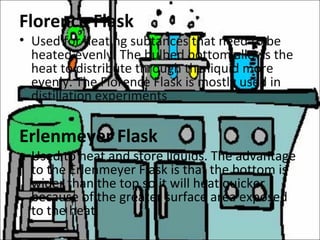
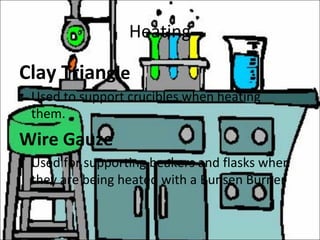
Science laboratory equipment can be classified into categories based on material and includes glasswares, porcelainwares, and other accessories. Glasswares are used for holding, heating, and storing liquids and include items like beakers, flasks, test tubes, and funnels. Porcelainwares contain heat-resistant materials like crucibles and evaporating dishes. Other equipment supports experiments through set-ups for heating, microscopy, distillation, and titration.