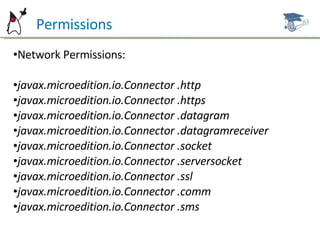
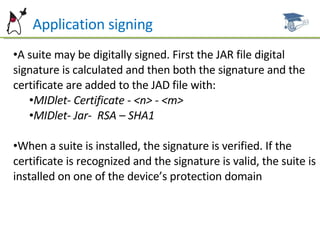
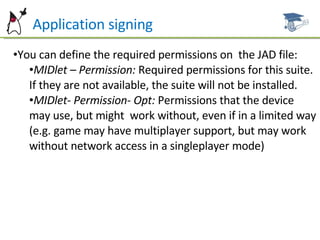
MIDP has a security model based on permissions for operations that could expose vulnerabilities, like network or data access. There are predefined permissions for things like network access, messaging, and media recording. Applications are installed into protection domains based on whether they are signed, and permissions within domains have modes like blanket access or requiring user approval each time. Developers can define required and optional permissions in the JAD file to control installation and access for the application.








![References ALVES F. Eduardo. SCMAD Study Guide, 27/04/2008. JAKL Andreas, Java Platform, Micro Edition Part 01 slides, 12/2007. Sun Certification Mobile Application Developer Website: [http://www.sun.com/training/certification/java/scmad.xml].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter14-1224037003078813-9/85/Scmad-Chapter14-13-320.jpg)