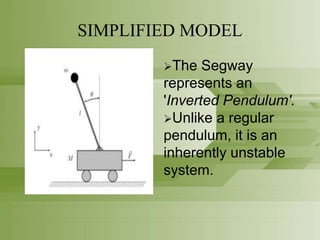
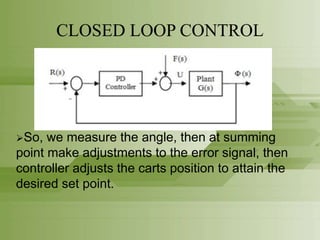
This document provides an overview of the Segway personal transporter. It describes the Segway's basic design as a self-balancing two-wheeled electric vehicle. It then models the Segway as an inverted pendulum, an inherently unstable system. It explains how sensors, PID control, and a motor are used in a closed-loop control system to stabilize the Segway and keep the rider upright through feedback of angle measurements. Applications of control theory allow the Segway to smoothly transition directions in response to the rider's movements.