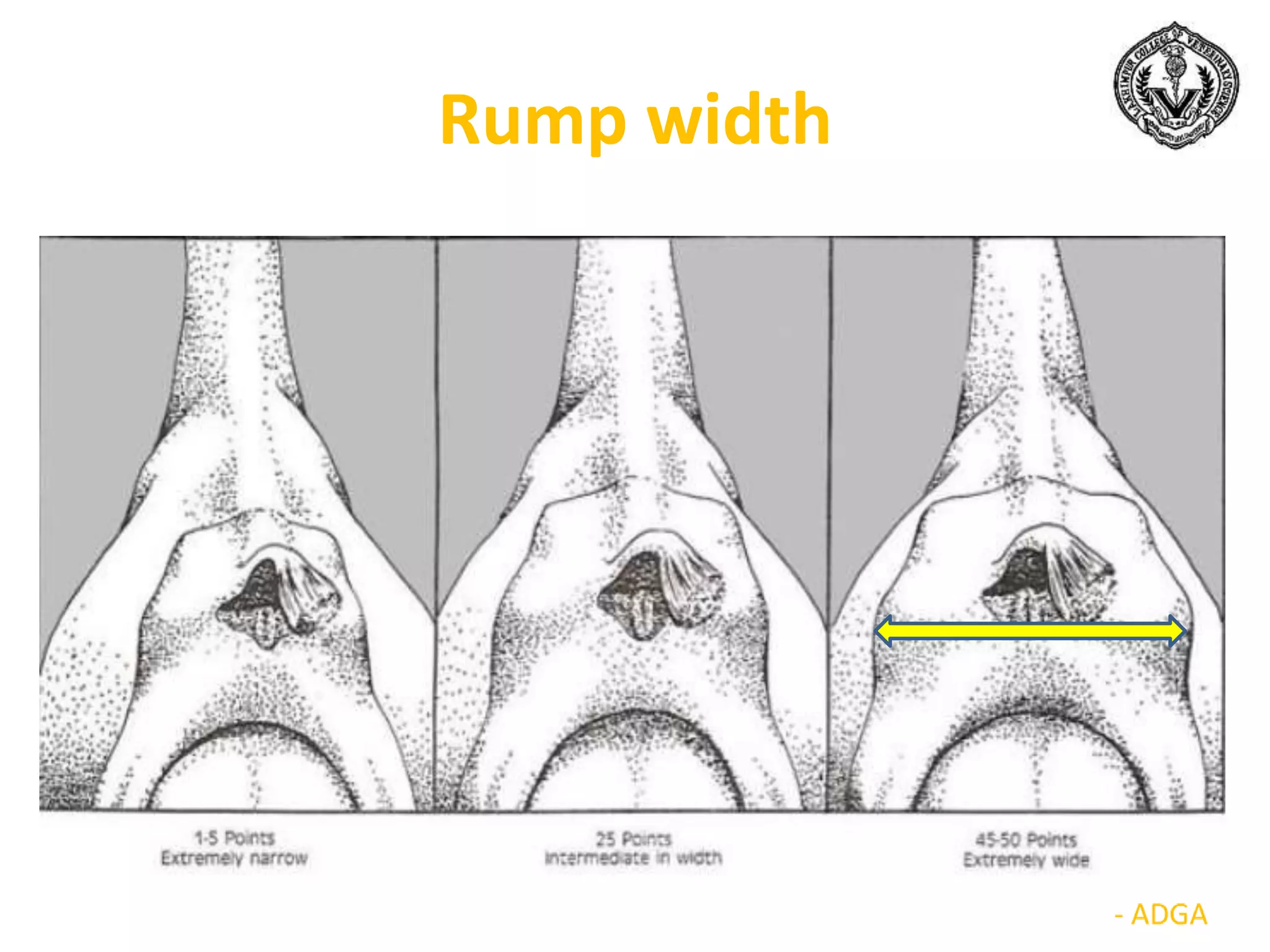
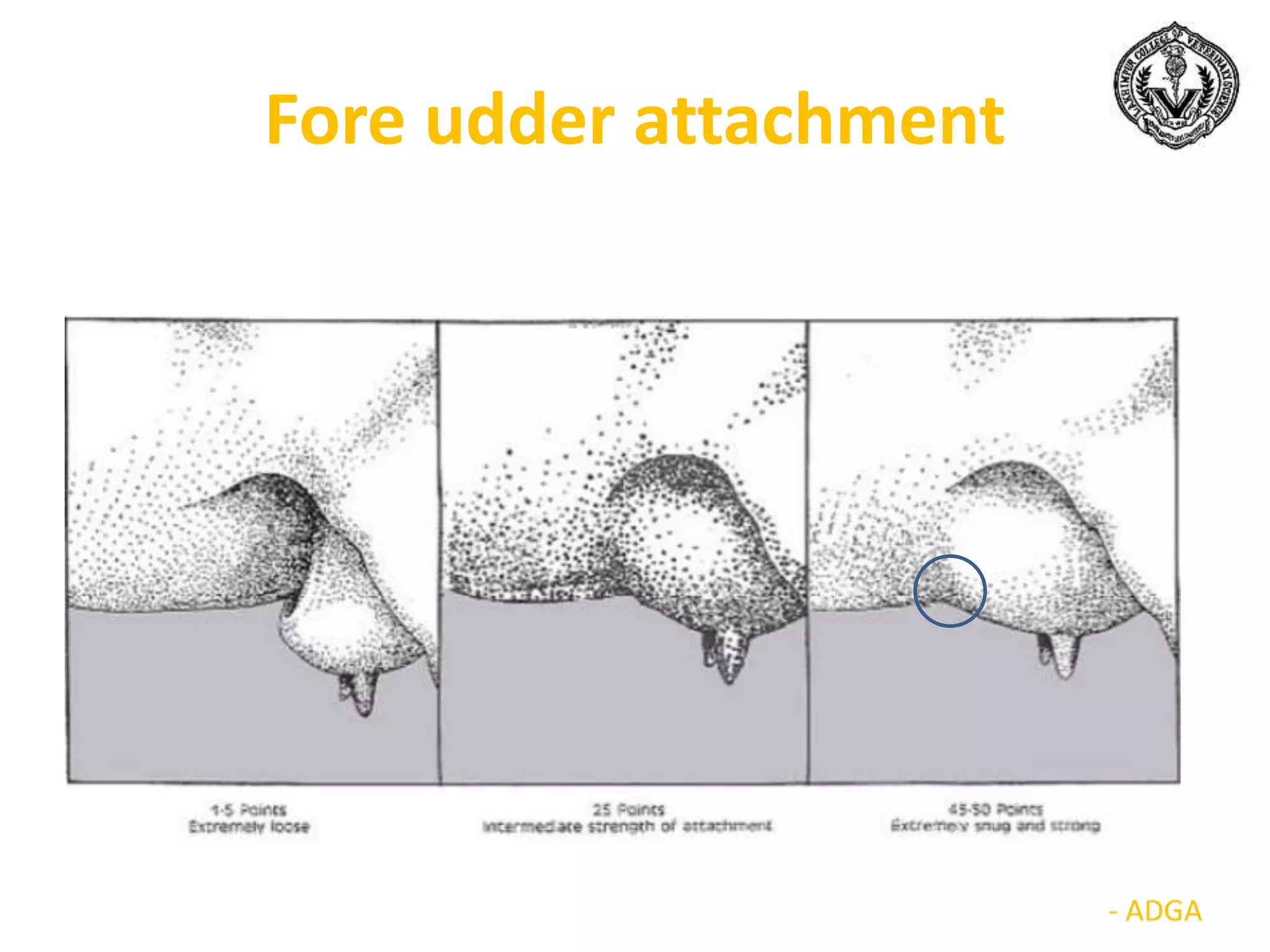
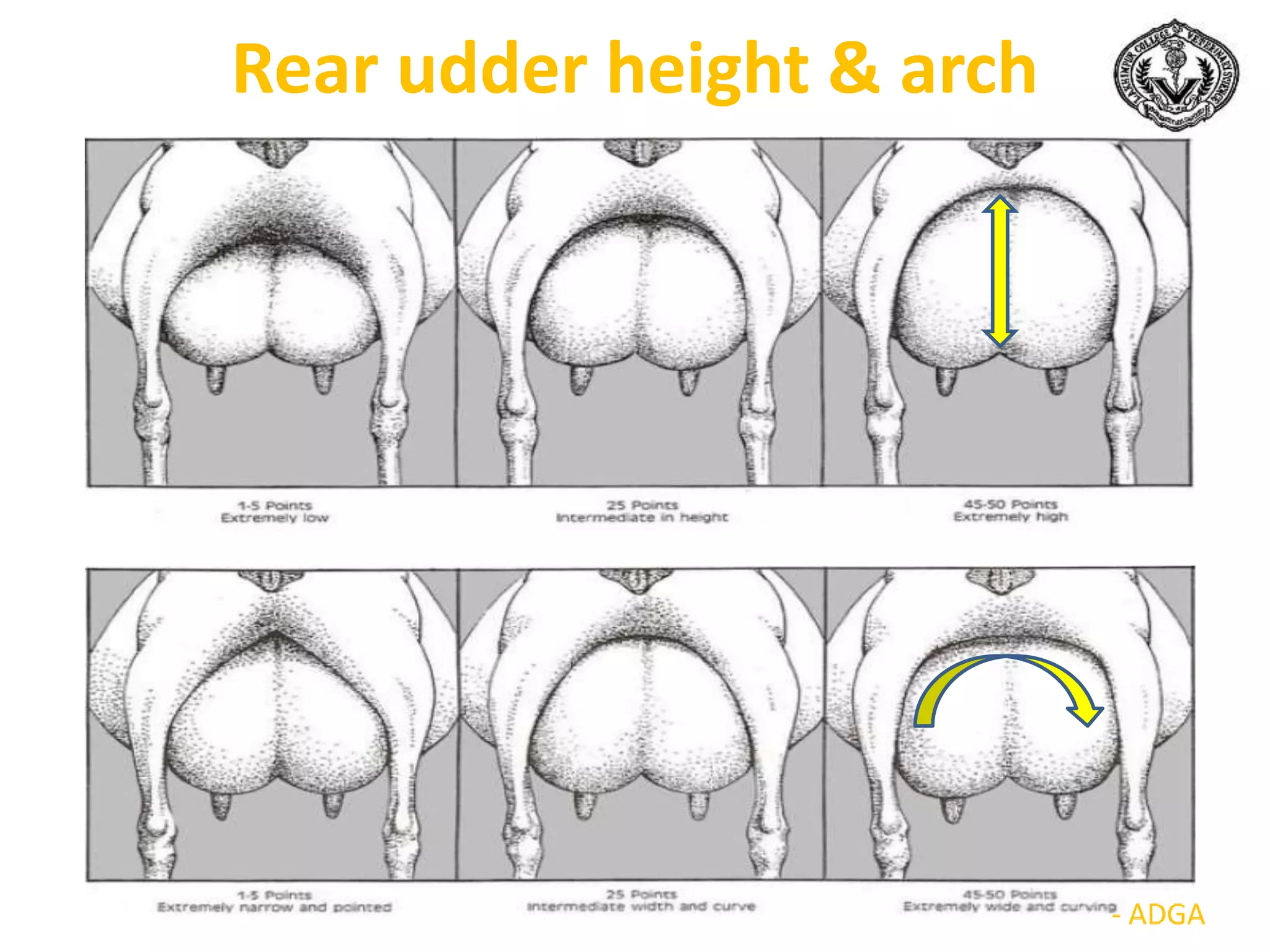
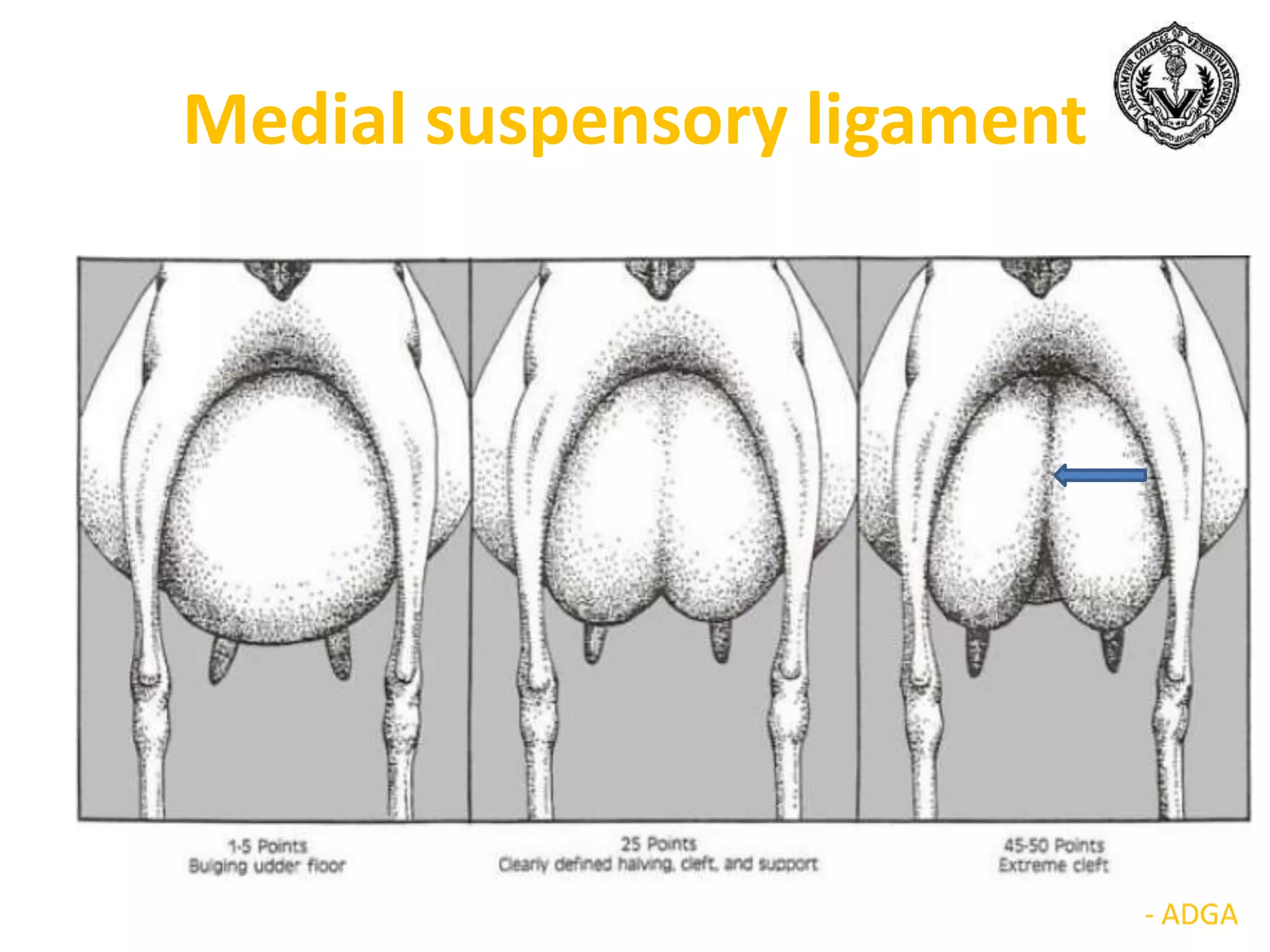
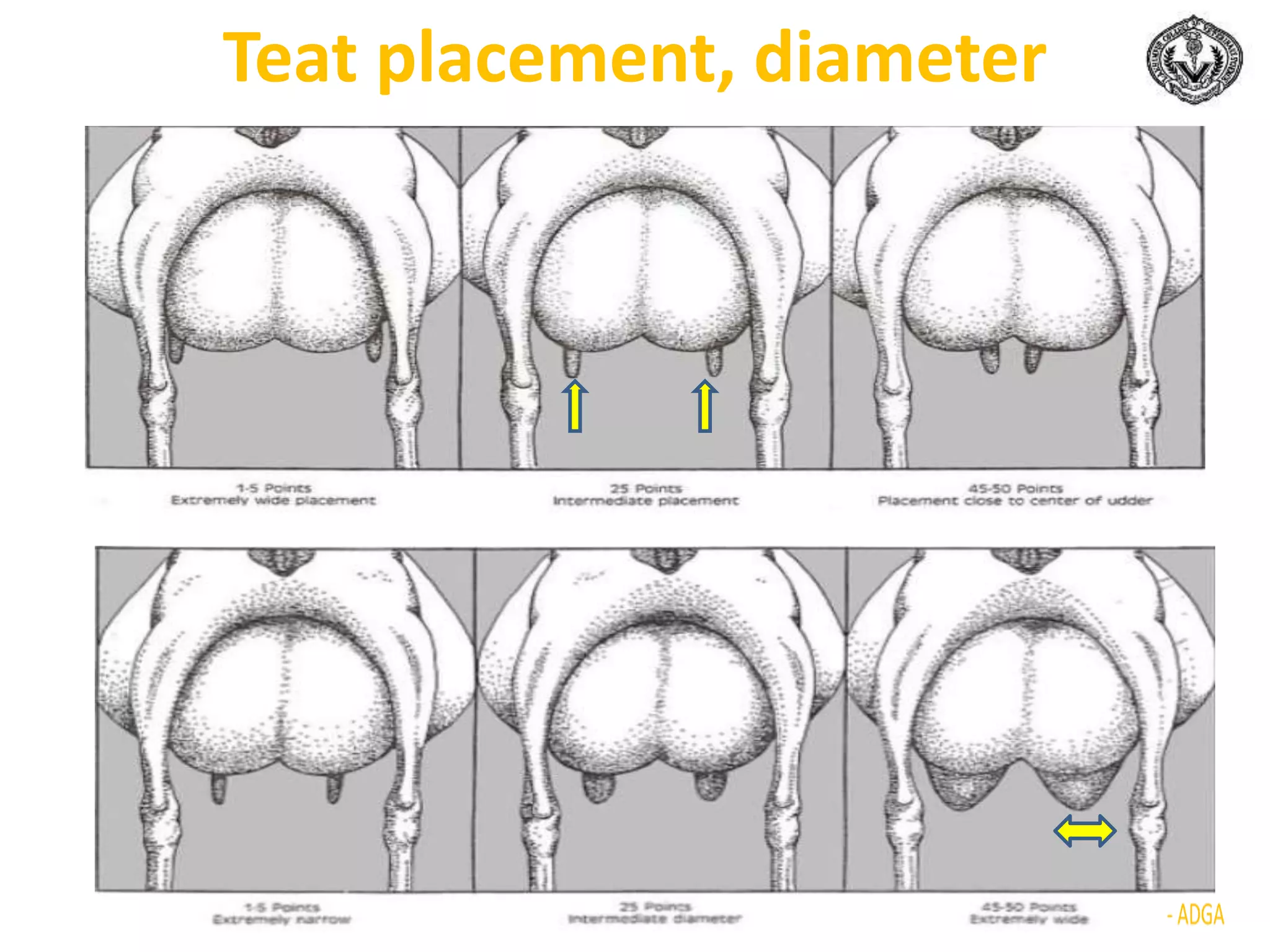
The document discusses selection of goats for farming. It begins by outlining why goat farming is important, noting that goats require less space, are easier to maintain than other livestock, and are well-suited to India's agro-climatic conditions. It then provides statistics on goat populations in India and the state of Assam. The document emphasizes the importance of selection and provides criteria for selecting bucks and does based on conformation, structure, muscling, growth, and symmetry. Proper dentition, udder development, and testicle size are some of the key traits discussed. The conclusion stresses that careful selection can enhance productivity and market value.