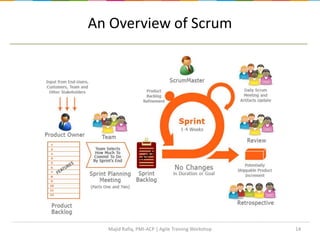
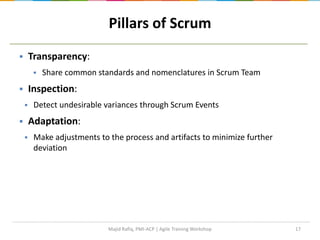
This document provides an agenda for an Agile training workshop. The agenda includes an introduction to Agile concepts like Scrum, XP, and Kanban. It covers the Agile manifesto and principles, an overview of Scrum including roles, ceremonies, and artifacts. Specific Scrum topics like user stories, planning poker, daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives are explained.