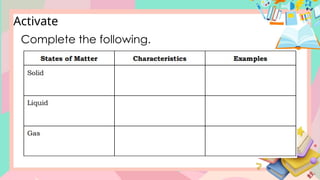
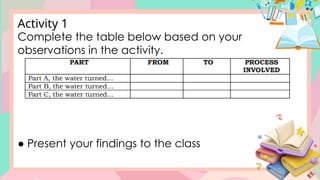
The document discusses the properties and changes of matter, focusing on physical and chemical changes, particularly through processes like melting and evaporation. It provides examples and applications of these changes, alongside activities for learners to observe and describe these phenomena. Topics include states of matter, real-life applications, and questions that engage learners in understanding the concepts of physical changes.