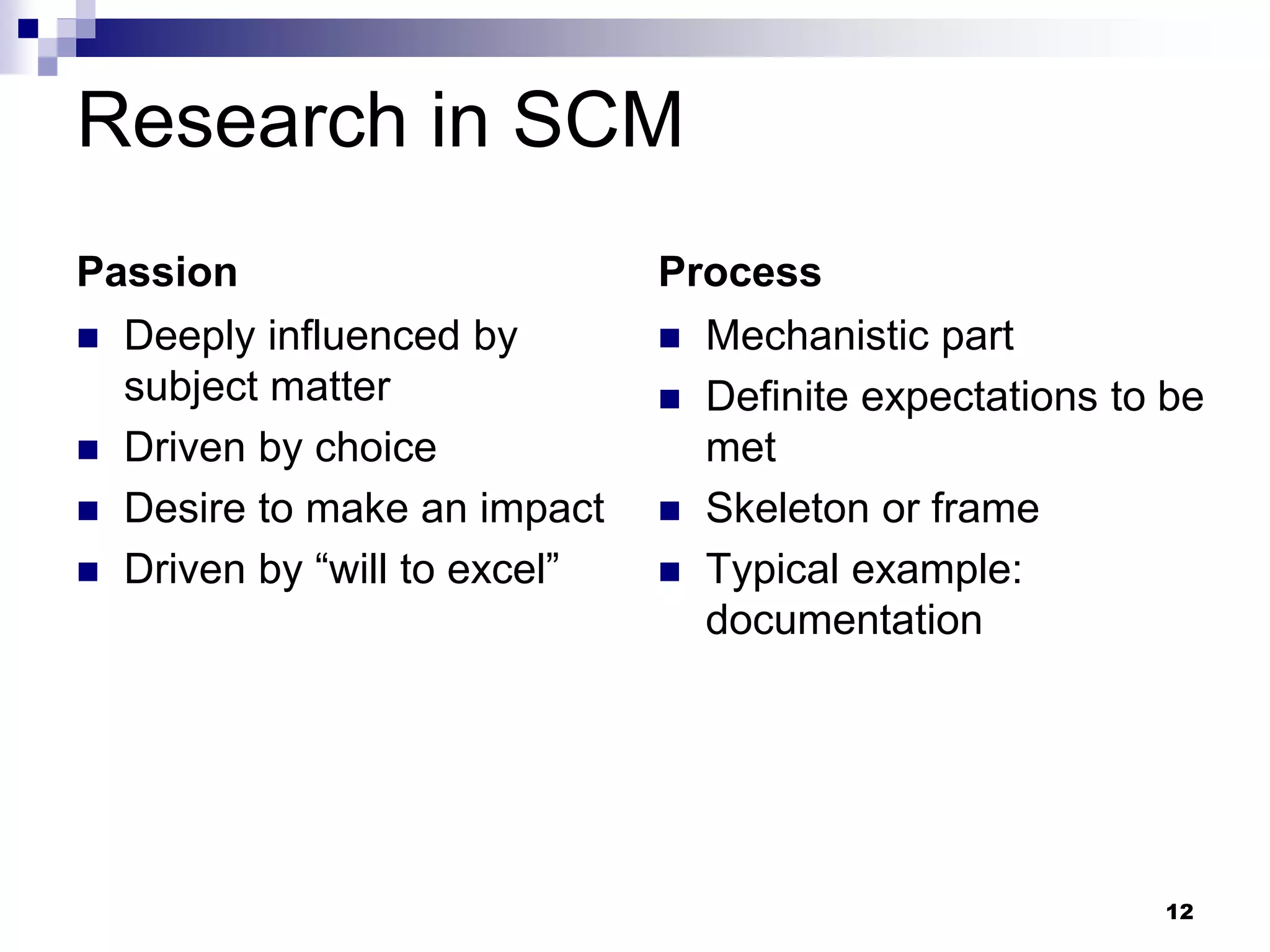
The document discusses the evolution and current trends in research within supply chain management (SCM), emphasizing the integration of digital technologies and interdisciplinary approaches. It highlights the need for visibility in research to ensure academic acceptance and societal impact, while also providing insights into opportunities for research in various sectors, including SMEs and unorganized sectors. The presentation concludes by affirming the importance of passion and process in impactful SCM research.