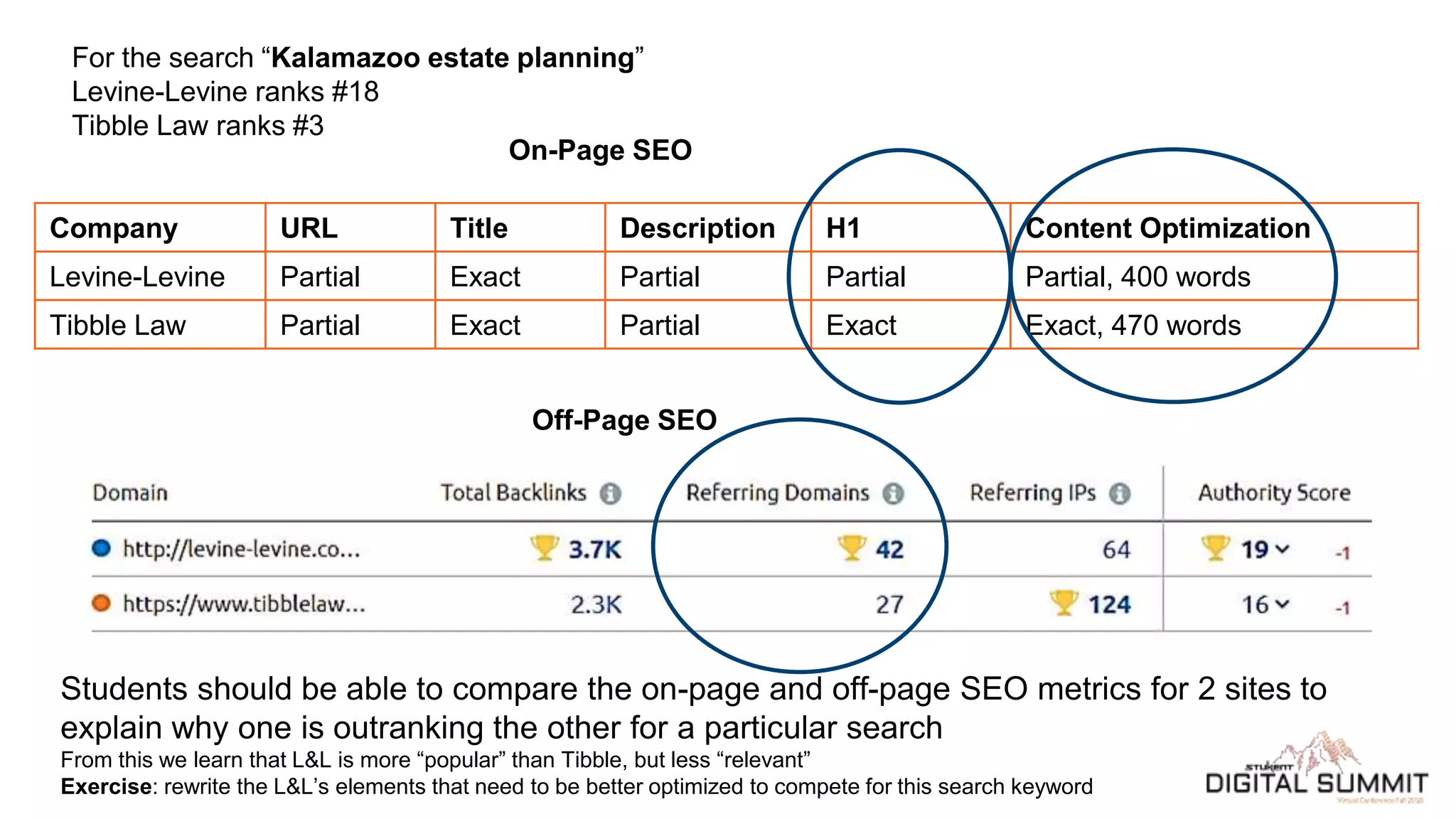
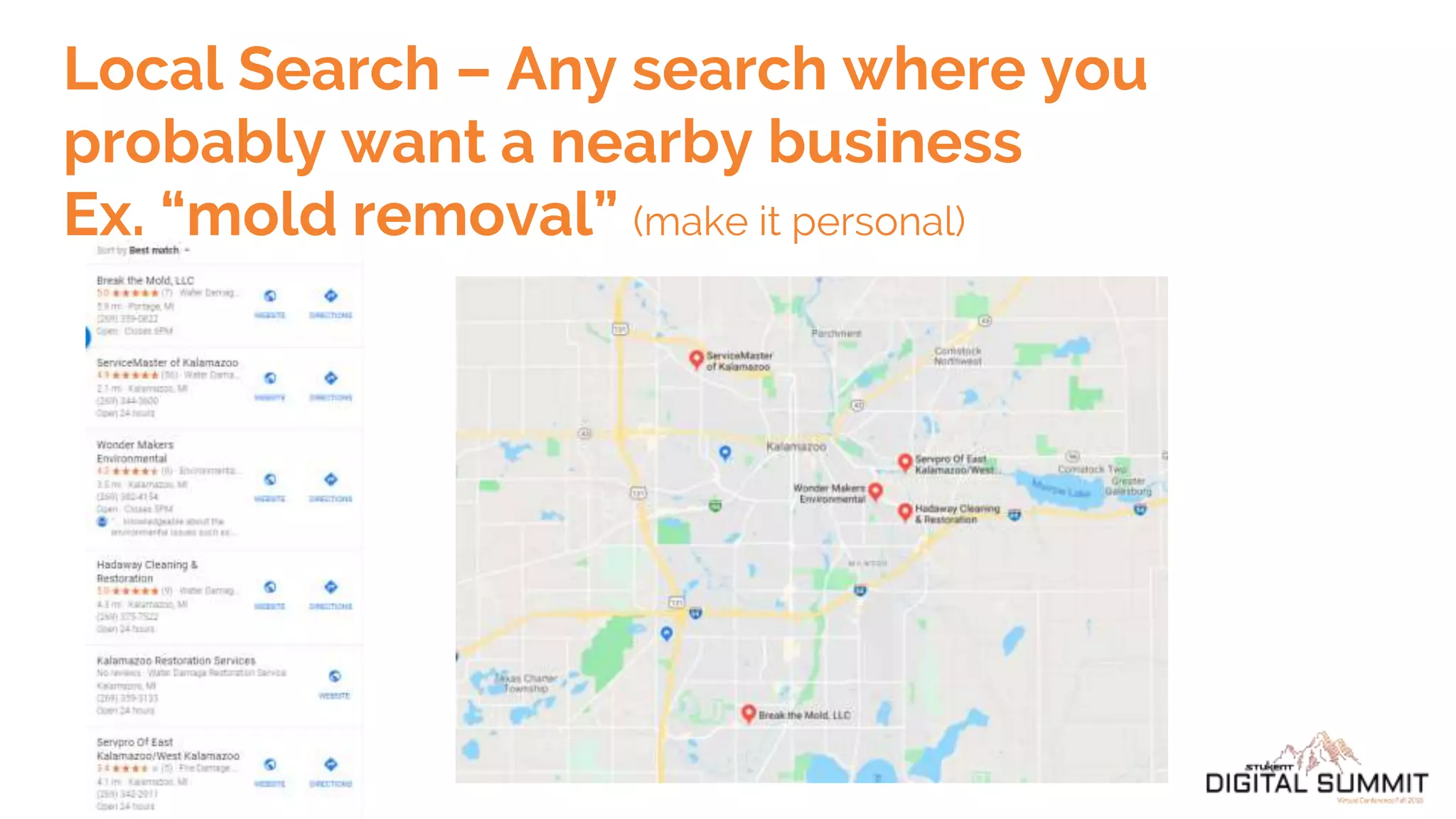
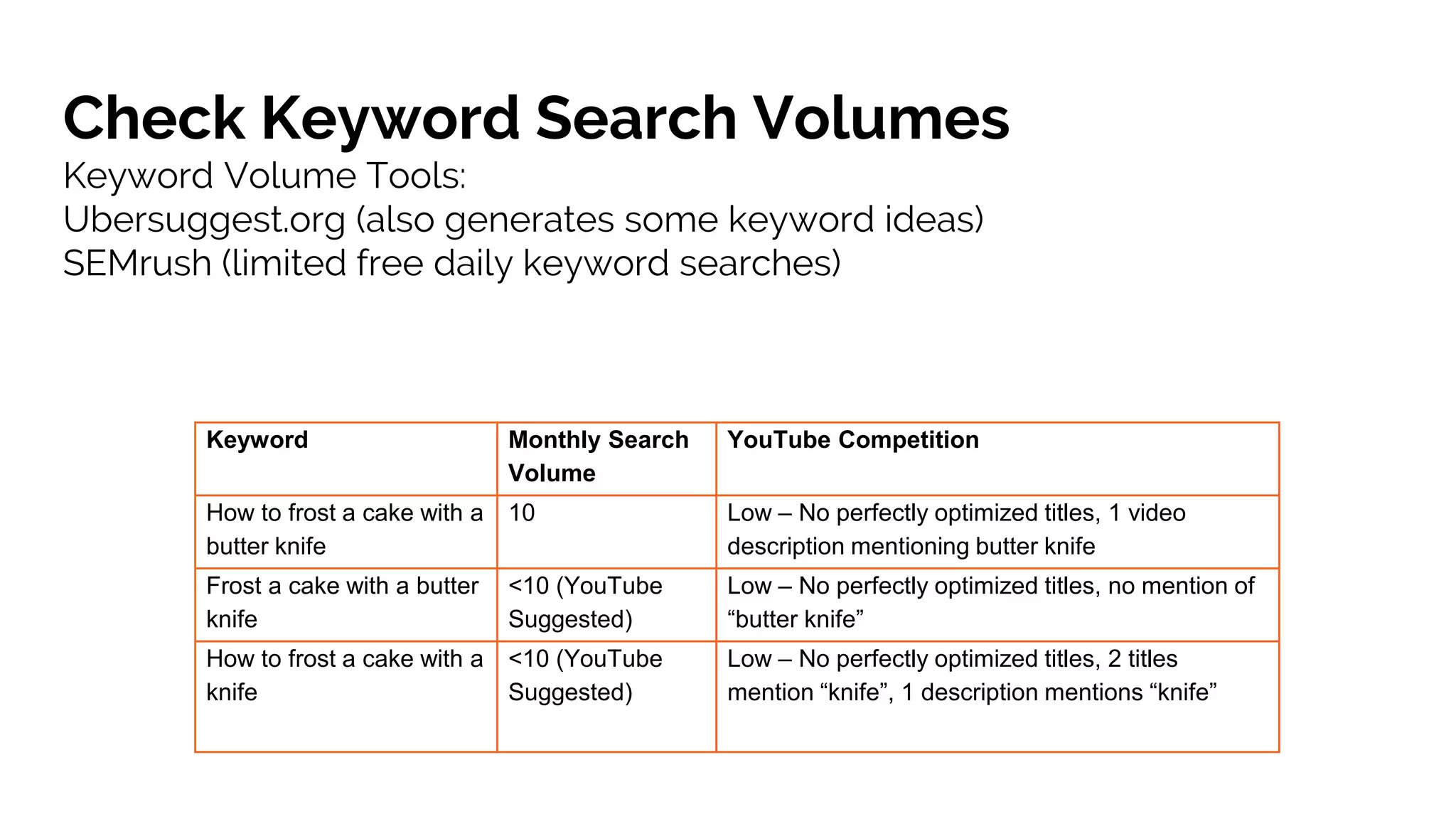
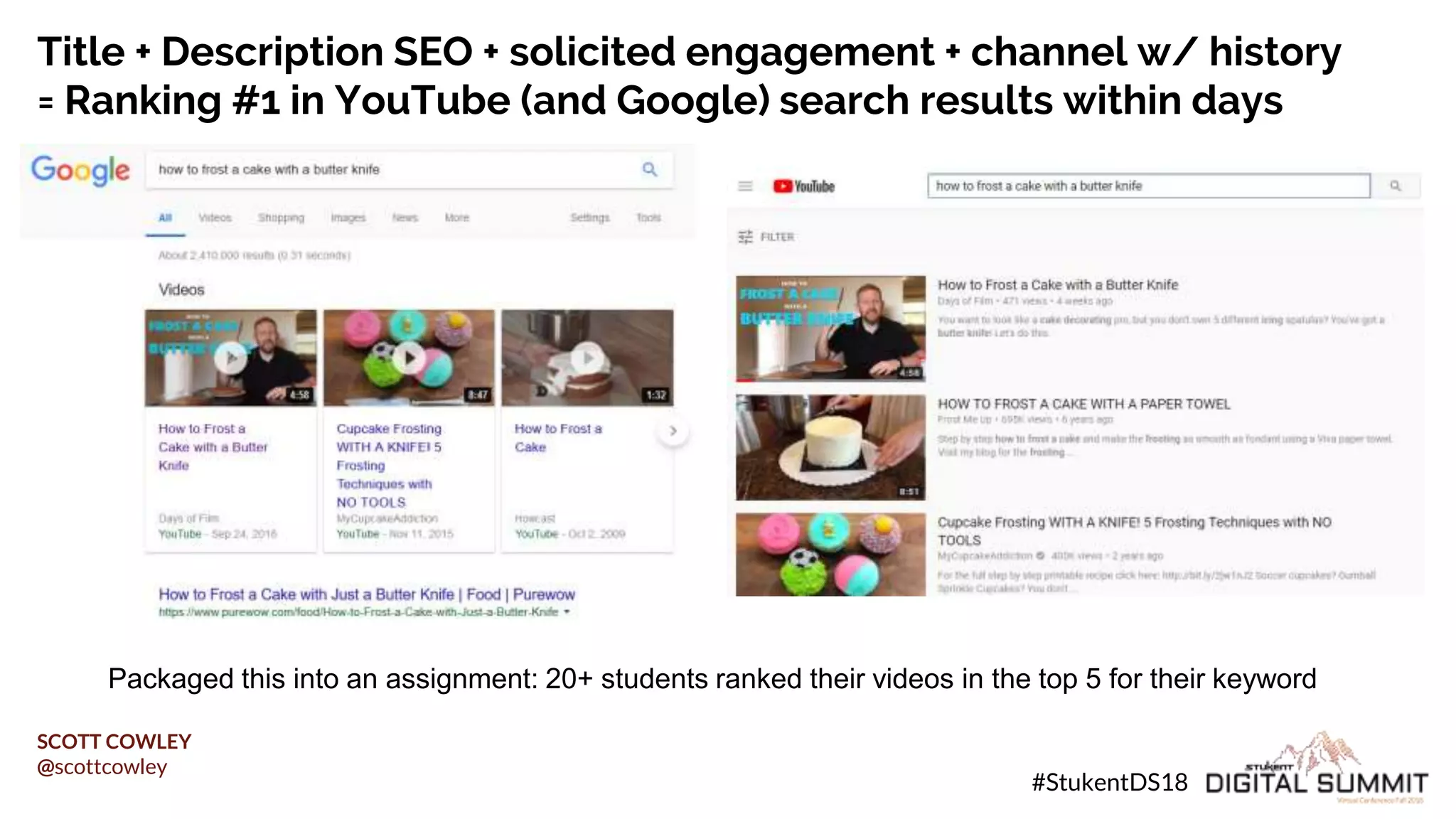
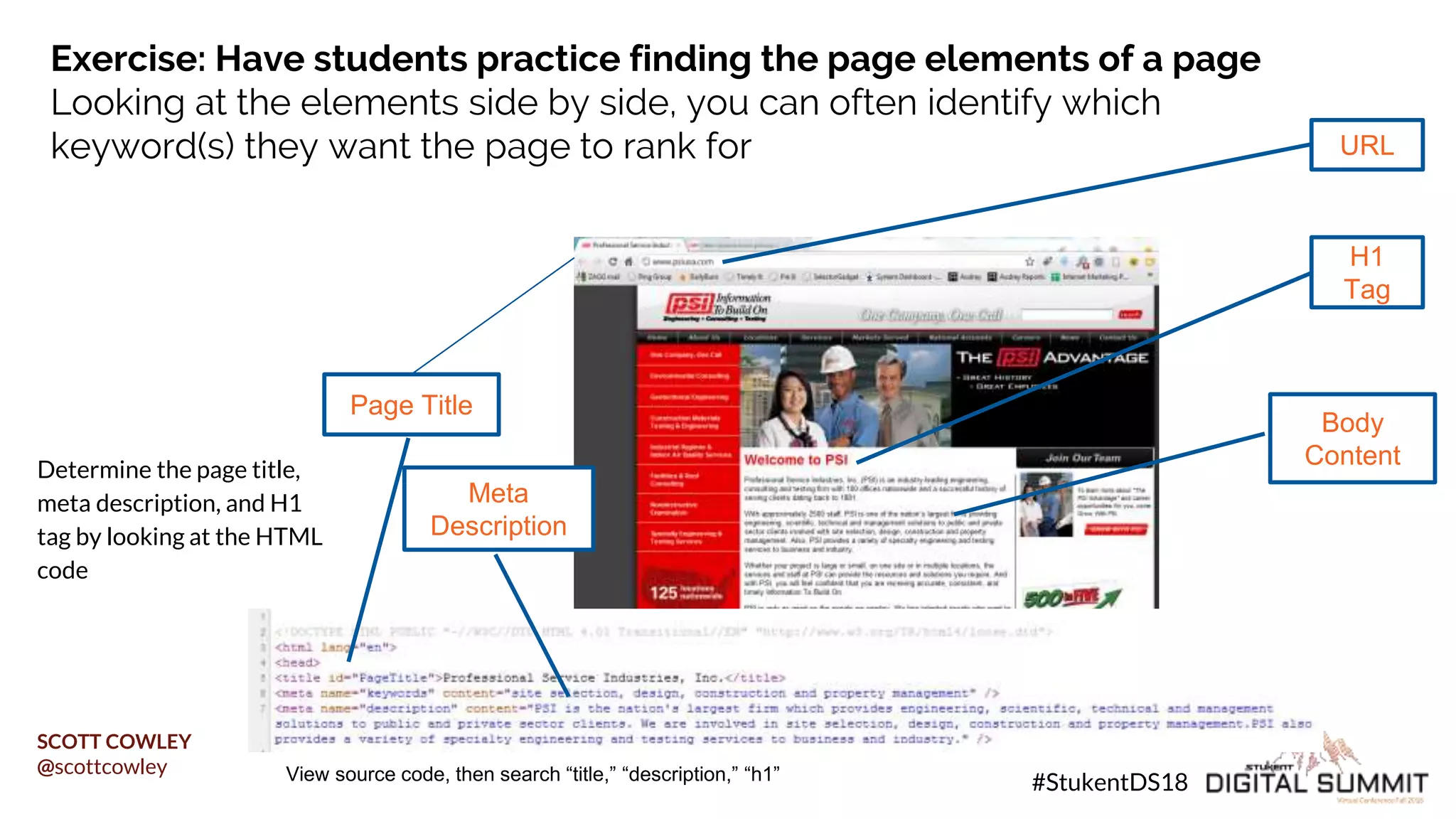
Scott Cowley provides guidance on how to teach SEO effectively to students. He recommends starting with local SEO since it is relatively straightforward, then moving to YouTube SEO which is more complex, and finally teaching full website SEO. For each topic, he outlines the key ranking factors and provides exercises for students to analyze search results and optimize pages. The overall approach is to ease students into SEO concepts from easy to more difficult, while giving them hands-on practice at each stage.






















![A brief guide to off-page SEO
• Every time a website links to ours, it’s like a vote for us – it makes us seem more popular
• To compare the popularity of one web page to another, use tools to see how one webpage’s backlink
portfolio compares to another (SEMrush [below] or OpenSiteExplorer.org)
• I look at “Referring Domains” to measure popularity– how many different websites link to us? There
are many other metrics that capture quantity and quality of links, but this simple heuristic is accurate
most of the time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scottcowley-sdsfallslides-181024200517/75/Scott-Cowley-Fall-Stukent-Digital-Summit-27-2048.jpg)