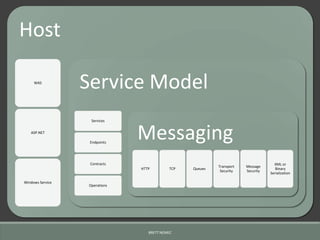
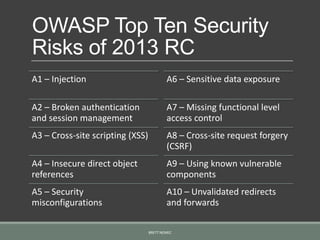
This document discusses securing Microsoft .Net hosted services. It provides an overview of Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) and ASP.NET MVC Web API for building services, and examines the top 10 security risks from the OWASP project. For each risk, it describes how it could apply to hosted services and recommendations for mitigation, such as using parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection, encrypting sensitive data, and implementing role-based access controls.










![A4 – Insecure direct object
references
Authorize attribute
◦ Using role-based authentication
◦ When a message is sent to an endpoint, service calls custom role provider
for the requested operation
◦ Example:
[Authorize(“Administrators”)]
public void GetAllUsers();
BRETT NEMEC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capstonepresentation-130423230845-phpapp01/85/Securing-Net-Hosted-Services-13-320.jpg)






