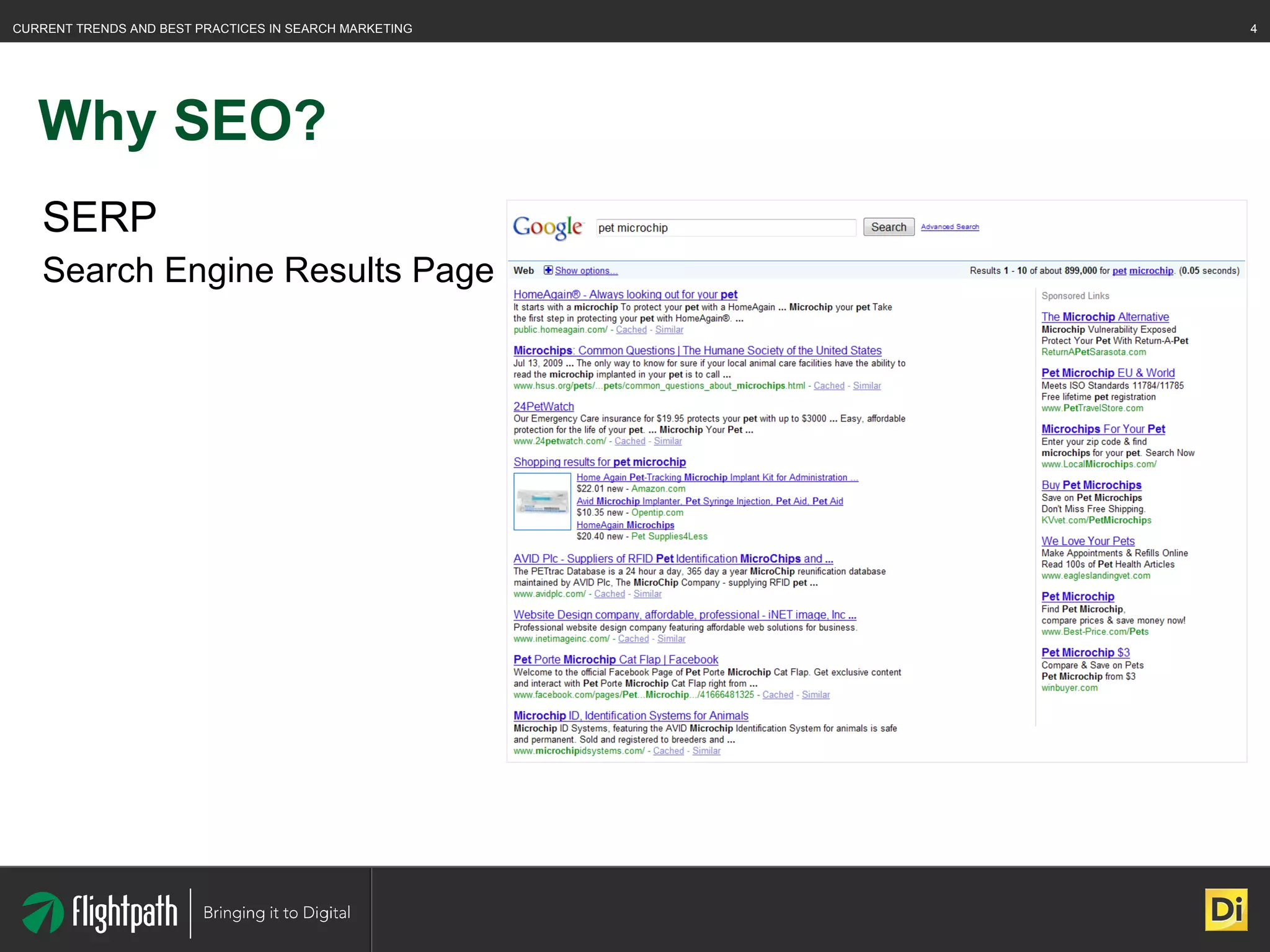
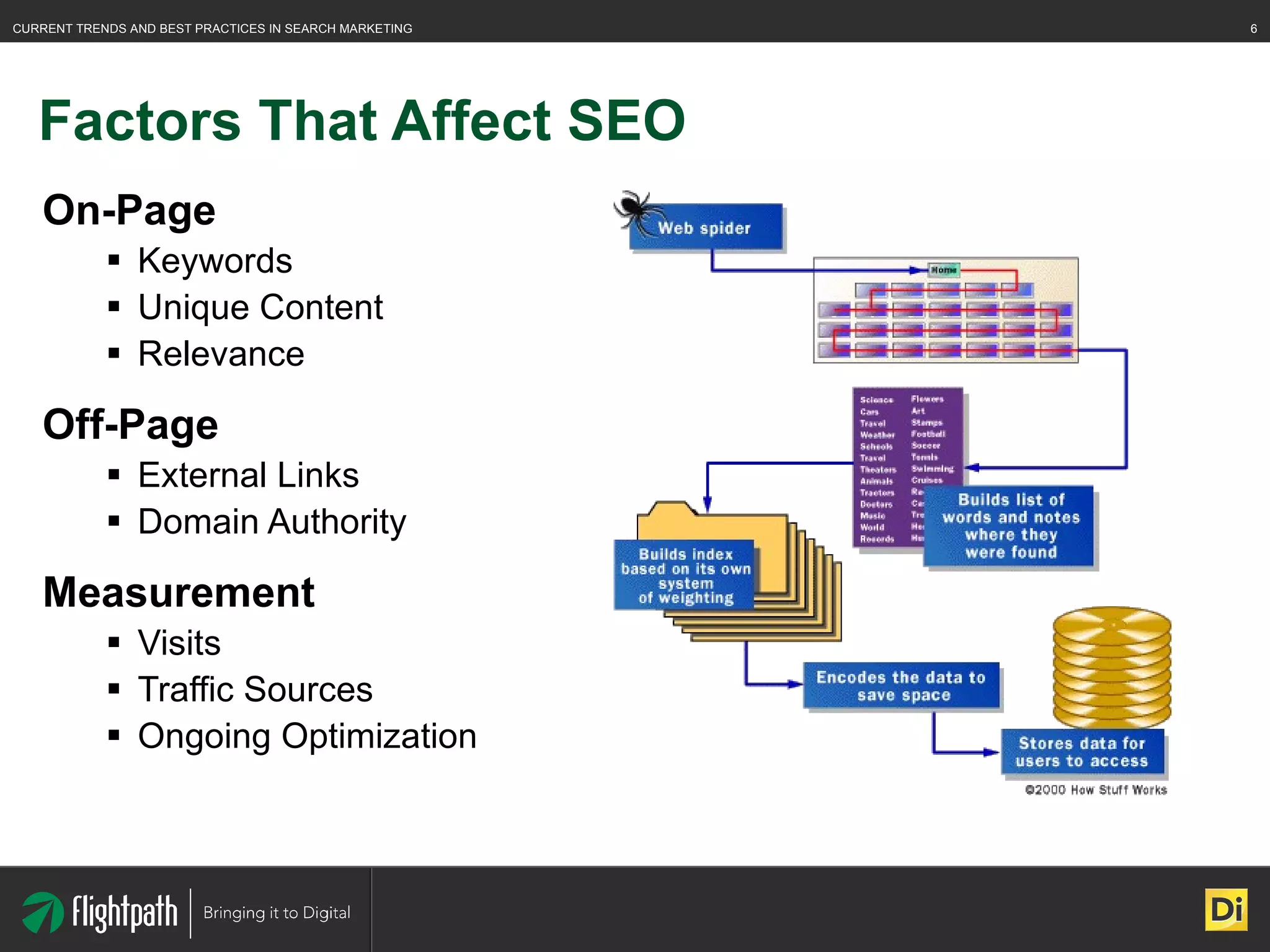
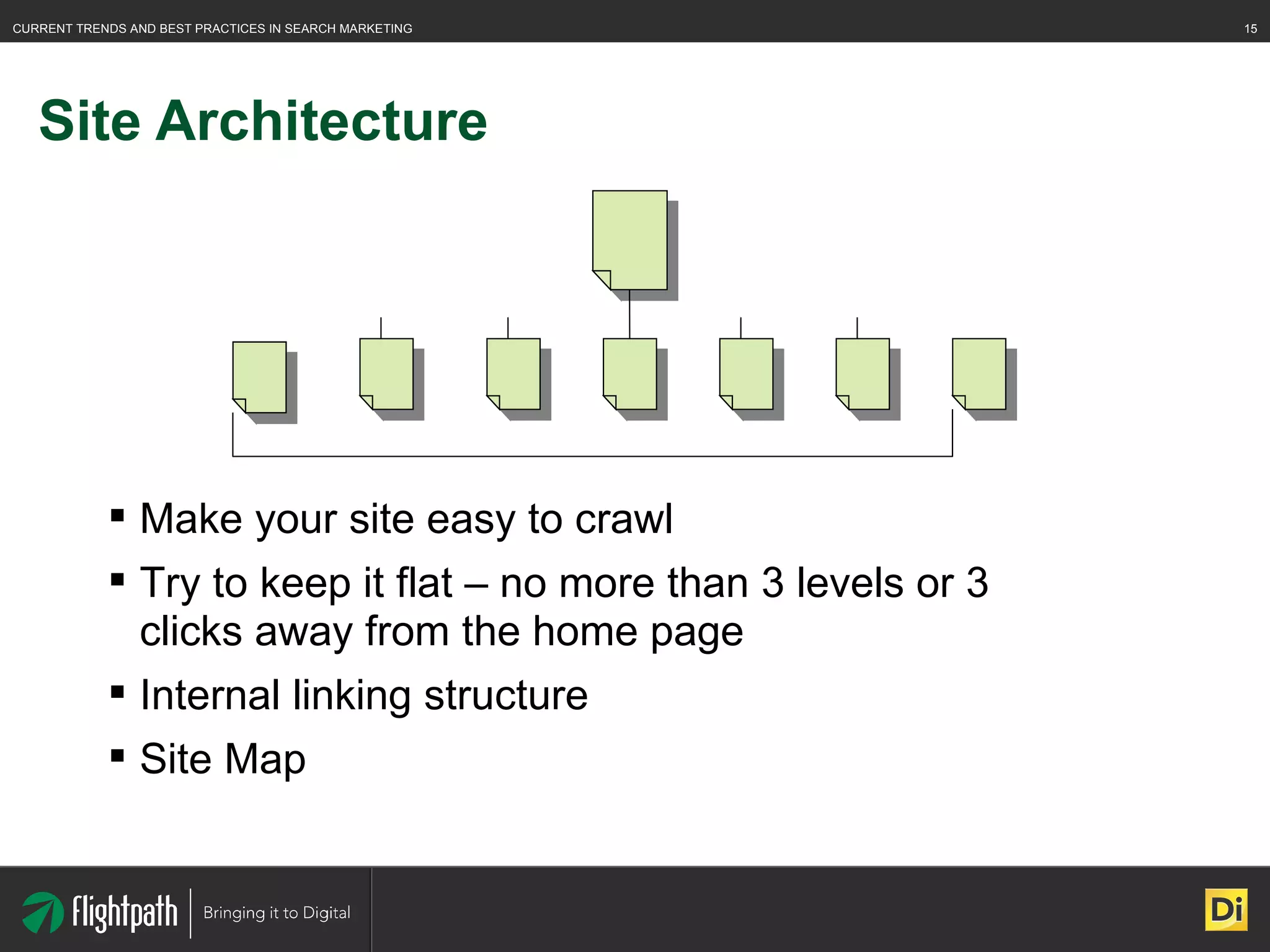
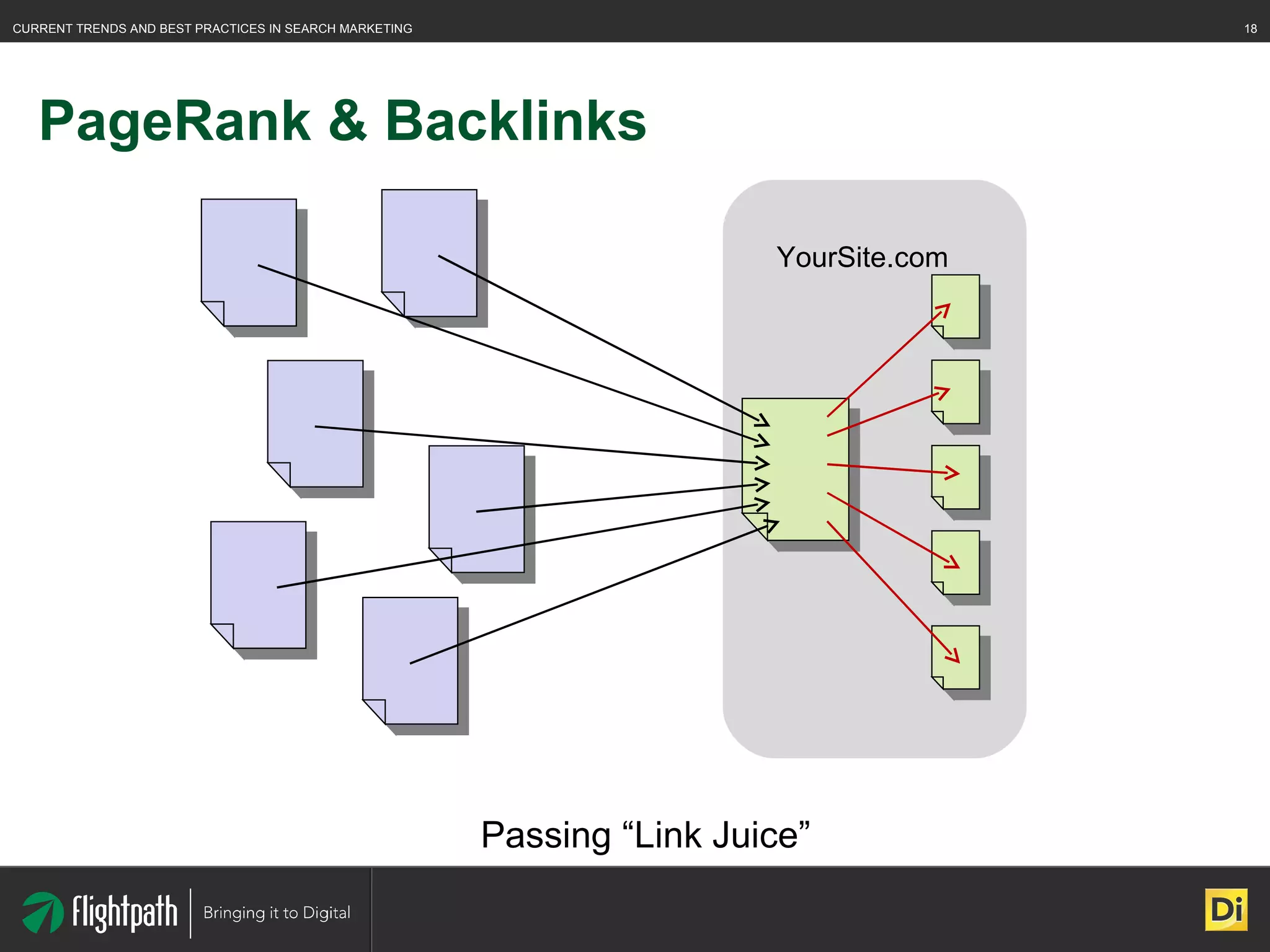
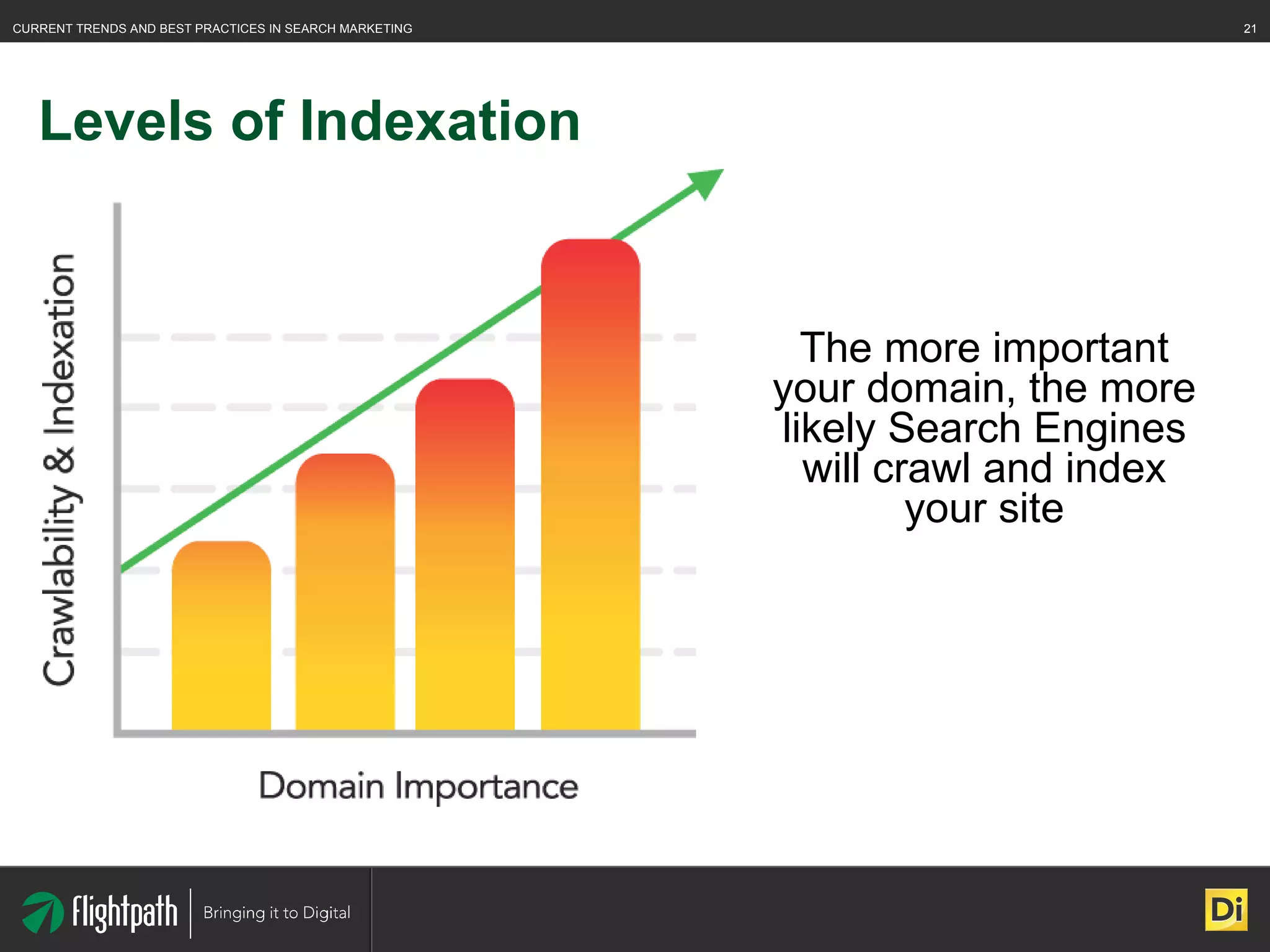
The document discusses the evolving landscape of search engine optimization (SEO), outlining its importance in improving website rankings and visibility in search engine results pages. It emphasizes best practices for on-page and off-page SEO, including keyword usage, quality content creation, and effective link-building strategies. Key factors affecting SEO performance are also highlighted, such as domain authority and site architecture.