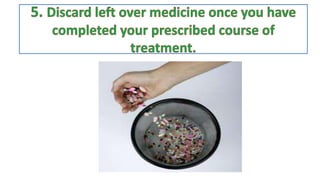
The document discusses the importance of antibiotics in treating infections and highlights their role in saving lives since the 20th century. It addresses the issue of antibiotic resistance, identifying its causes and global impact, including the loss of lives and the burden on healthcare systems. The document emphasizes the need for infection prevention, better hygiene, and responsible use of antibiotics to combat this escalating crisis.