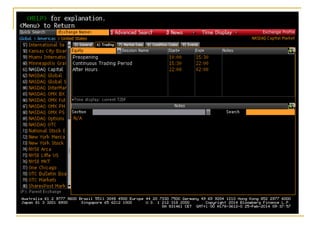
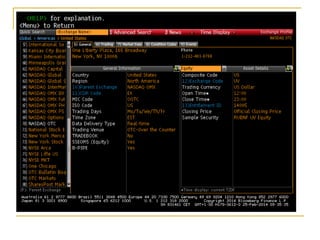
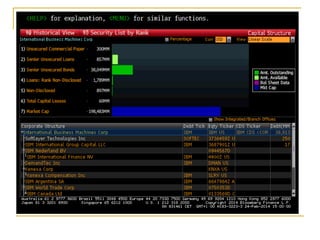
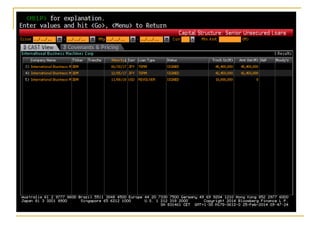
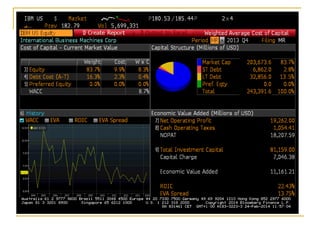
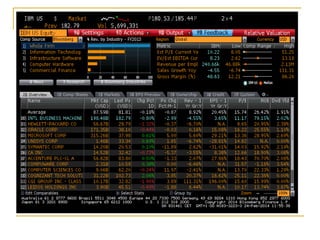
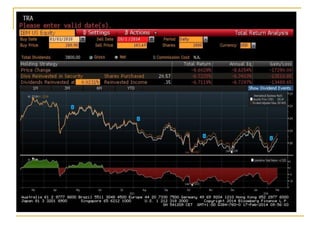
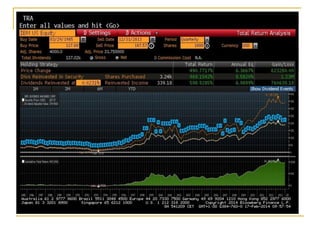
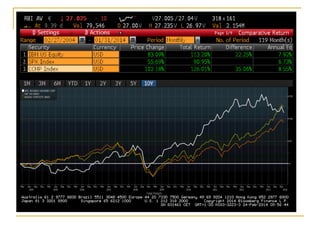
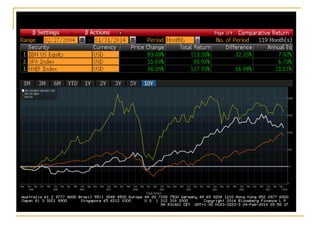
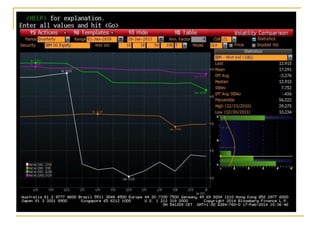
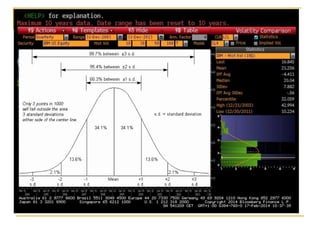
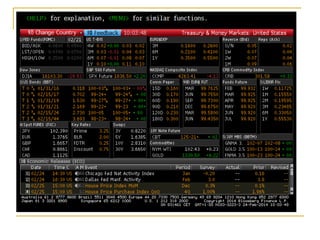
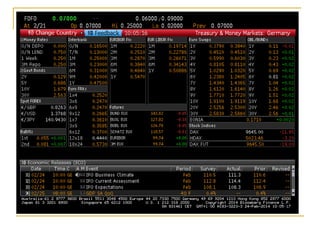
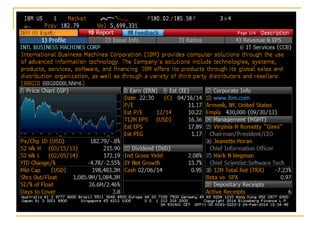
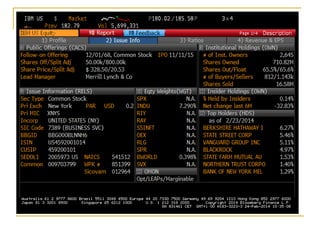
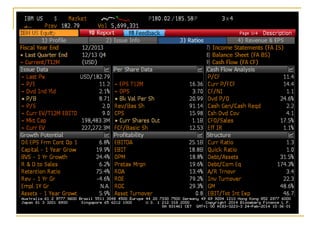
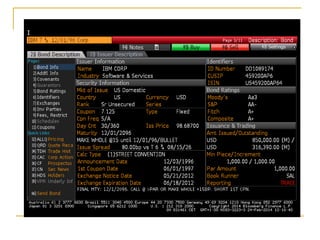
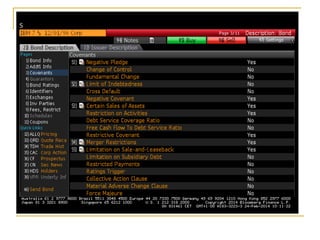
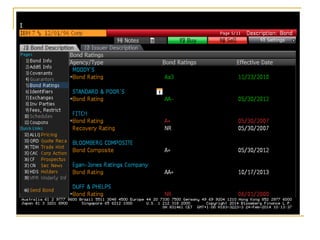
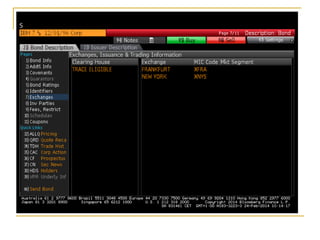
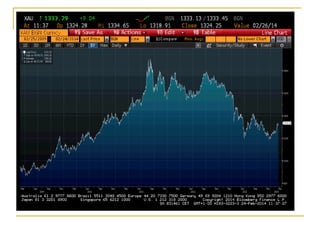
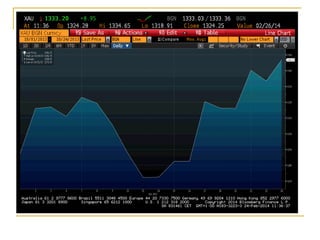
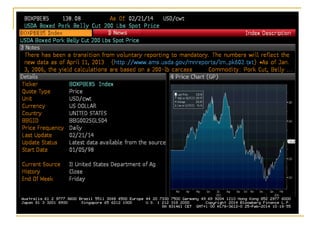
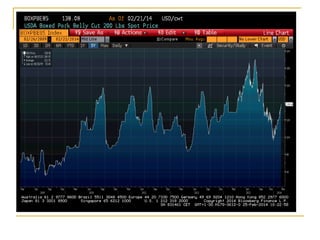
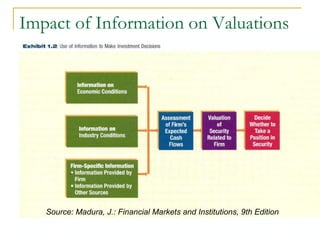
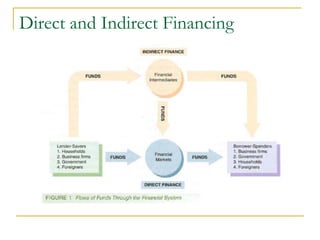
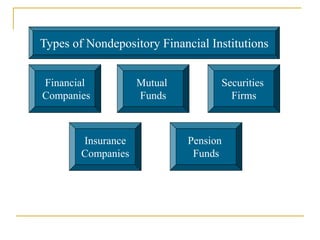
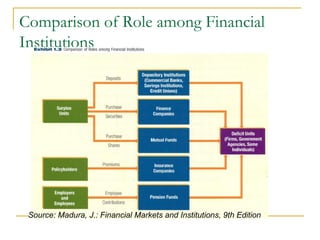
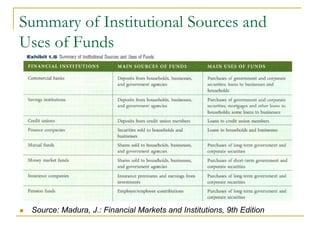
The document provides an overview of financial markets and institutions. It discusses the roles of financial markets in transferring funds from surplus units to deficit units through various debt and equity securities. It also describes different types of financial markets, securities, and regulations. Financial institutions help reduce transaction costs and facilitate indirect financing between lenders and borrowers.