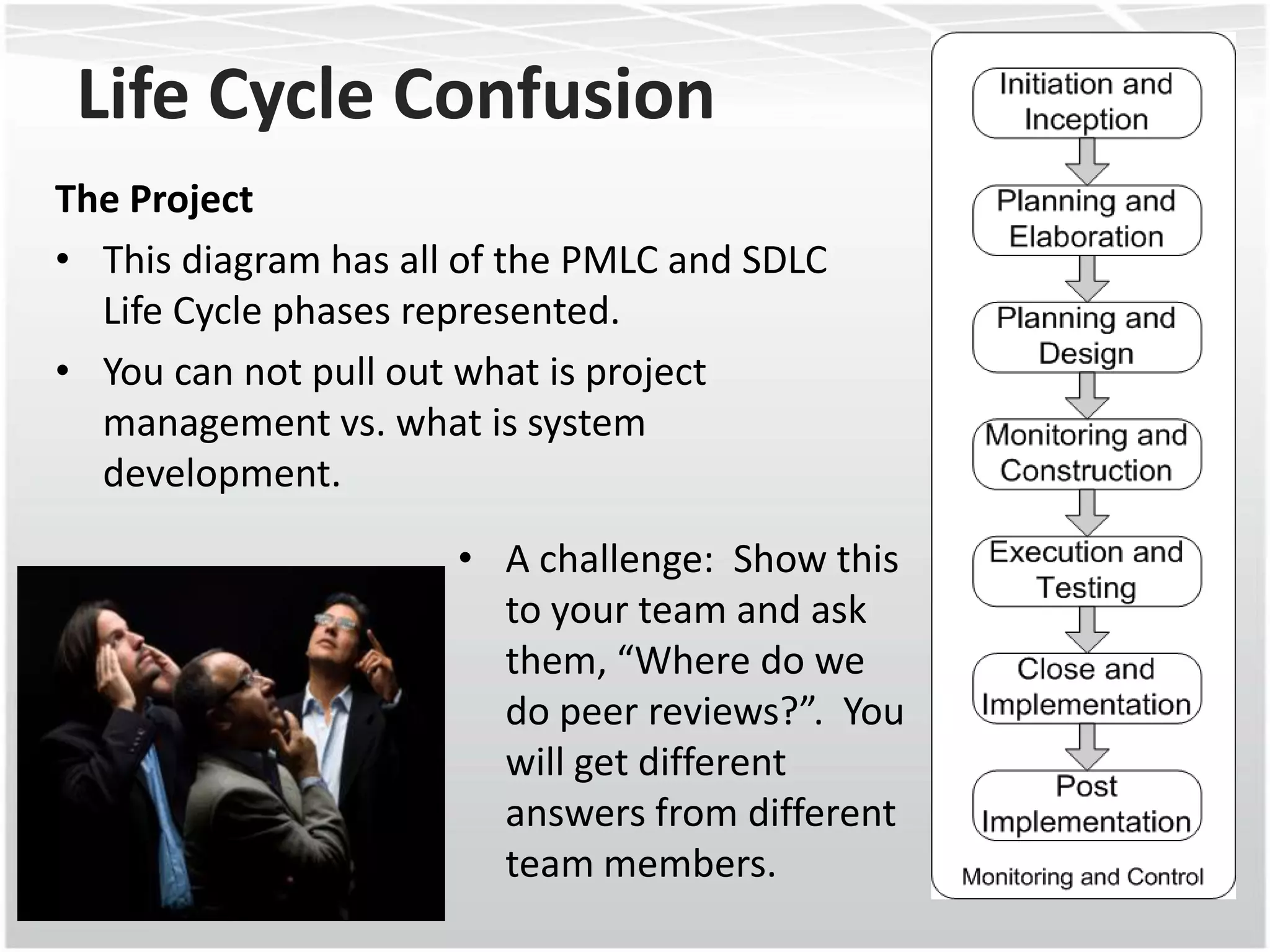
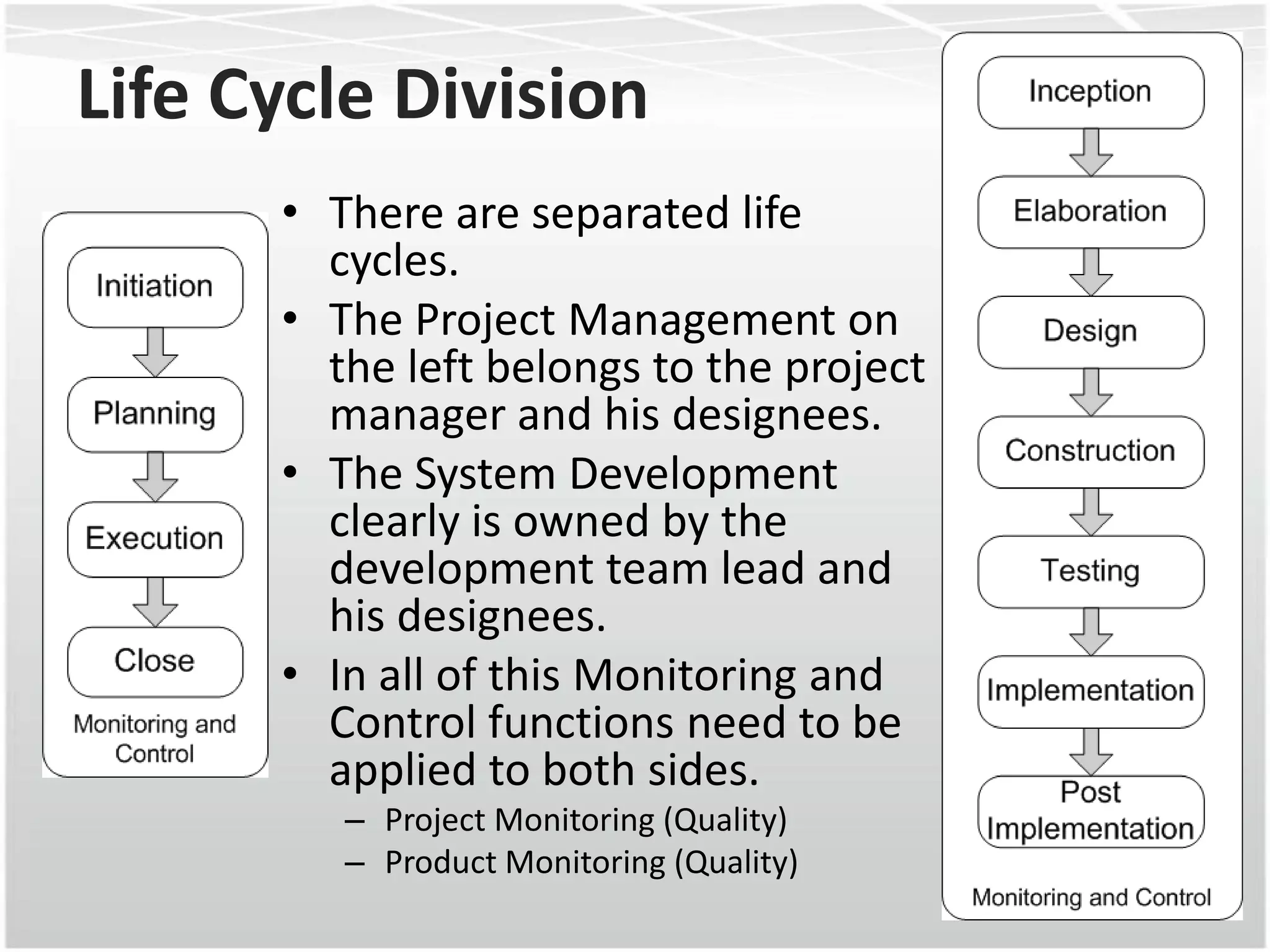
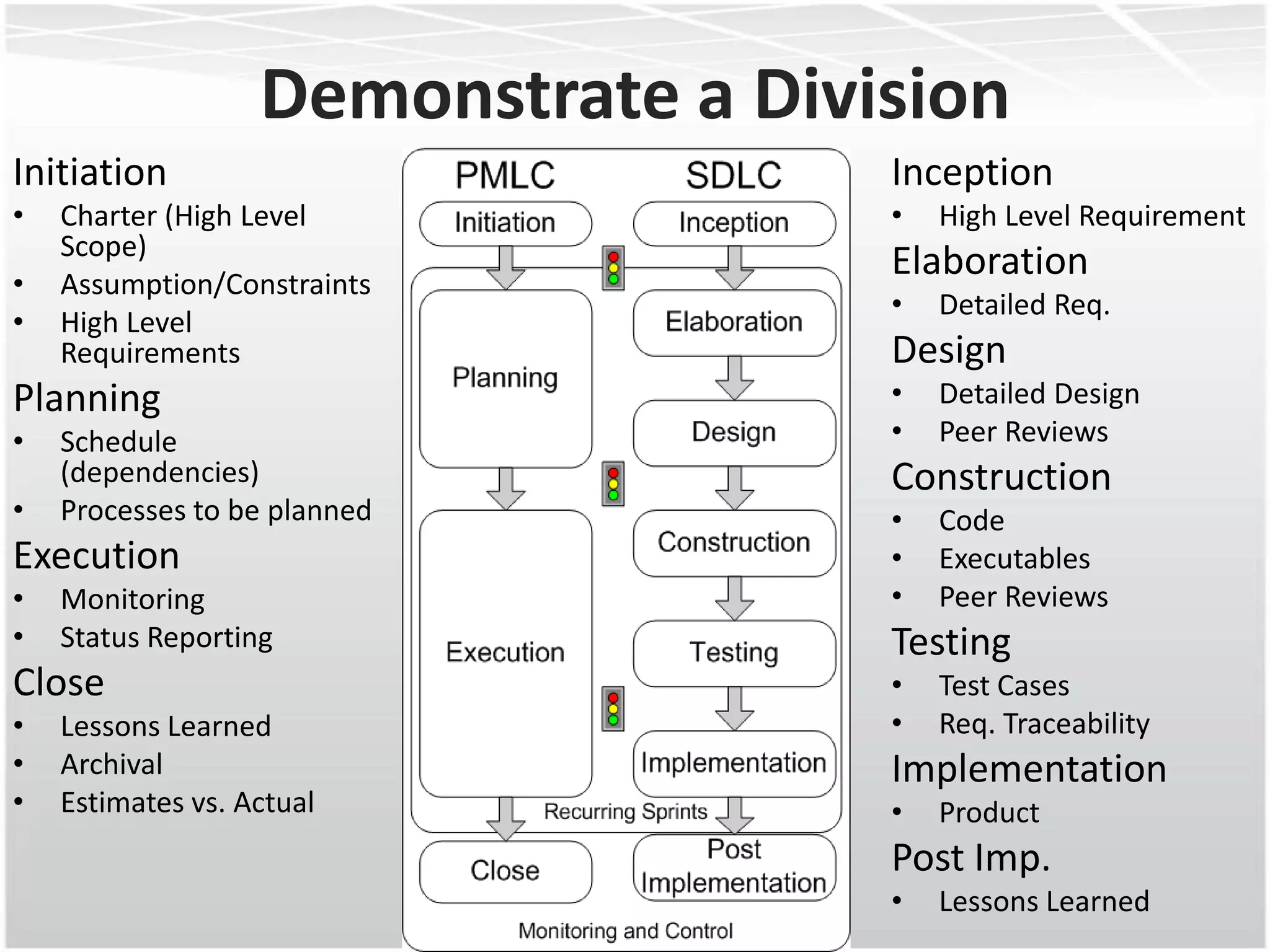
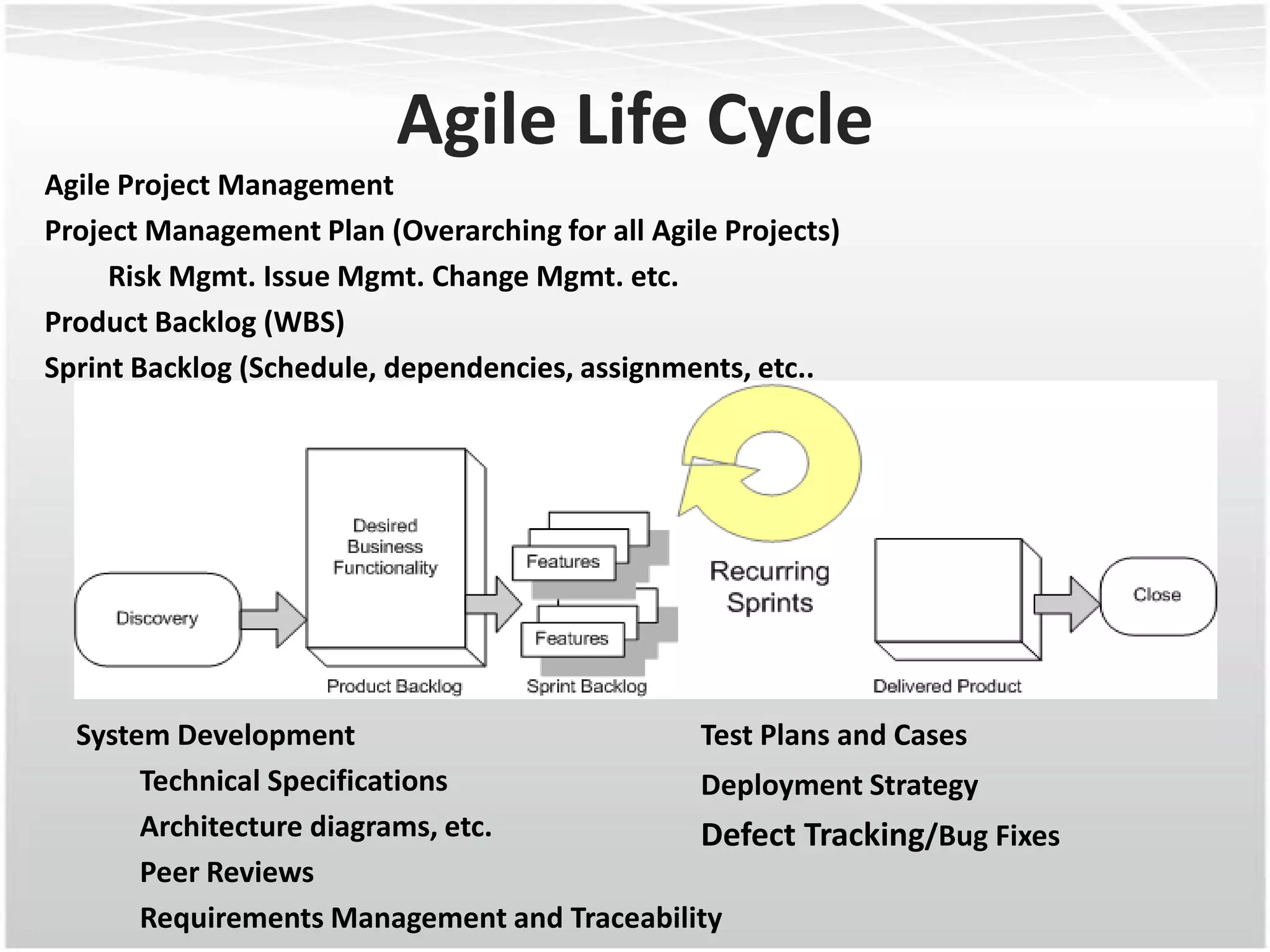
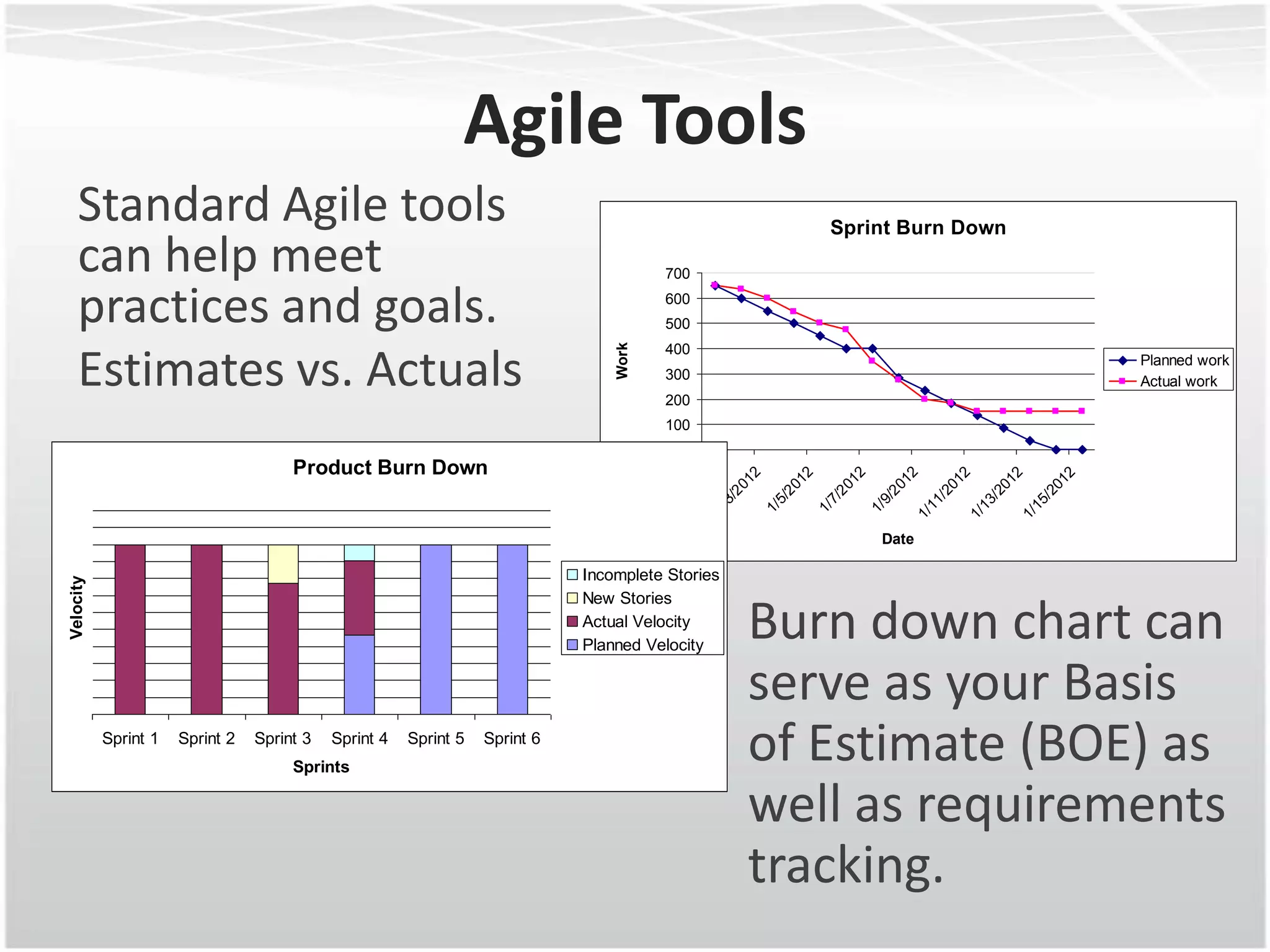
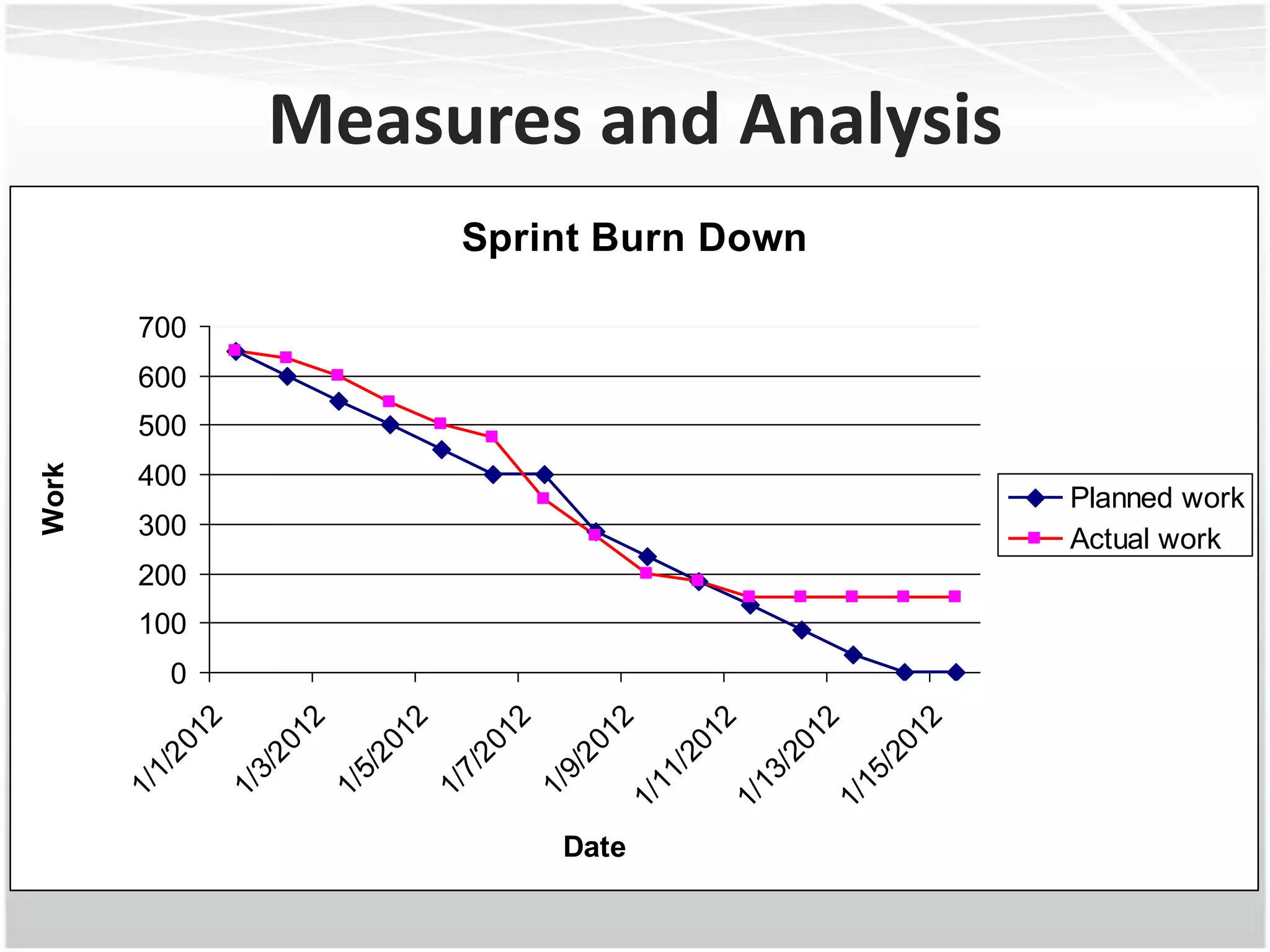
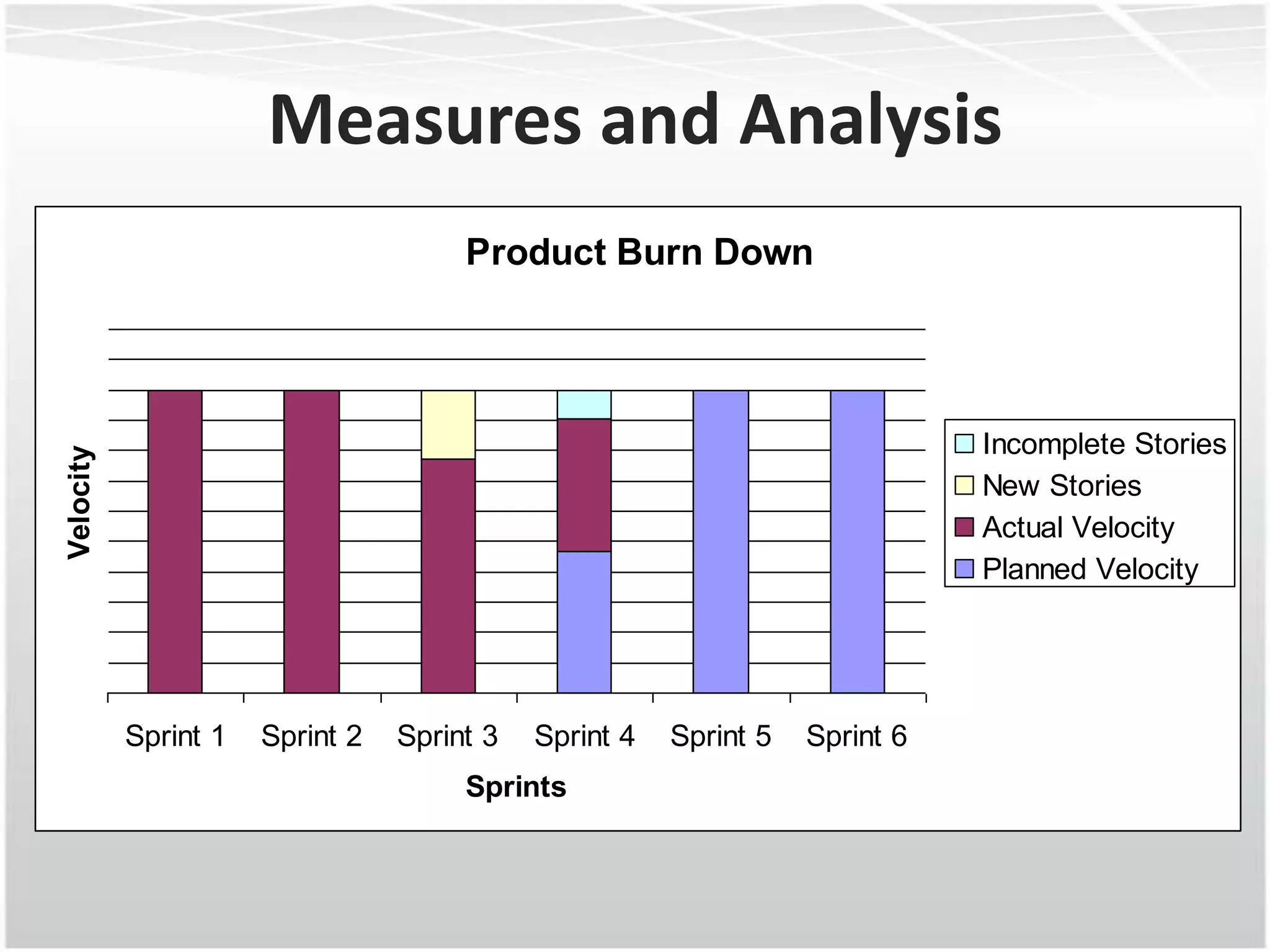
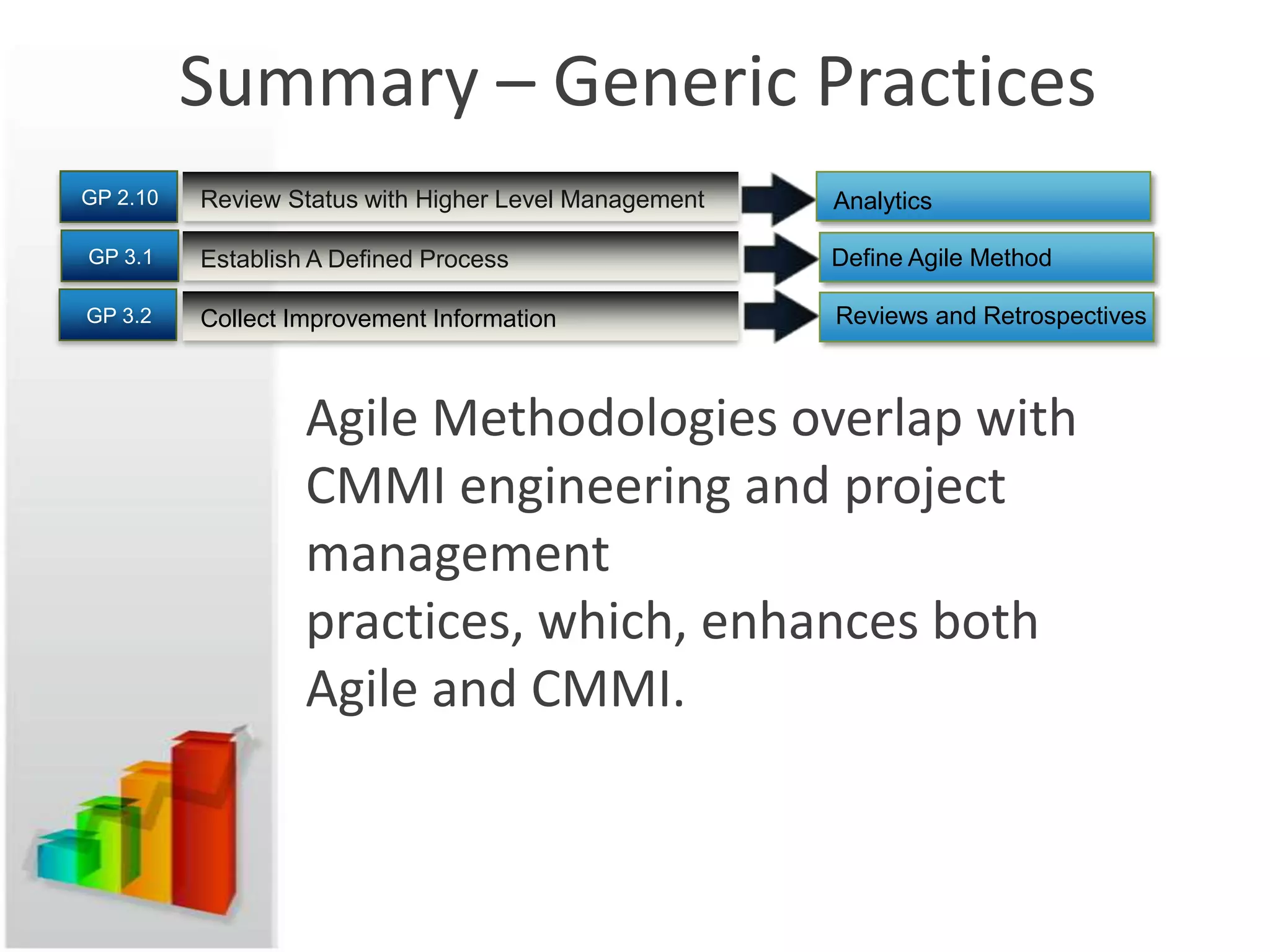
This document discusses how agile methodologies can overlap with the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) framework. It provides an overview of CMMI and the agile manifesto. It then explains how tools like sprint burn down charts and velocity charts can help meet CMMI generic practices like monitoring and controlling processes, objectively evaluating adherence, and collecting improvement information. The document demonstrates how agile artifacts like product and sprint backlogs align with CMMI work breakdown structures and responsibilities. In summary, it argues that agile methodologies can enhance both CMMI and agile by bringing practices from each approach together.



![Agile Manifesto
“We are uncovering better ways of developing software by
doing it and helping others do it. Through this work we
have come to value [the following]:
• Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
• Working software over comprehensive documentation
• Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
• Responding to change over following a plan
That is, while there is value in the items on the right, we
value the items on the left more.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agilematurityv11-ppt-120525134845-phpapp02/75/SCRUM-CMMI-SCRUMMI-5-2048.jpg)