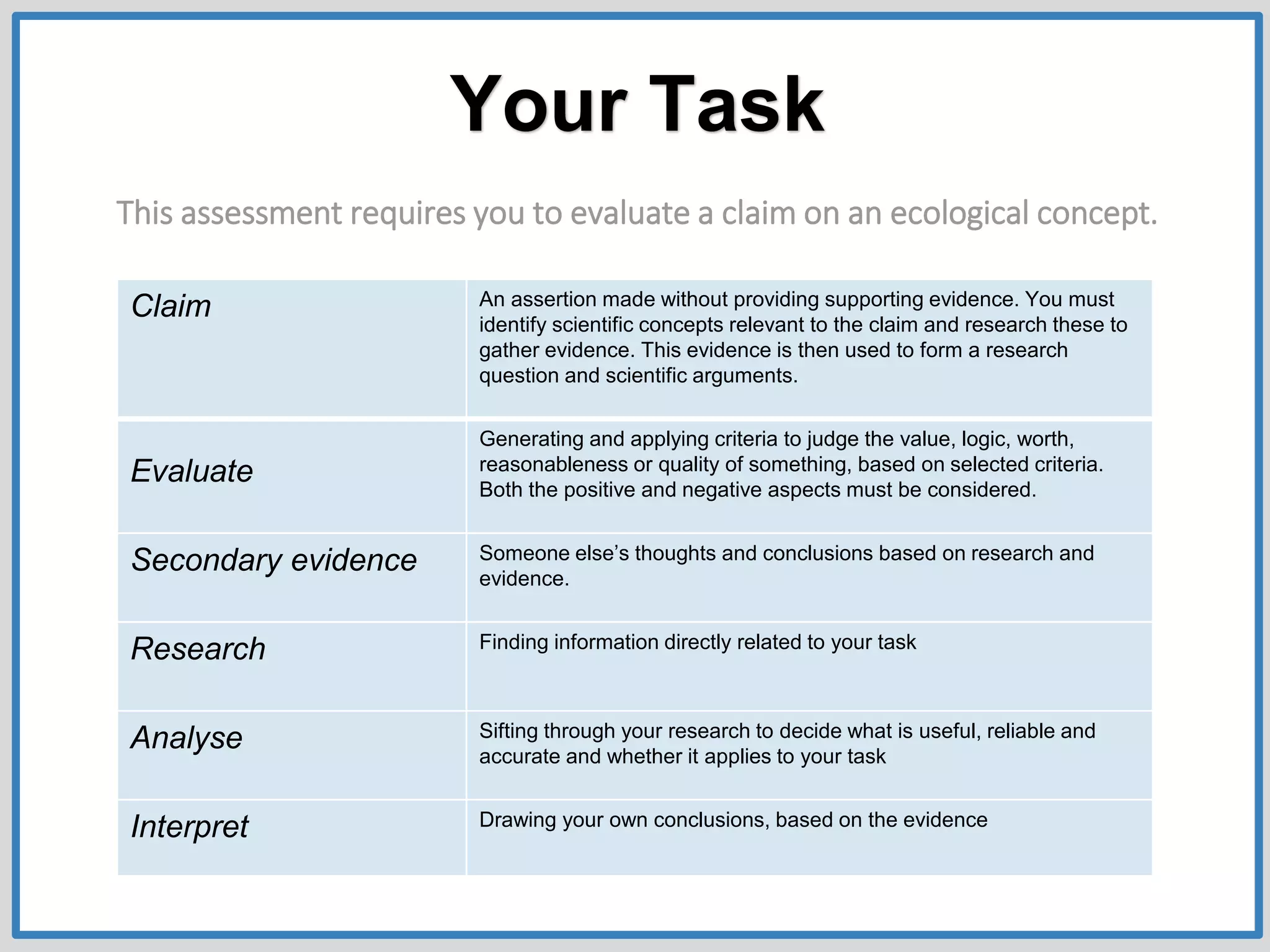
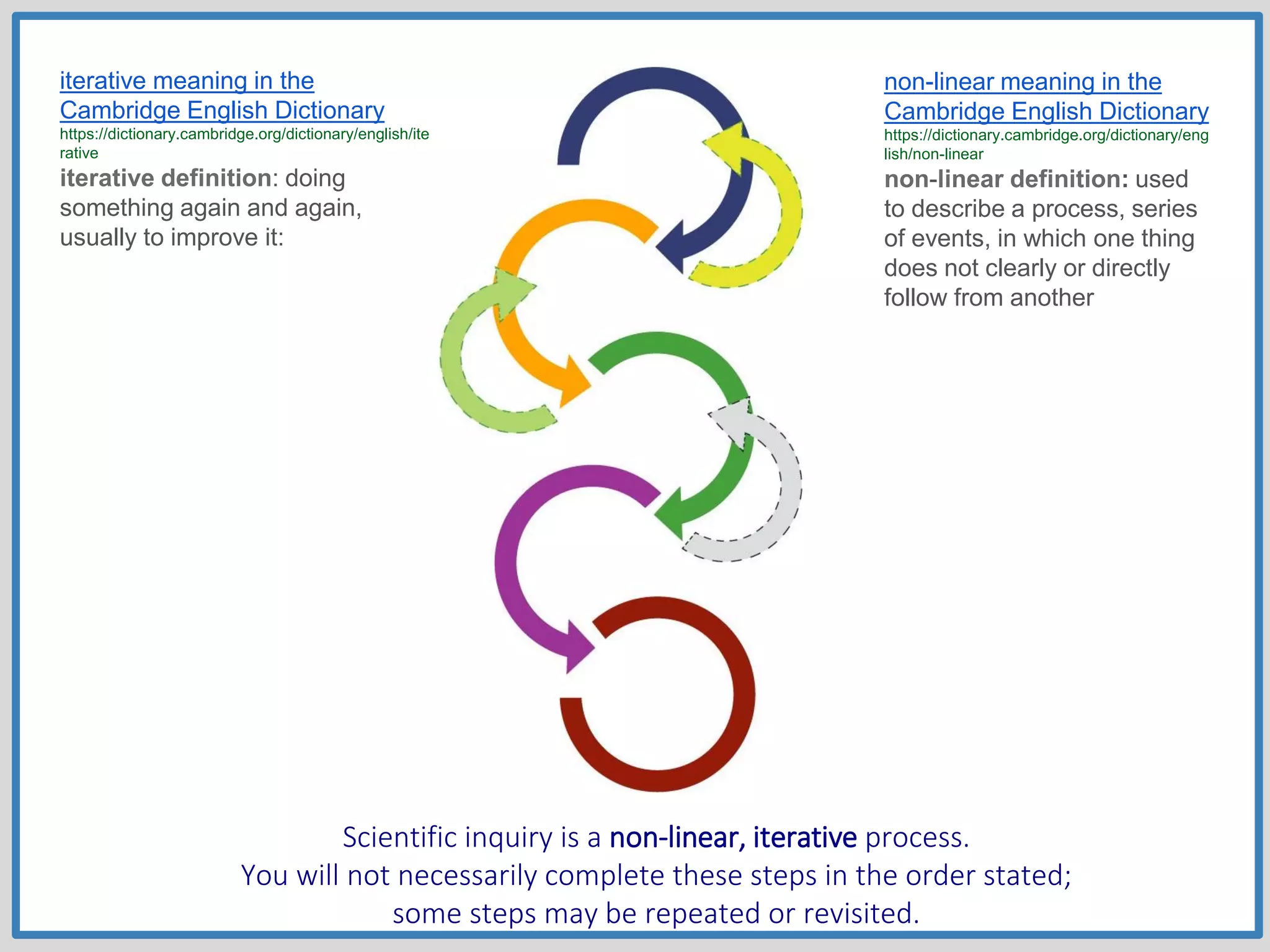
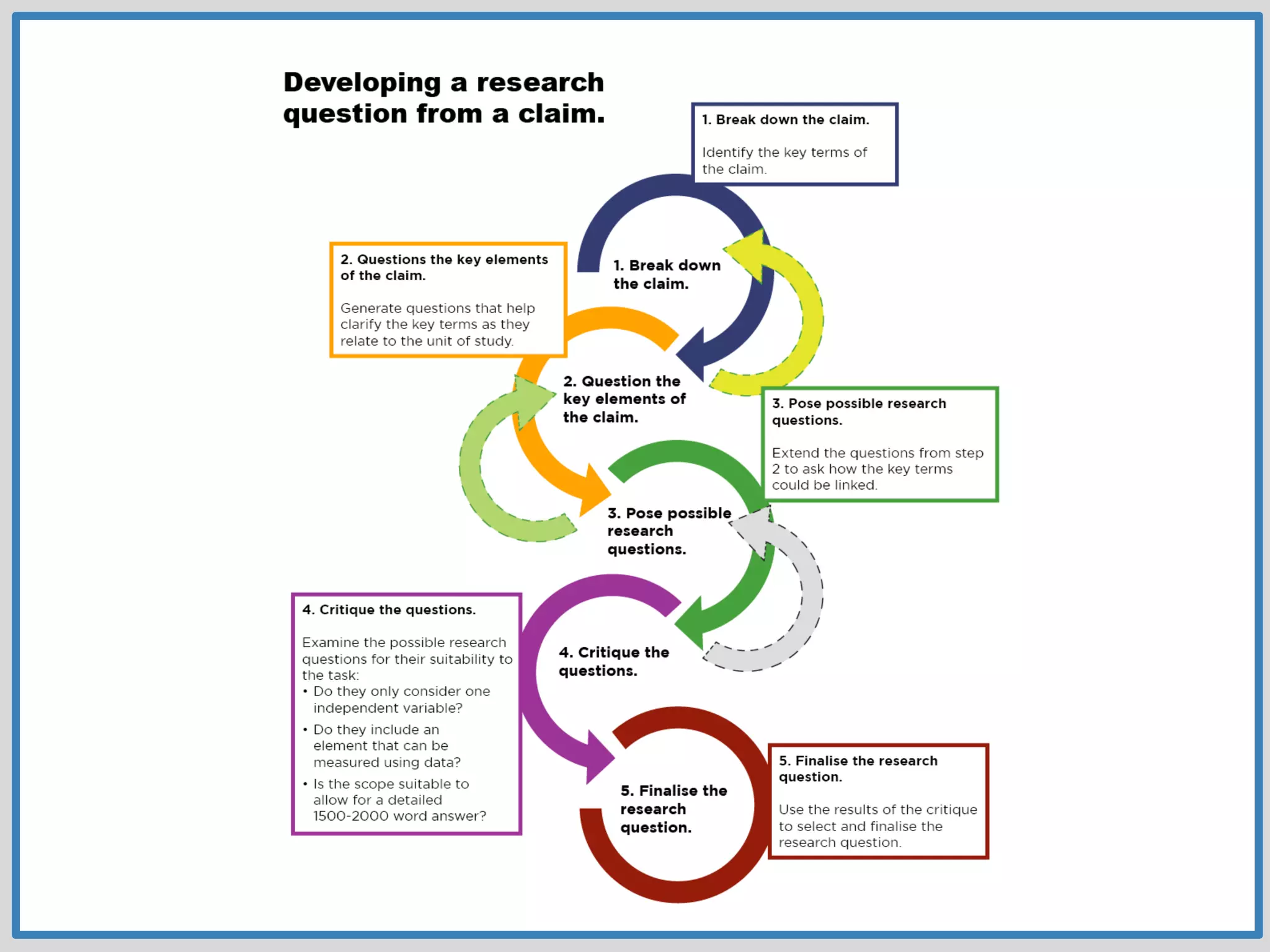
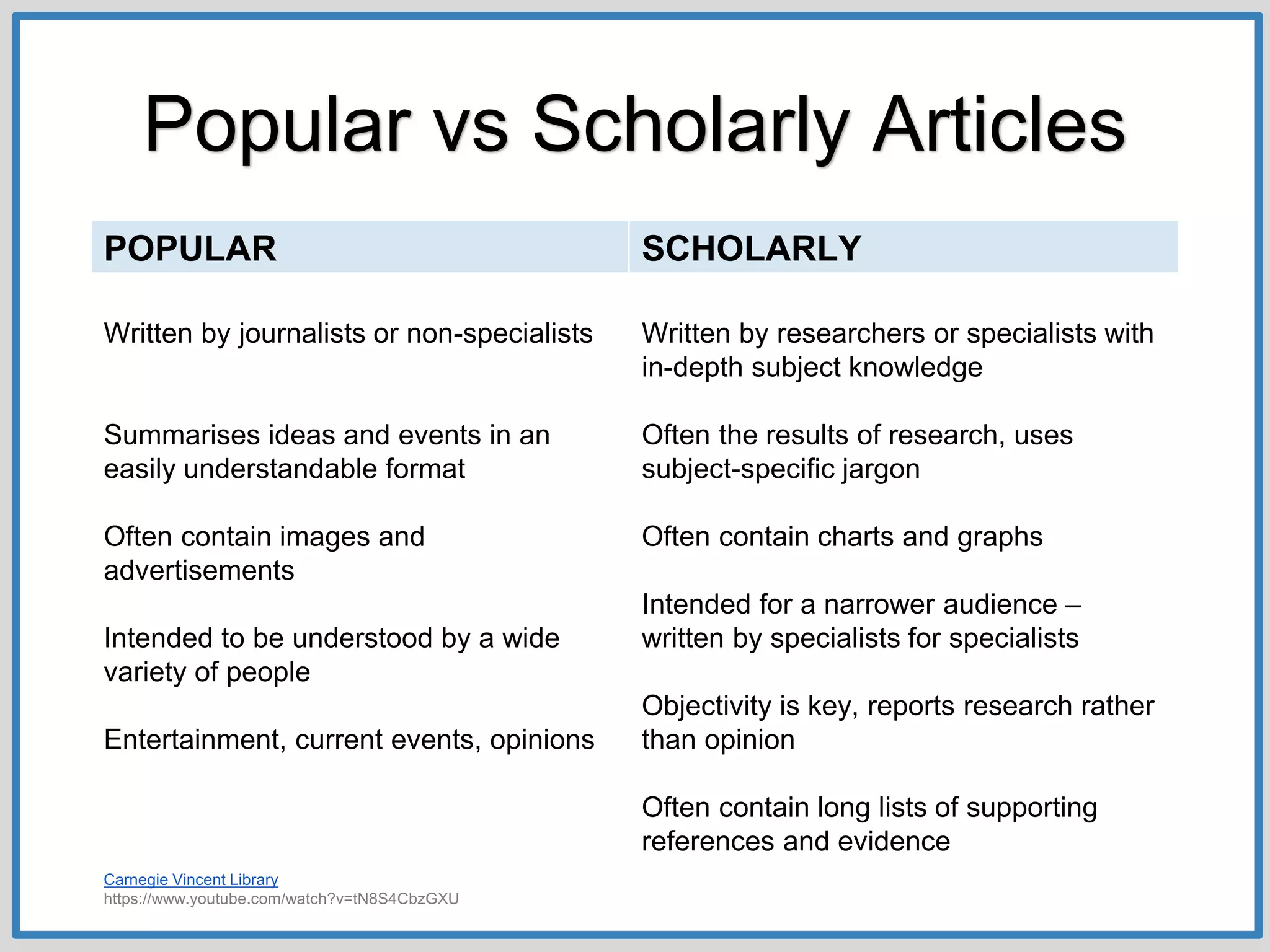
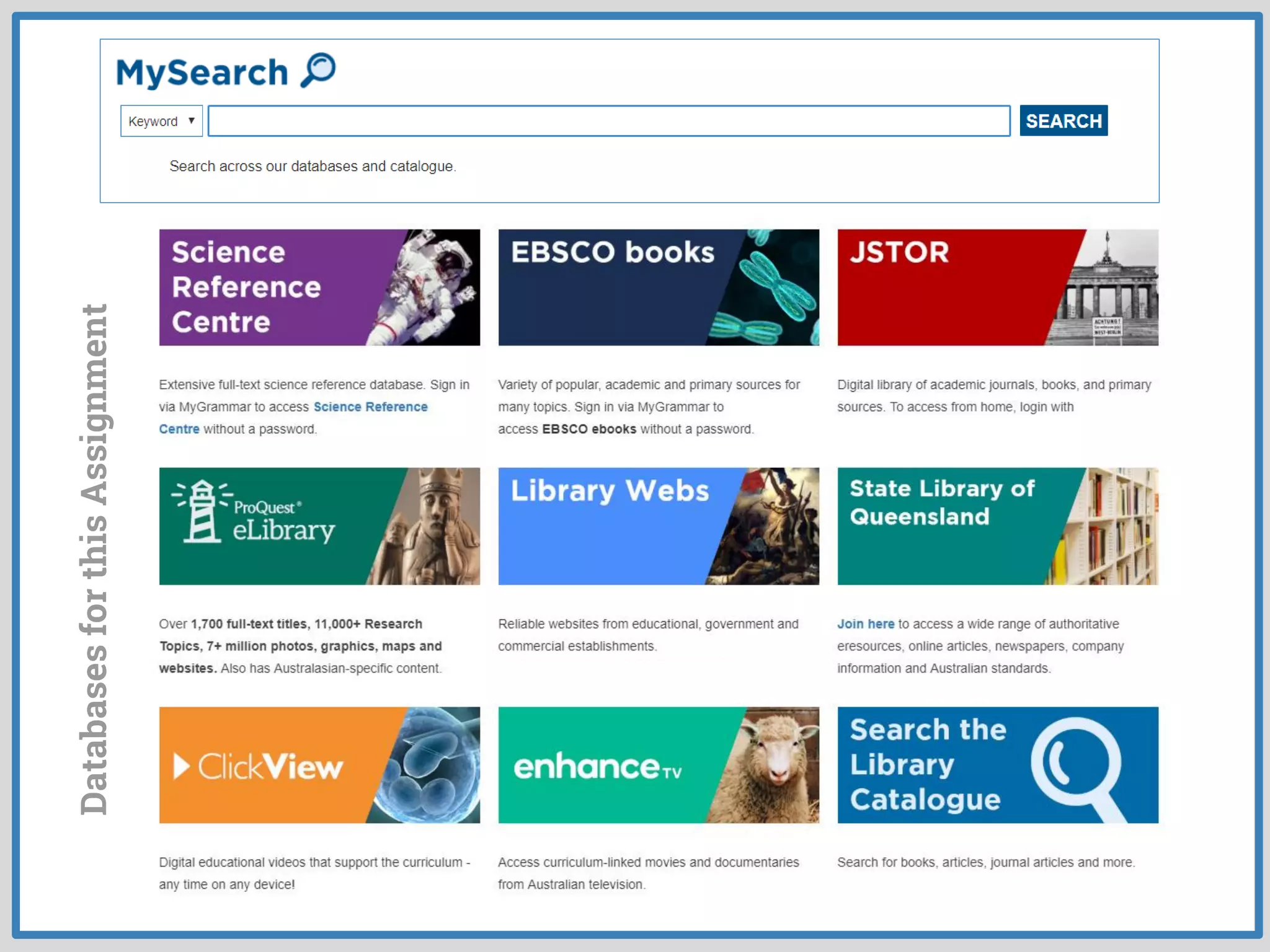
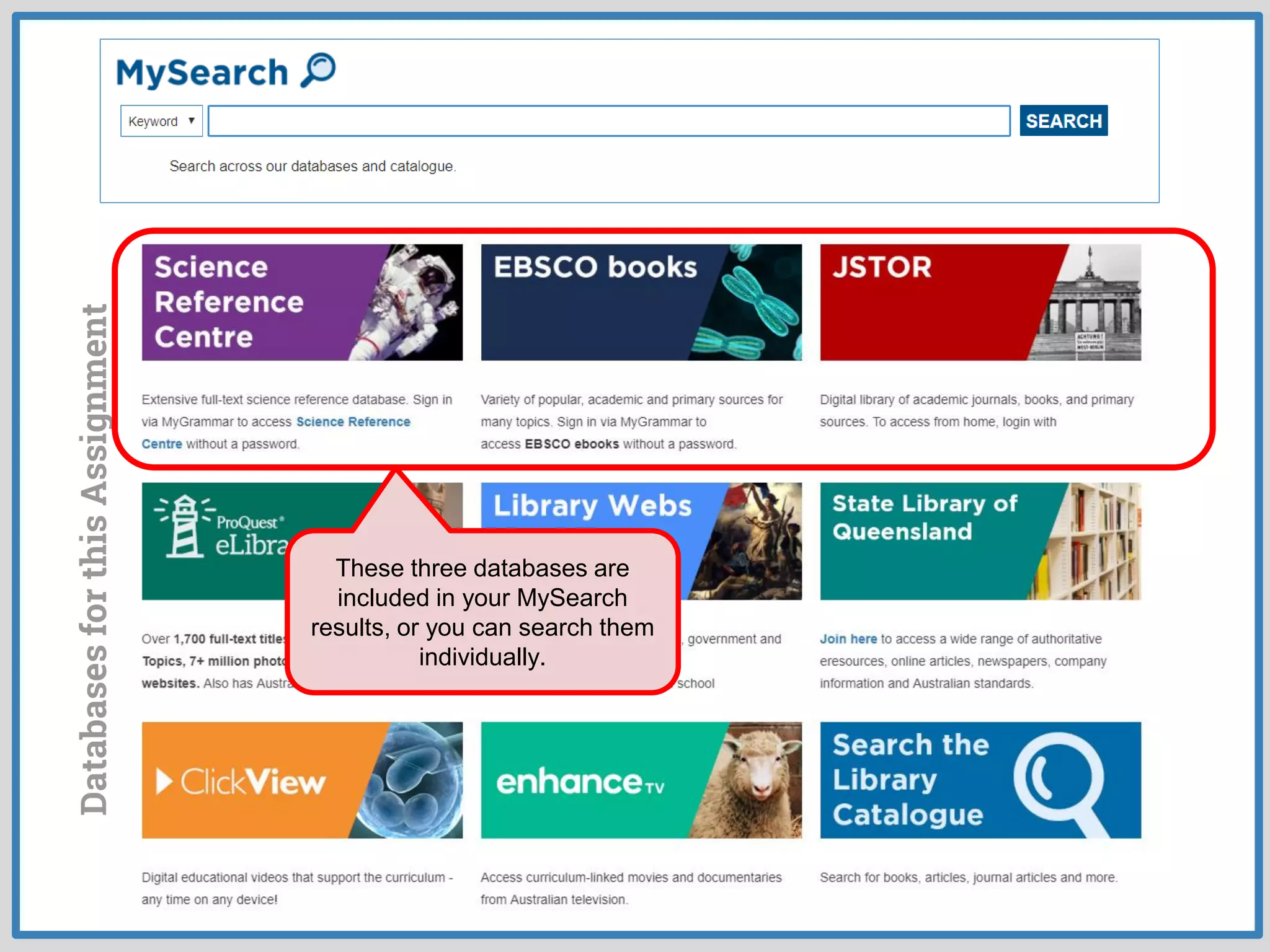
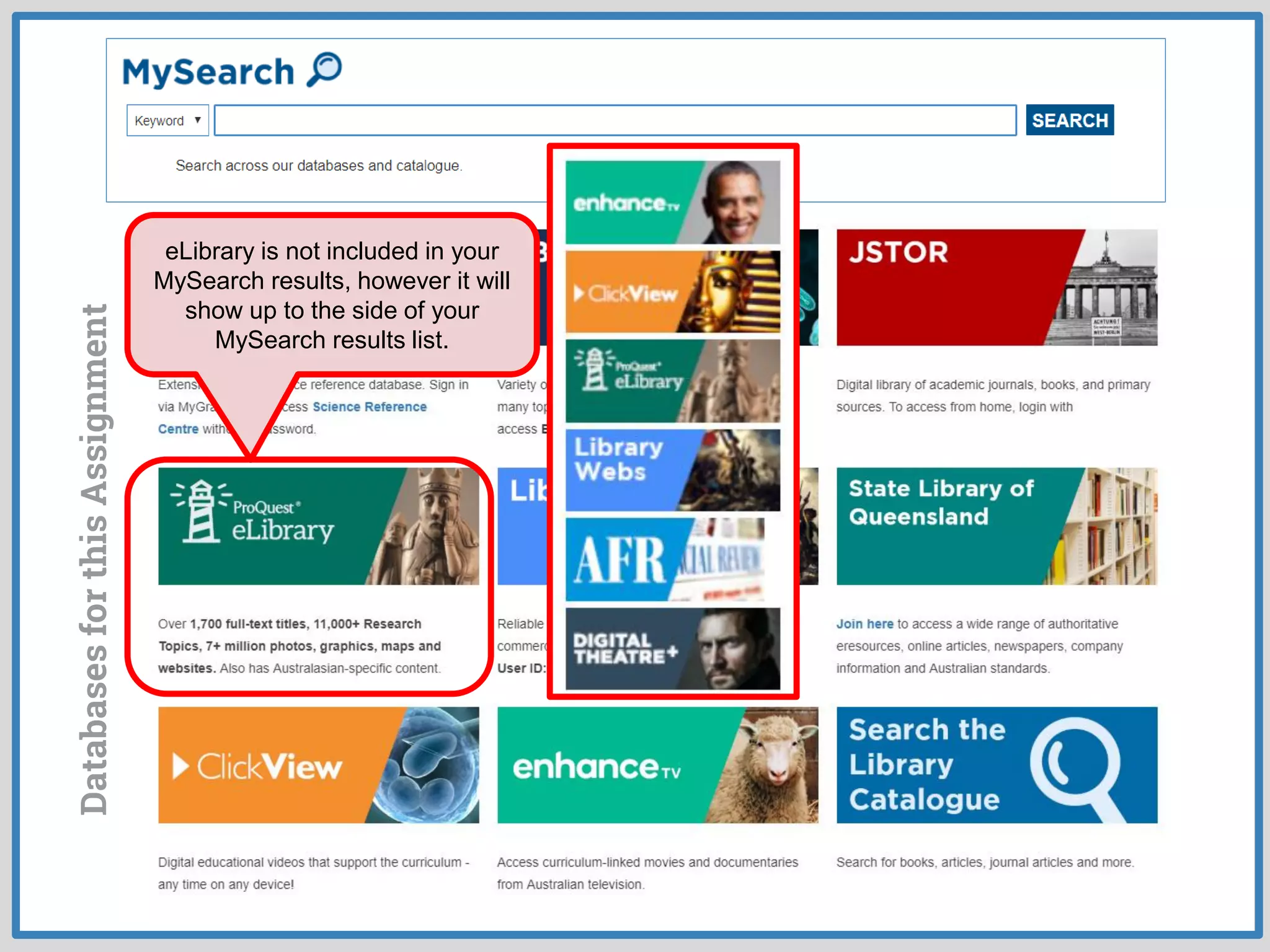
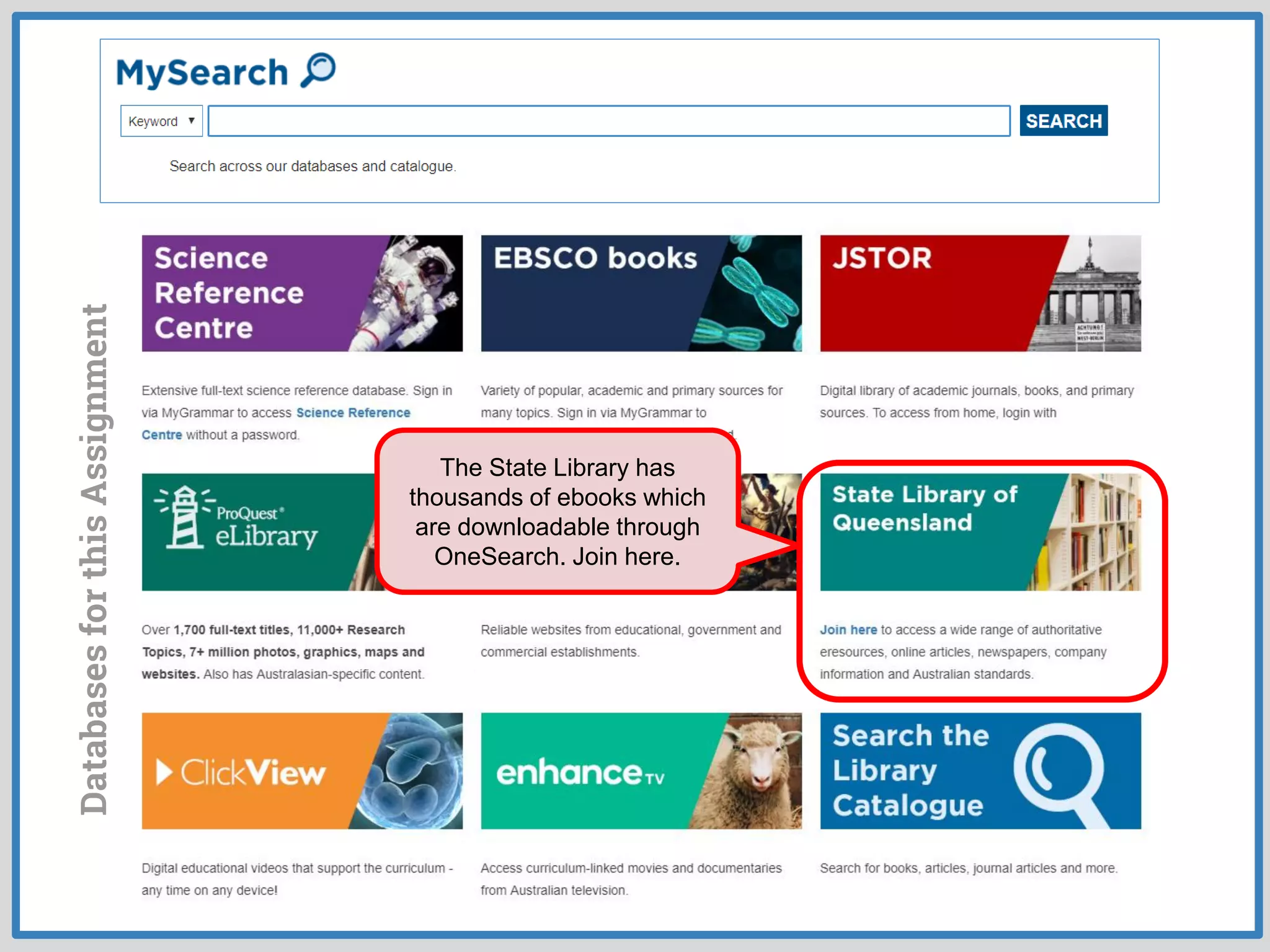
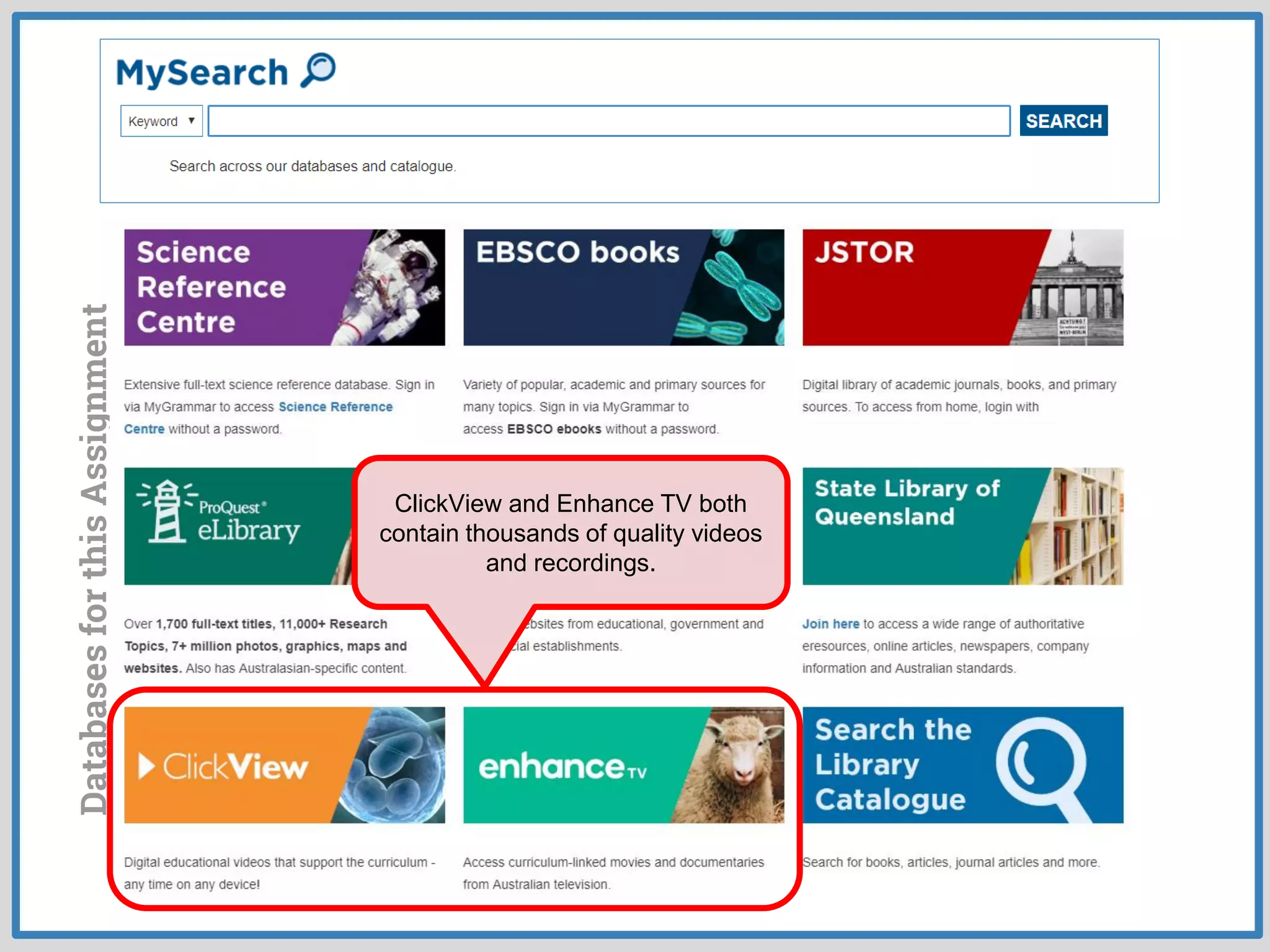
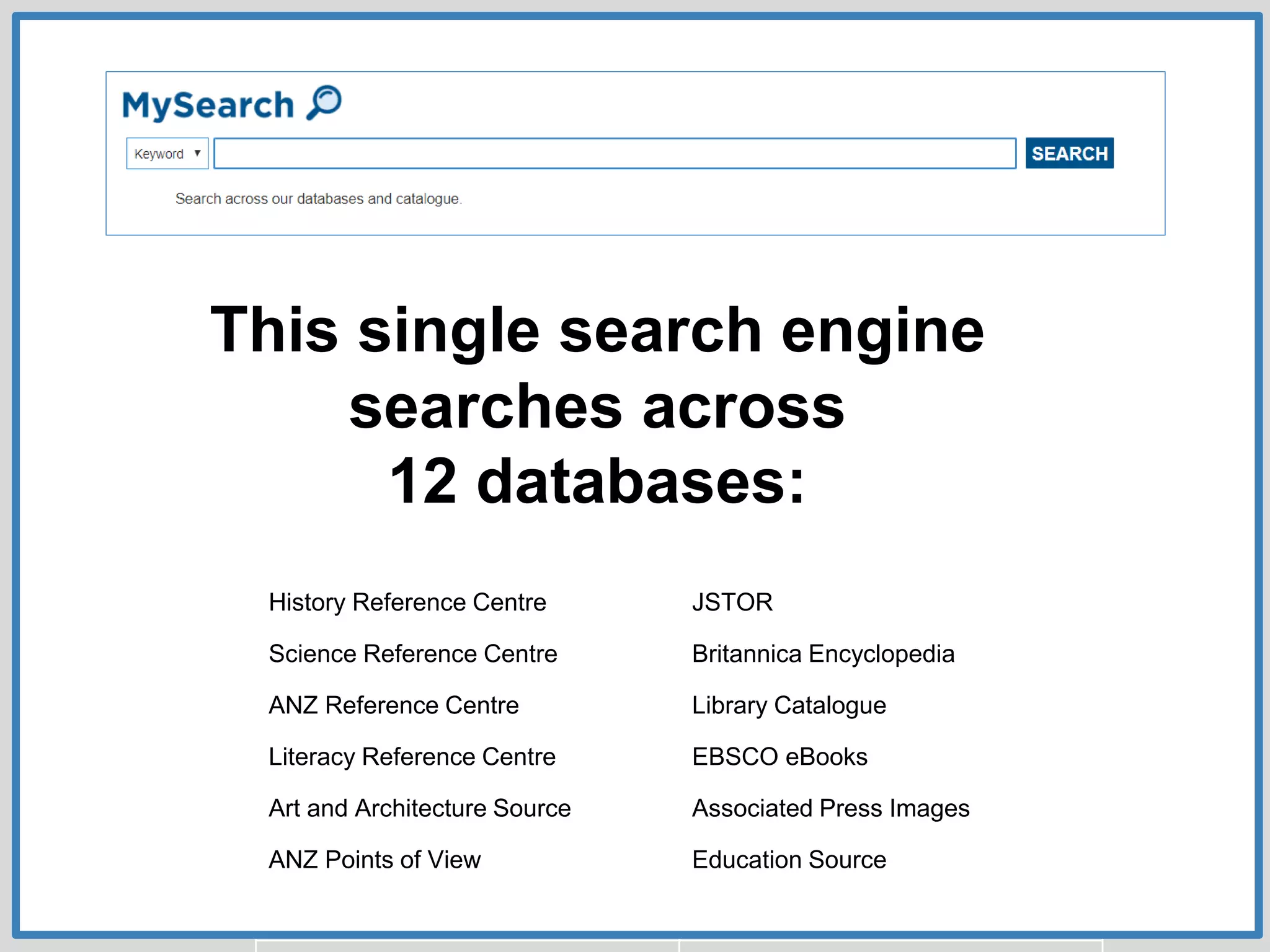
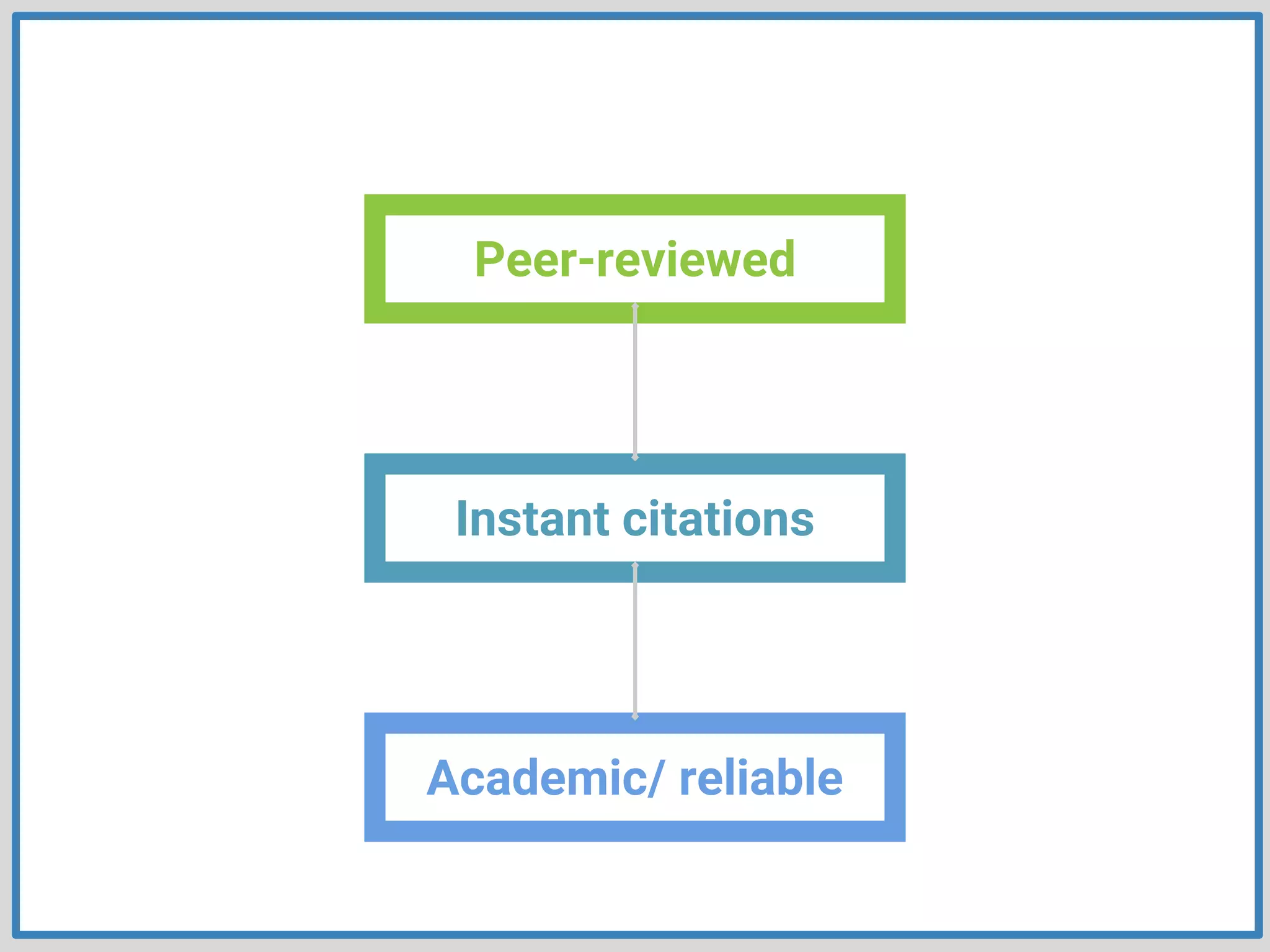
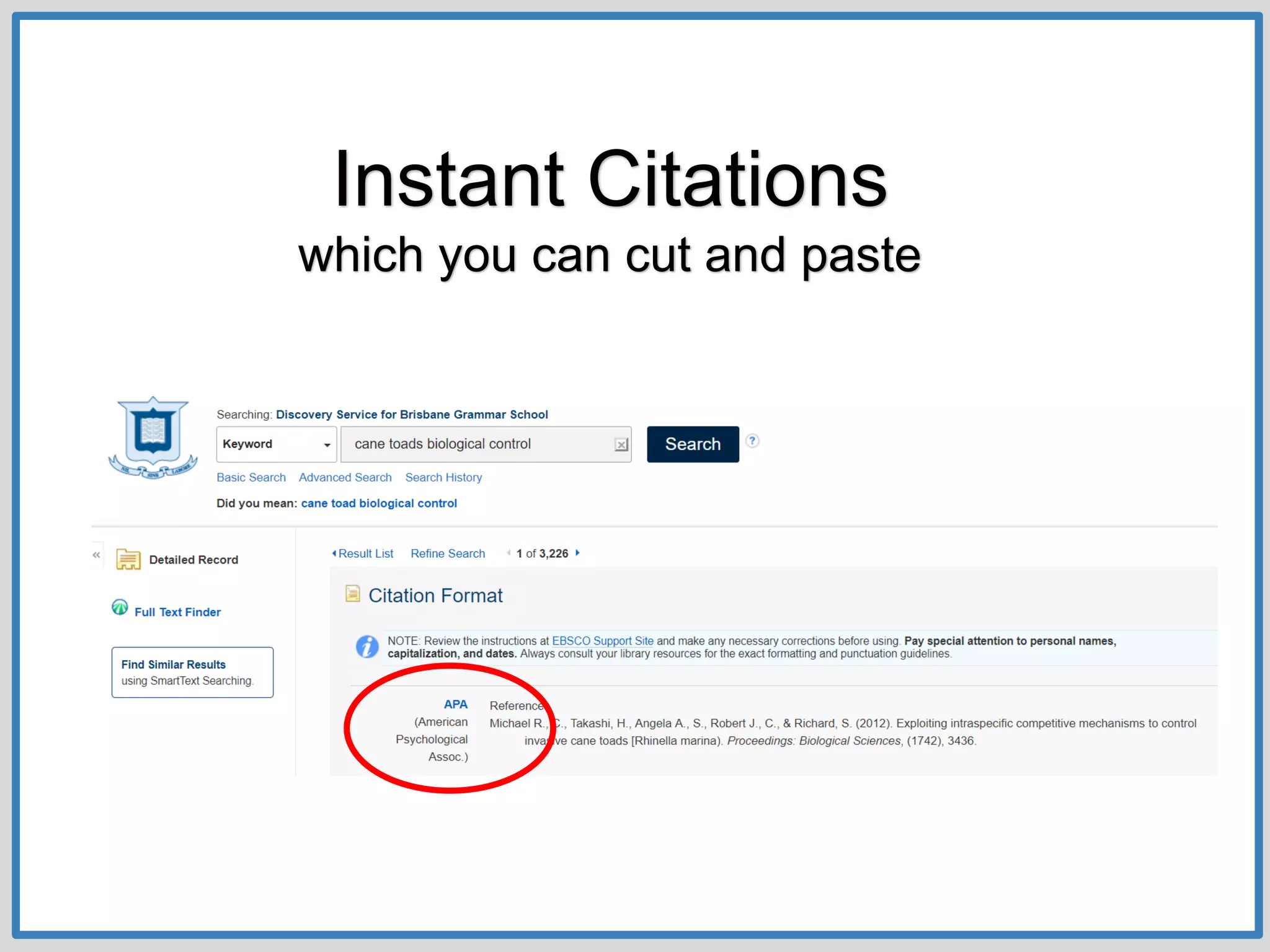
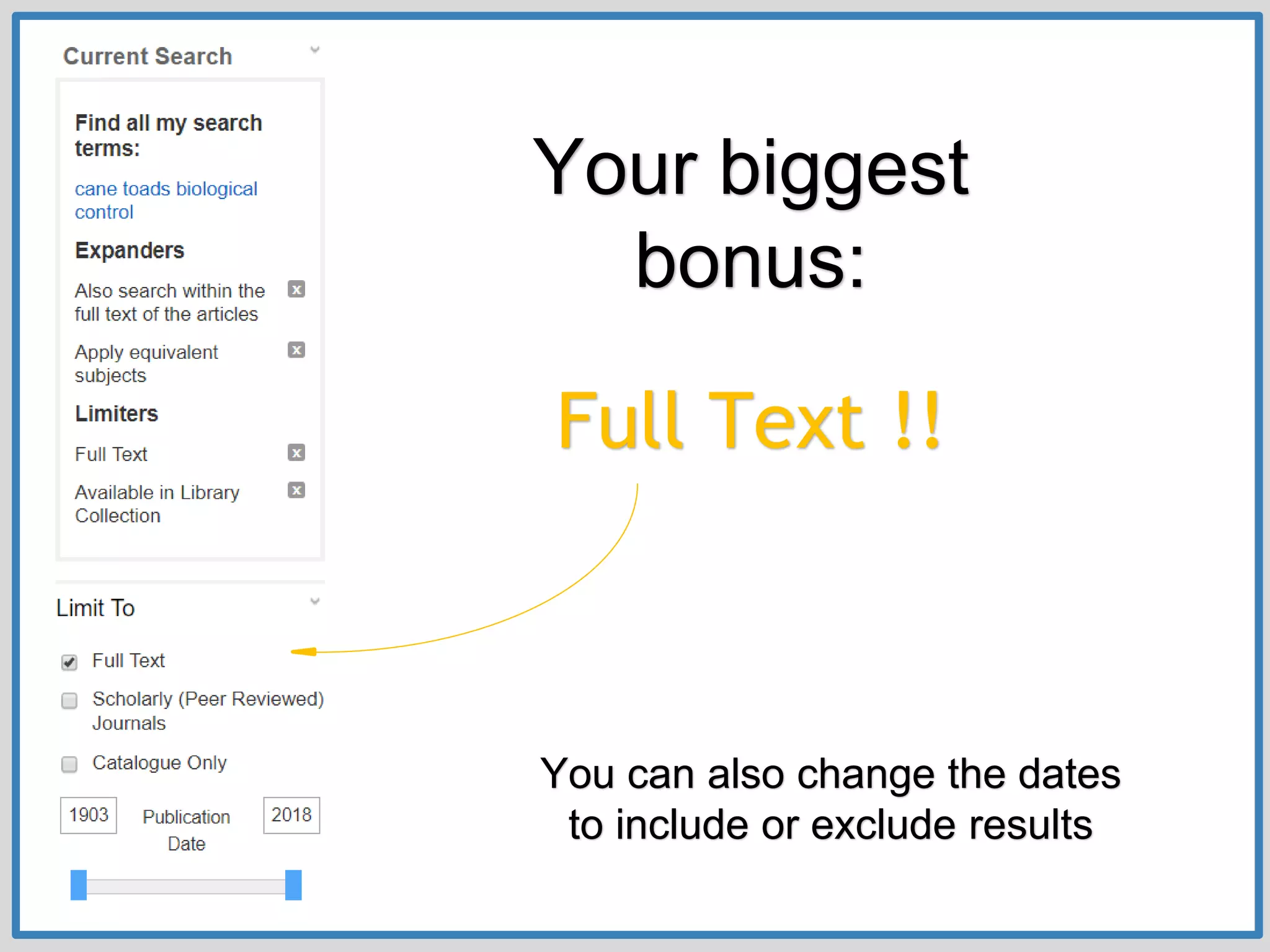
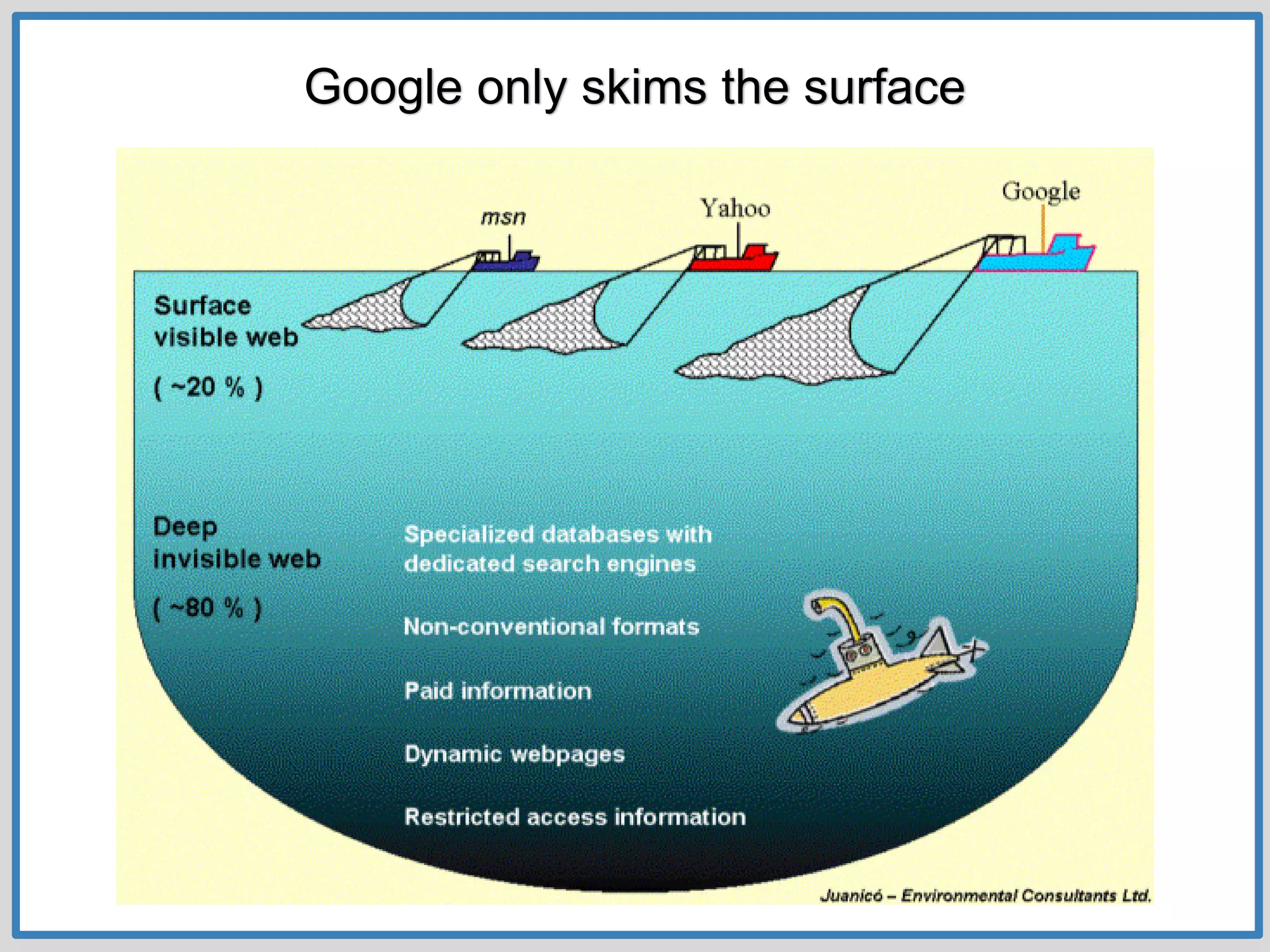
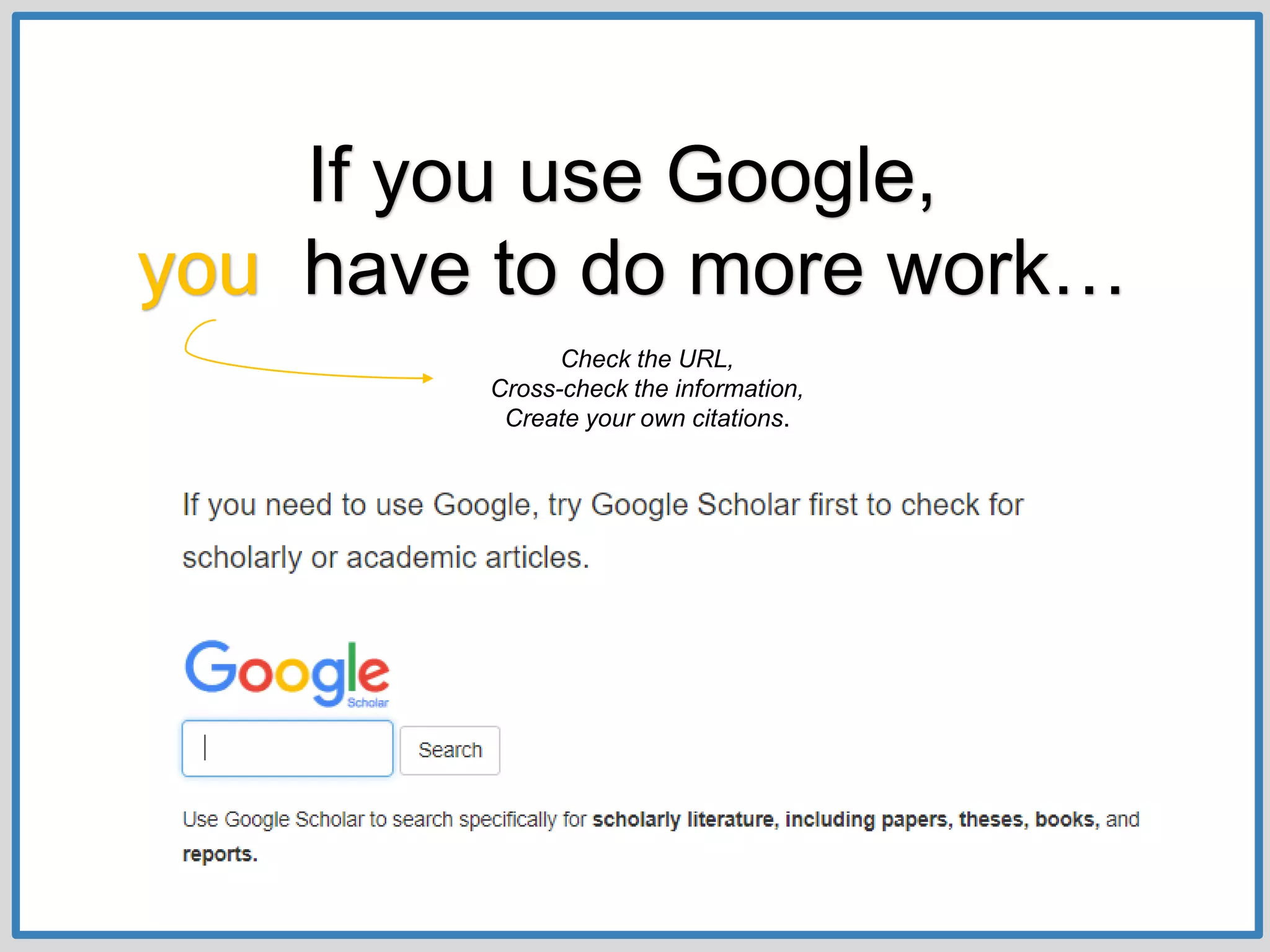
This document provides guidance on conducting research for an assignment at Brisbane Grammar School Library. It outlines the task of evaluating a claim on an ecological concept by identifying relevant scientific concepts, gathering evidence through research, and using the evidence to form a research question and arguments. It describes the research process as non-linear and iterative. Students are advised to obtain evidence from scientifically credible sources like scholarly journals, books by credentialed scientists, and university/government websites. Popular sources are not recommended. Specific databases are suggested for researching the given assignment topics.