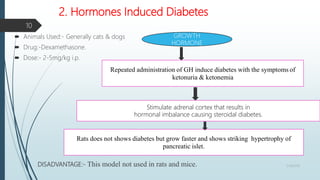
This document summarizes various screening models for diabetes, including in vivo and in vitro models. For in vivo models, it describes chemically-induced diabetes models using alloxan and streptozotocin in rodents, as well as spontaneous genetic rodent models like BB rats and KK mice. In vitro models discussed include isolated pancreatic islet cells, cultured human myotubes for glucose uptake studies, and the Gluc-HET chick embryo model for assessing insulin mimetic compounds. The document provides details on the procedures, advantages and limitations of each type of screening model.








![Insulin antibody induced diabetes
Principle: - A transient diabetic syndrome can be Induced by injecting guinea pigs with anti insulin serum.
Preparation of antibody:-
Procedure:-
Bovine insulin, dissolved in
acidified water [ph 3.0] at a
dose of 1mg /ml
Injected into
guinea pigs
Anti insulin sera is
collected after two
weeks of antigenic
challenge
Adult albino rats are
injected
with 0.25-1.0 ml of guinea
pig
anti- insulin serum.
Blood glucose level 300
mg/ dl.
The drug sample to be
screened is given and
blood glucose level is
analyzed to determine
the activity.
5/18/2018
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14kundlik-180518121511/85/screening-model-for-diabetes-10-320.jpg)
![VIRUS INDUCED DIABETES
PURPOSE:- Infecting and destroying B-cells in pancreas.
Viruses producing systemic effects, not directly affecting B-cells.
Viruses inducing diabetes include:
a) RNA picornoviruses
b) Coxsackie-B4
c) Encephalomyocarditis virus
Procedure:-
Limitation:- 5/18/2018
11
Old mice are 6-8 week injected with D- variant of encephalomyocarditis [EMC] i.p.
pretreatment is given with the cyclosporine A
Drug to be screened is administered orally for a period of 6 weeks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14kundlik-180518121511/85/screening-model-for-diabetes-12-320.jpg)
![Spontaneously or genetically derived animals
Spontaneously diabetic animals of type 2 diabetes may be obtained from the animals with one or
several genetic mutations transmitted from generation to generation (e.g., ob/ob, db/db mice) or
by selected from non-diabetic outbred animals by repeated breeding over several generation
[e.g., (GK) rat, Tsumara Suzuki Obese Diabetes (TSOD) mouse].
These animals generally inherit diabetes either as single or multigene defects as seen in KK mouse,
db/db mouse, or Zucker fatty rat.
Other Rats & Mice
RATS MICE
1. BB rat
2. WBN/KOB rat
3. GOTO/KAKIZAKI
4. ZUKKAR fatty rat
5. WDF/ TA-FArat
6. BHE rat
1. KK mice
2. KK-Ay mice
3. NOD mice
4. Obese hyperglycemic mice
5. New Zealand obese mice
6. Transgenic mice
5/18/2018
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14kundlik-180518121511/85/screening-model-for-diabetes-13-320.jpg)