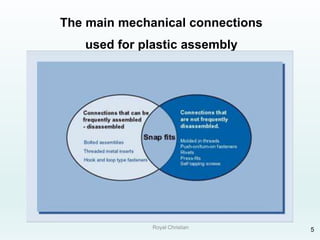
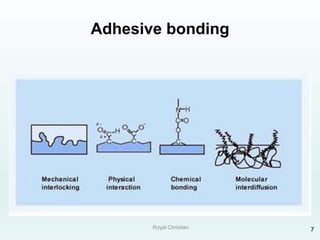
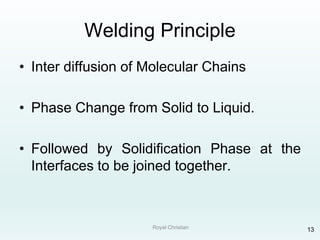
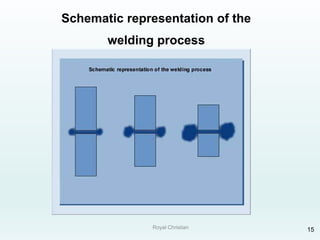
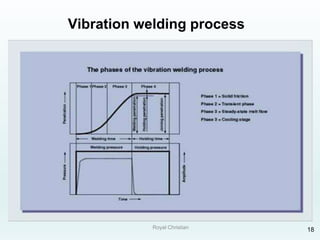
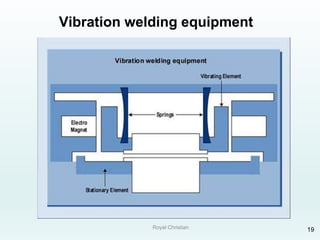
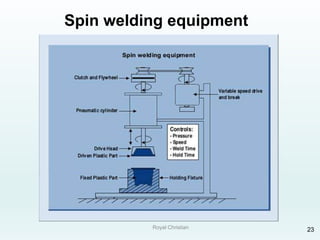
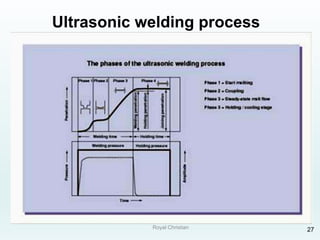
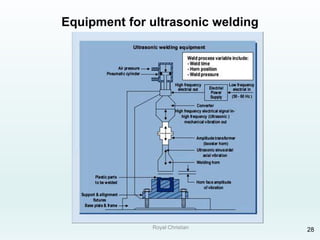
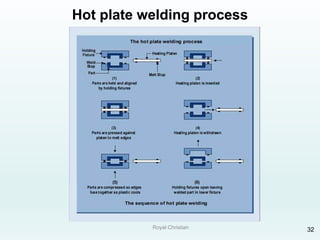
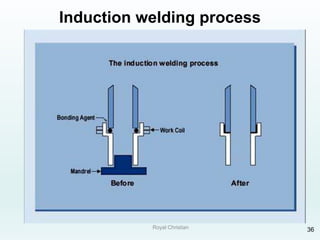
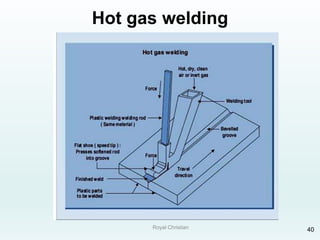
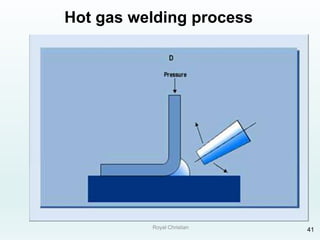
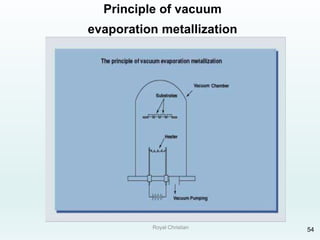
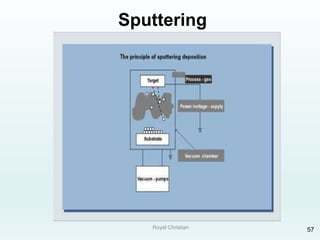
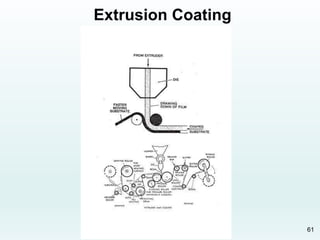
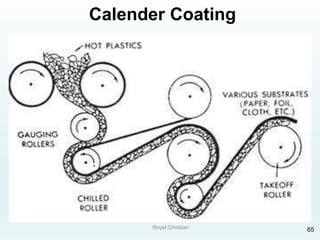
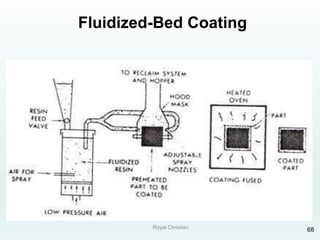
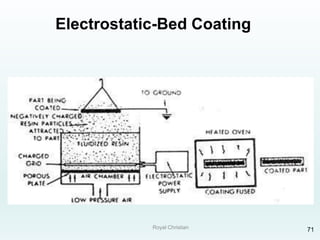
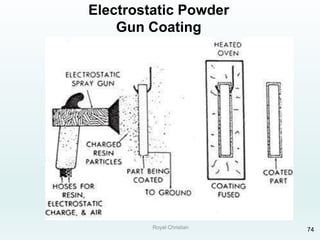
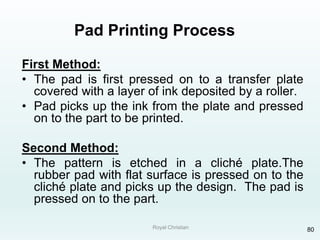
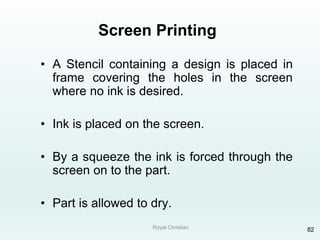
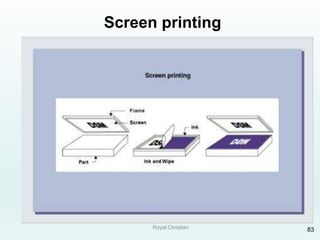
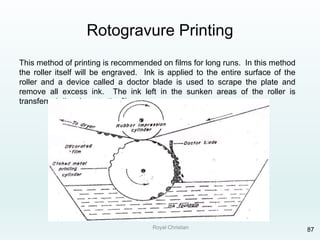
The document discusses various joining, assembling, and surface modification methods for plastics, including mechanical connections, gluing, welding, machining, surface treatment, metallization, and coating processes. Some key joining methods discussed are vibration welding, spin welding, and ultrasonic welding, while common surface processes include flame treatment, corona treatment, and various vacuum metallization techniques. The advantages and disadvantages of different techniques are provided for joining, machining, and modifying plastic materials and components.