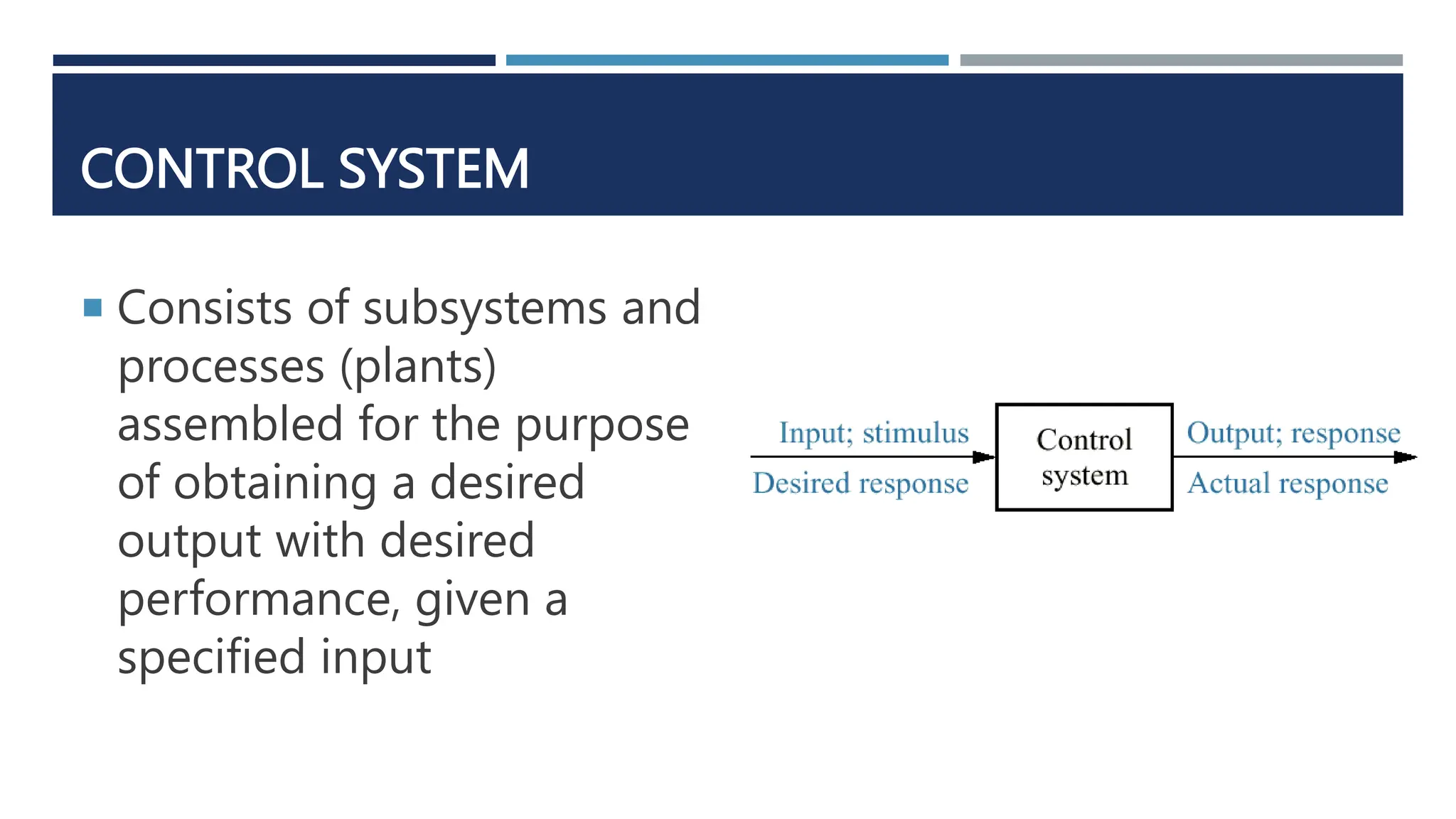
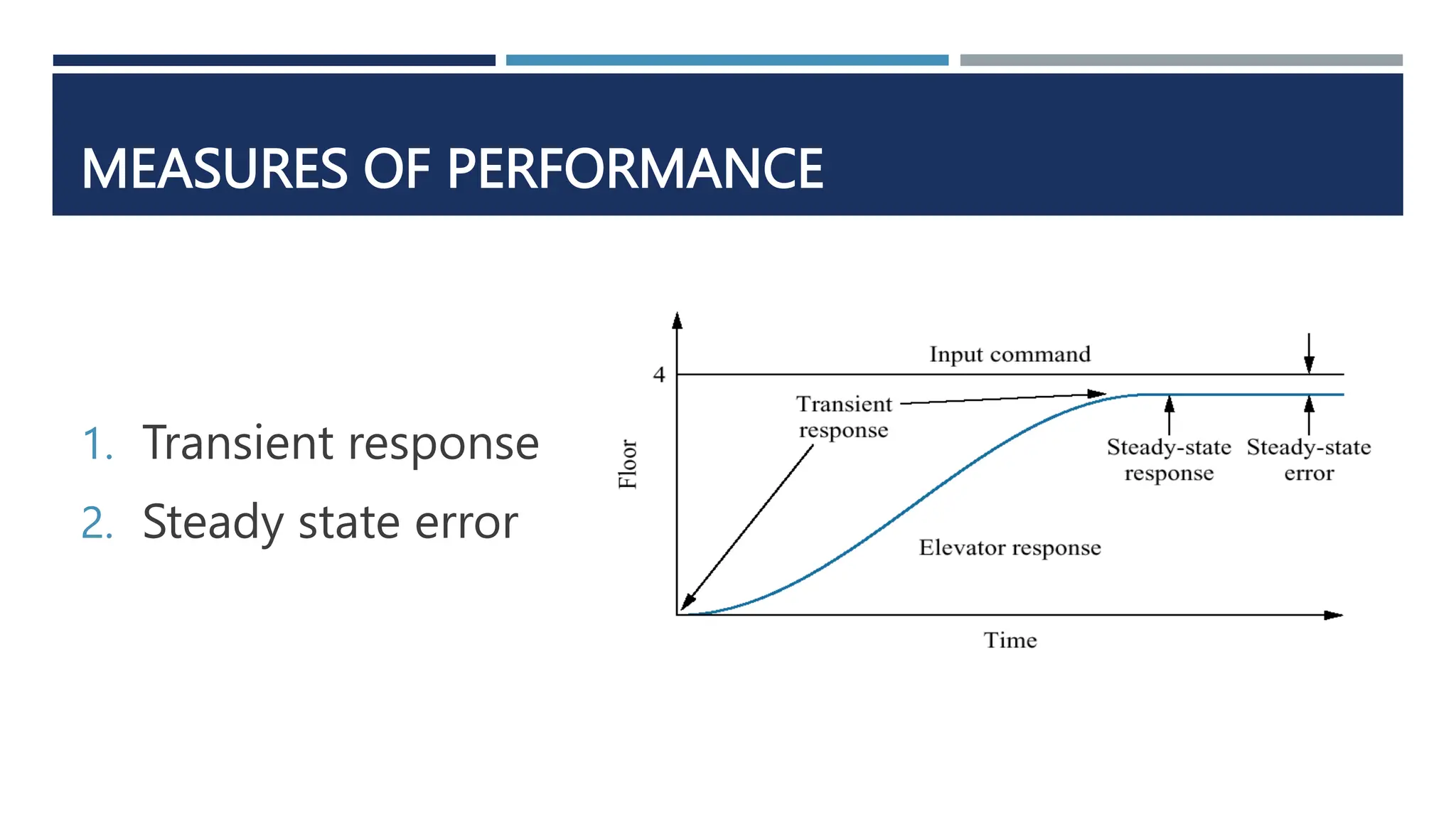
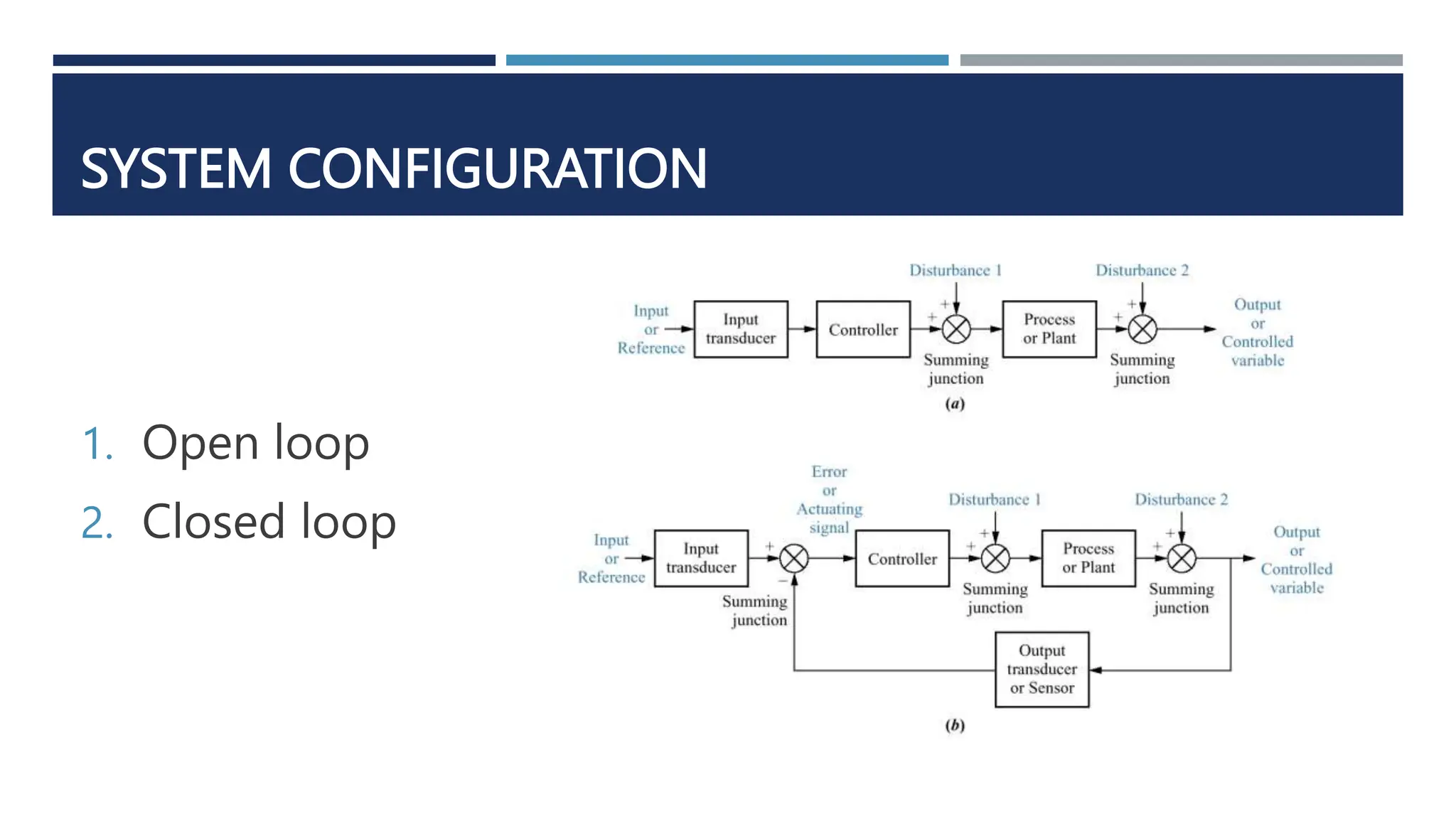
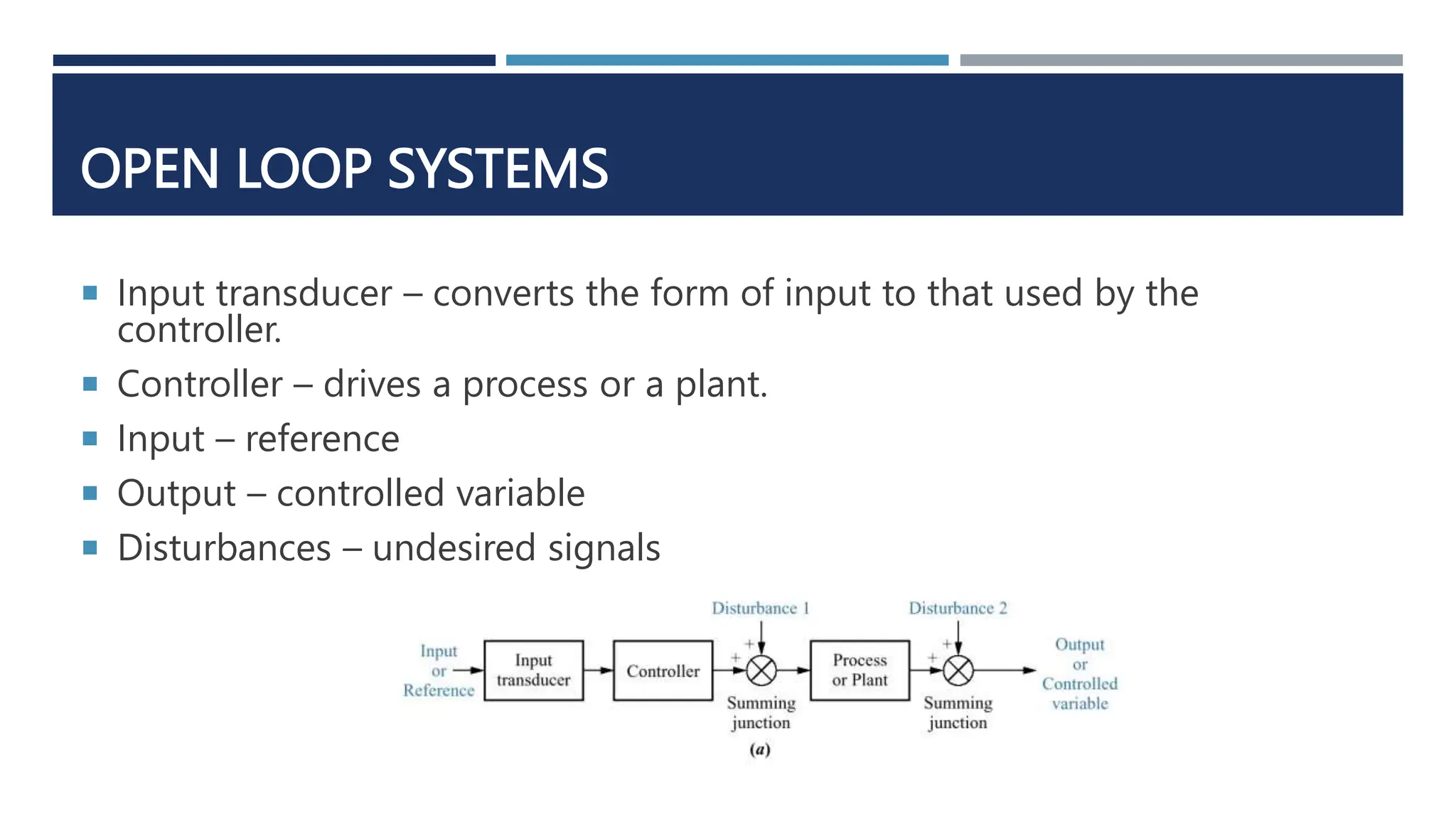
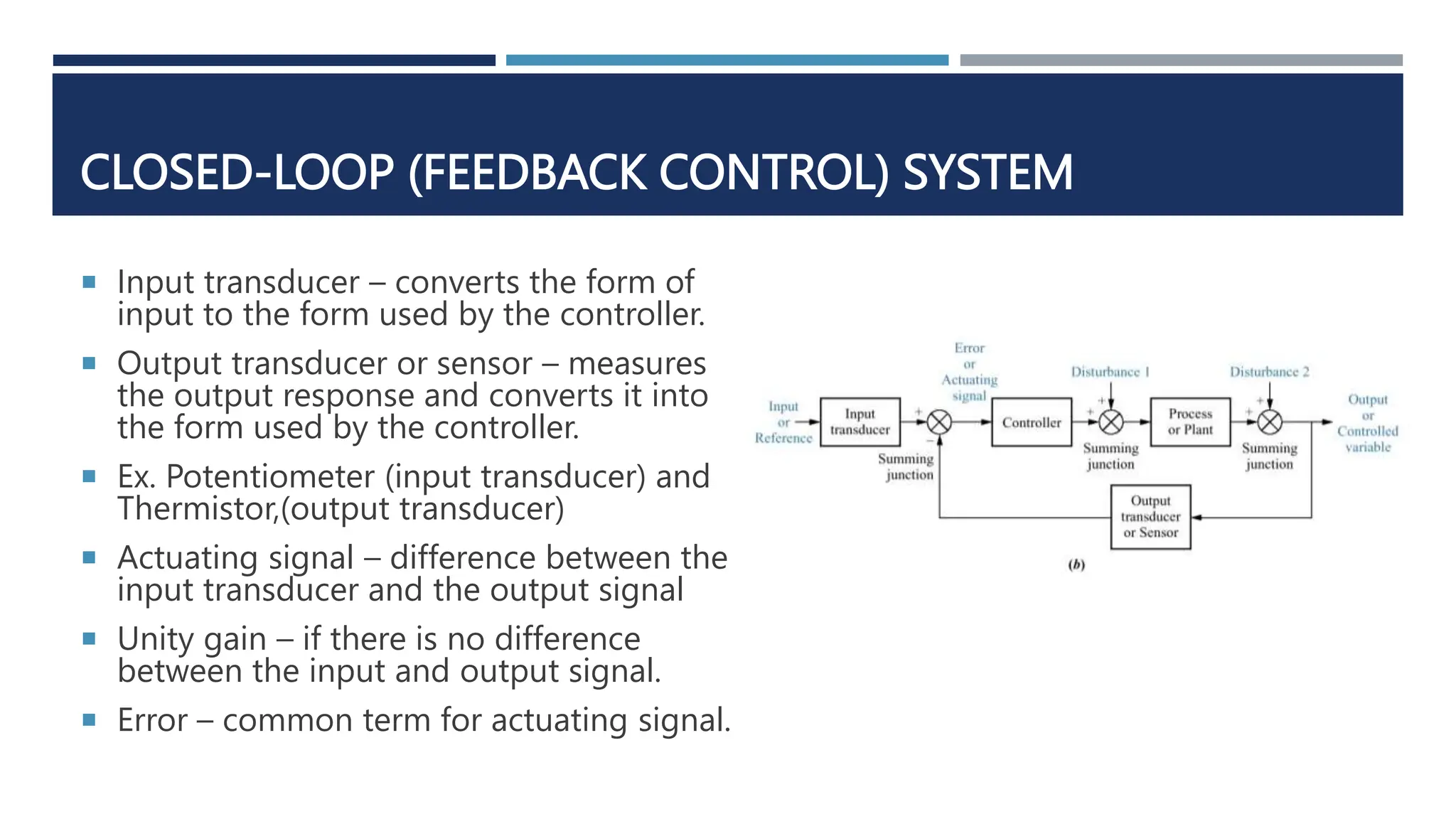
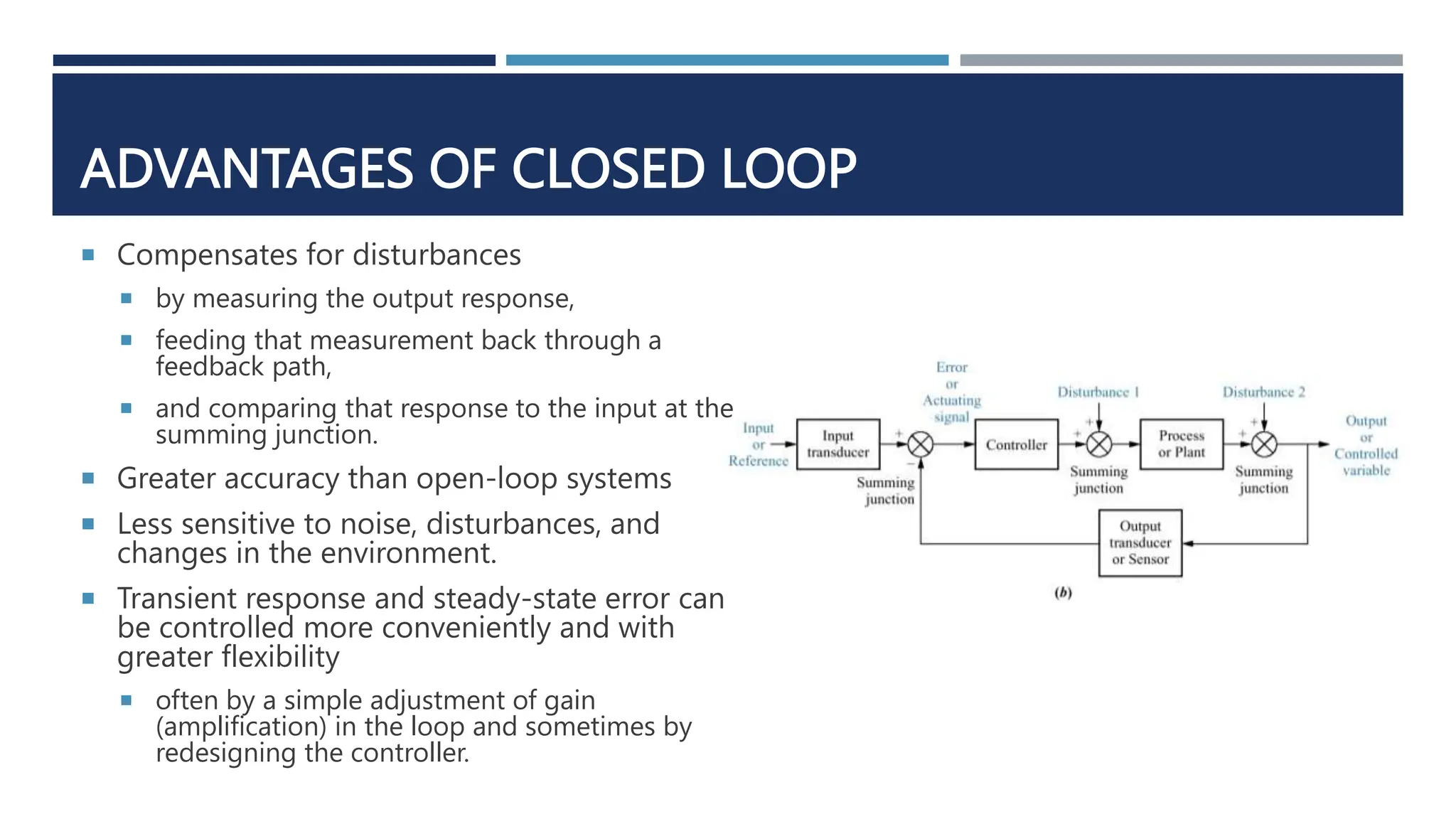
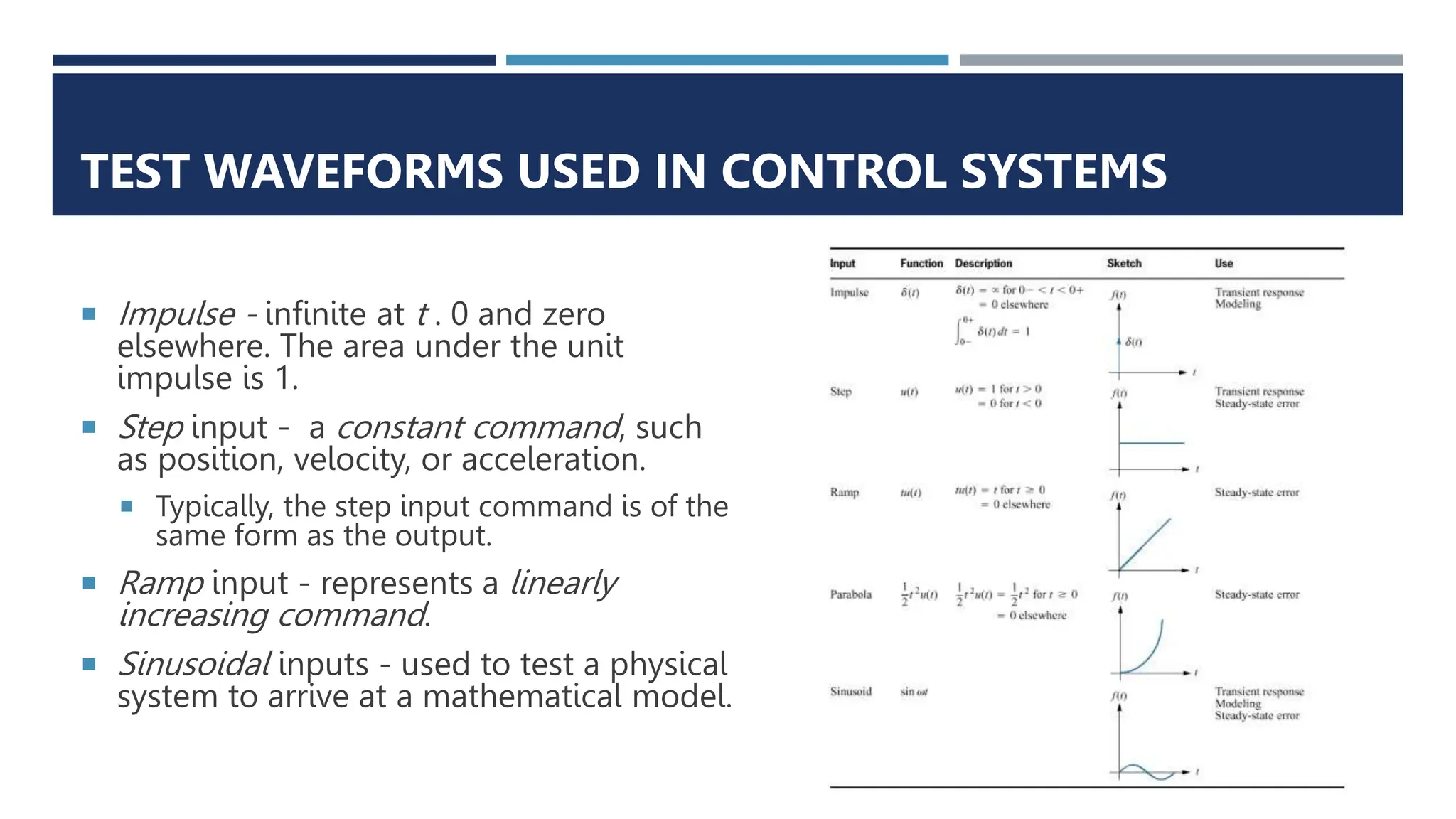
This document provides an overview of control systems engineering. It defines a control system as consisting of subsystems and processes assembled to obtain a desired output given an input. Control systems can be open-loop or closed-loop. Closed-loop systems use feedback to compensate for disturbances and improve accuracy over open-loop systems. The objectives of control system analysis and design are to achieve desired transient response, steady-state response, and stability. Test waveforms like impulses, steps, and sine waves are used to analyze system performance.