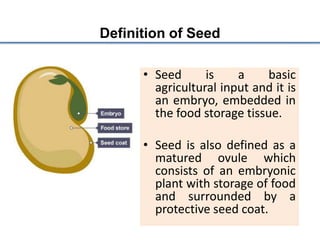
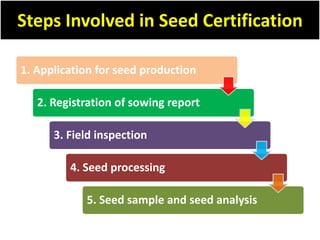
Seed certification is a quality assurance system that subjects seeds intended for marketing to official controls and inspections. It involves a series of seed multiplication steps - from breeder seed to foundation seed to registered seed to certified seed - to produce sufficient quantities of pure seed for commercial use while maintaining genetic purity. The key steps in seed certification include applying for seed production, registering sowing reports, conducting field inspections, processing seeds, sampling and analysis, tagging certified seeds that meet standards. This ensures farmers have access to high quality seeds of improved varieties.