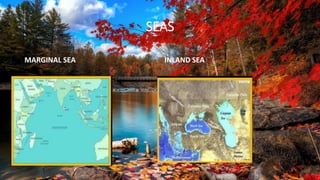
The document discusses major water bodies on Earth. It describes the five oceans: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Antarctic oceans. It provides details on the size and locations of each ocean. It also discusses seas and distinguishes between marginal seas and inland seas. Minor water bodies like bays, gulfs, lakes, lagoons, rivers, and straits are also outlined.