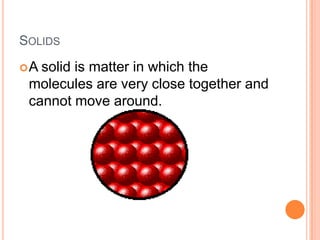
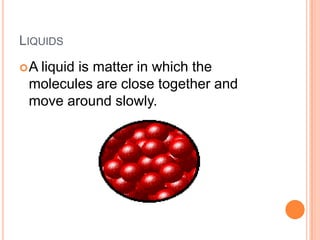
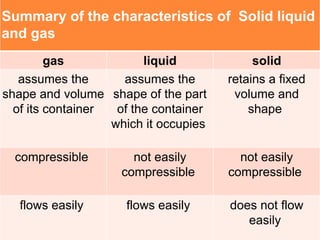
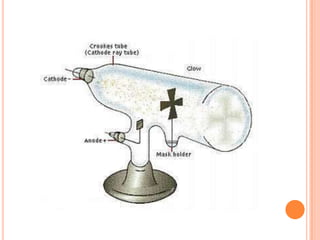
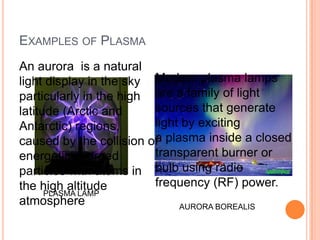
There are five phases of matter: solids, liquids, gases, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensates. Solids have fixed shapes and volumes, liquids flow easily but maintain the shape of their containers, and gases spread out freely and have high speeds. Plasma is formed when heat separates electrons and nuclei into ions and electrons. Bose-Einstein condensates were predicted in the 1920s and created in 1995 using super cold, unexcited atoms. Matter can change between phases through excitation of particles by heat or other means.