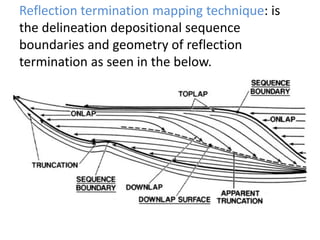
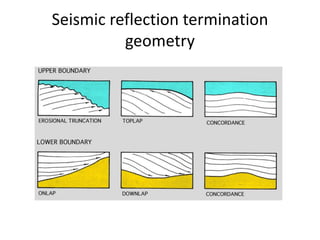
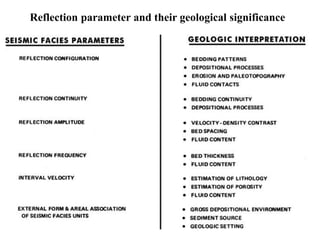
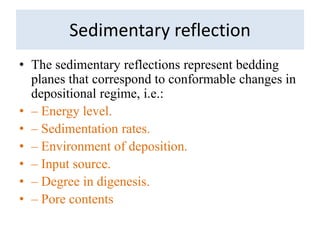
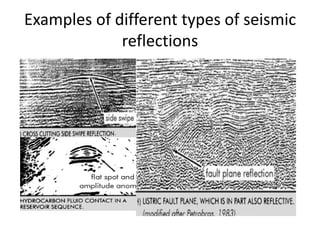
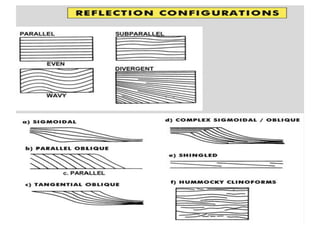
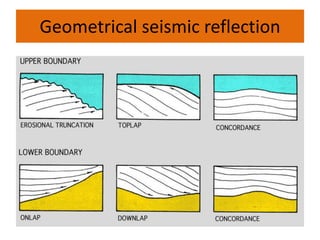
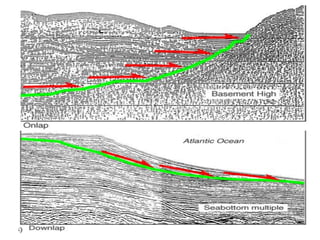
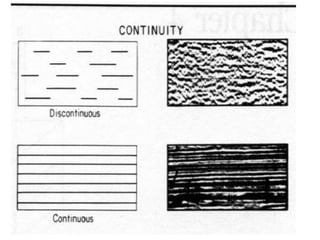
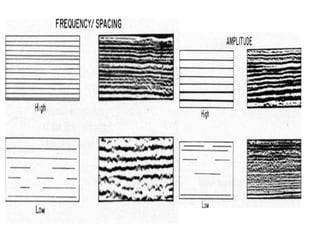
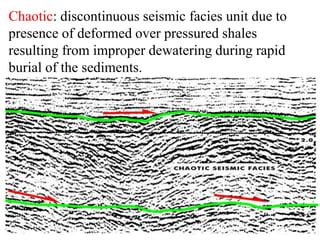
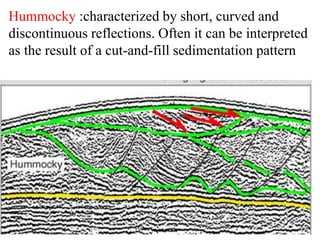
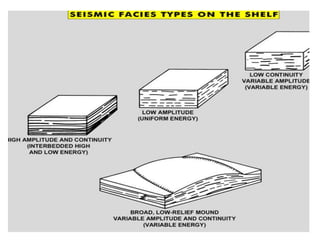
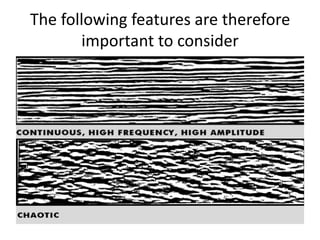
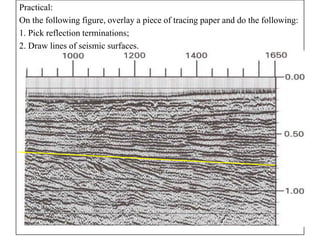
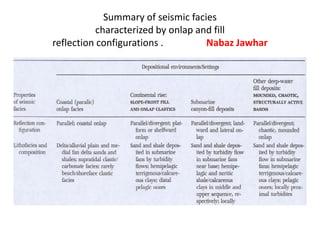
The document discusses techniques for seismic stratigraphy analysis and interpretation. It describes delineating depositional sequences using reflection termination mapping. Reflection terminations indicate strata discontinuities and can be truncation, toplap, baselap, onlap, or downlap. Seismic sequence analysis involves analyzing seismic sequences, facies, and interpreting depositional environments. Reflection configurations, continuity, amplitude, and frequency are used to define seismic facies units representing depositional environments and lithofacies.