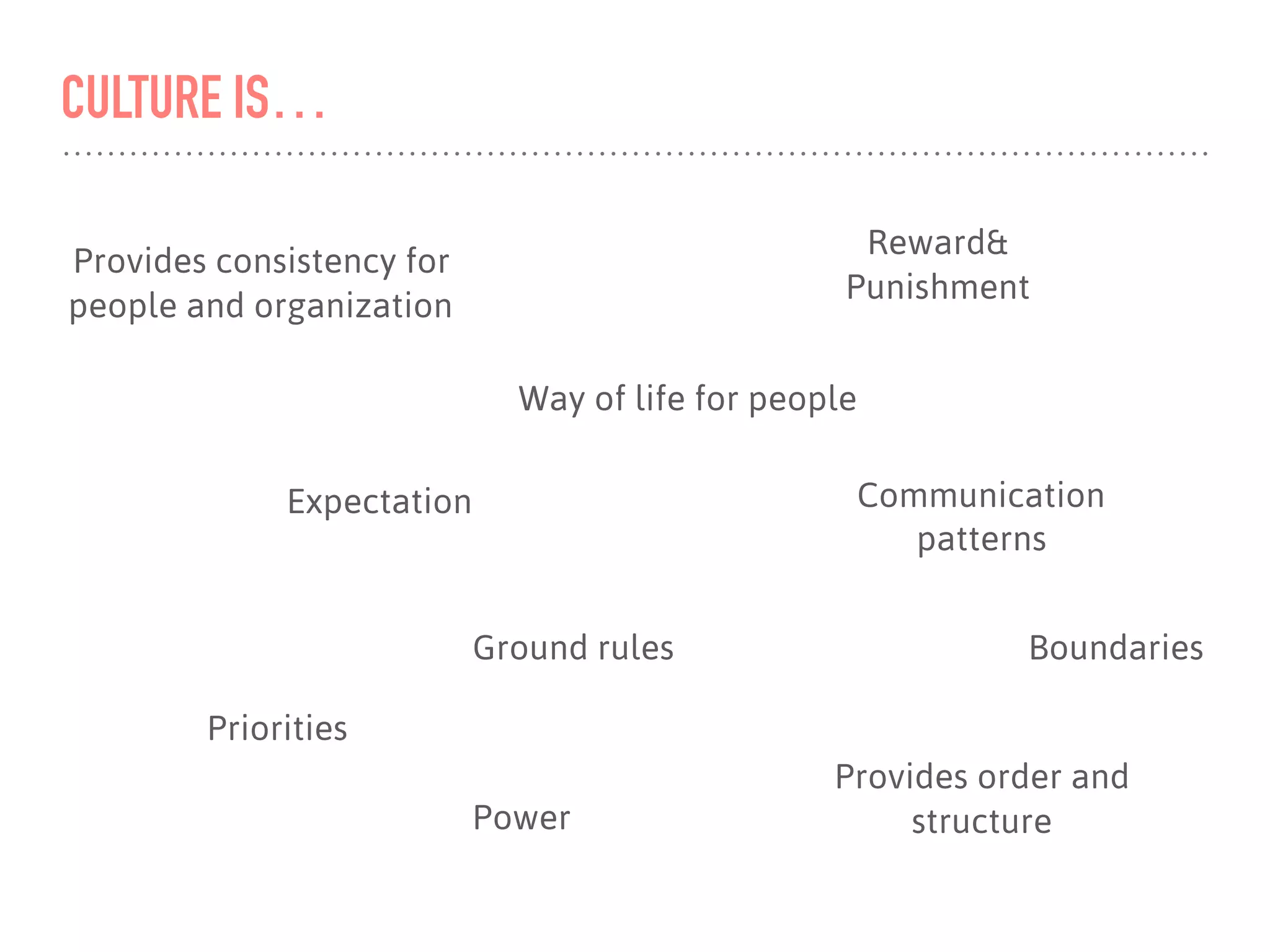
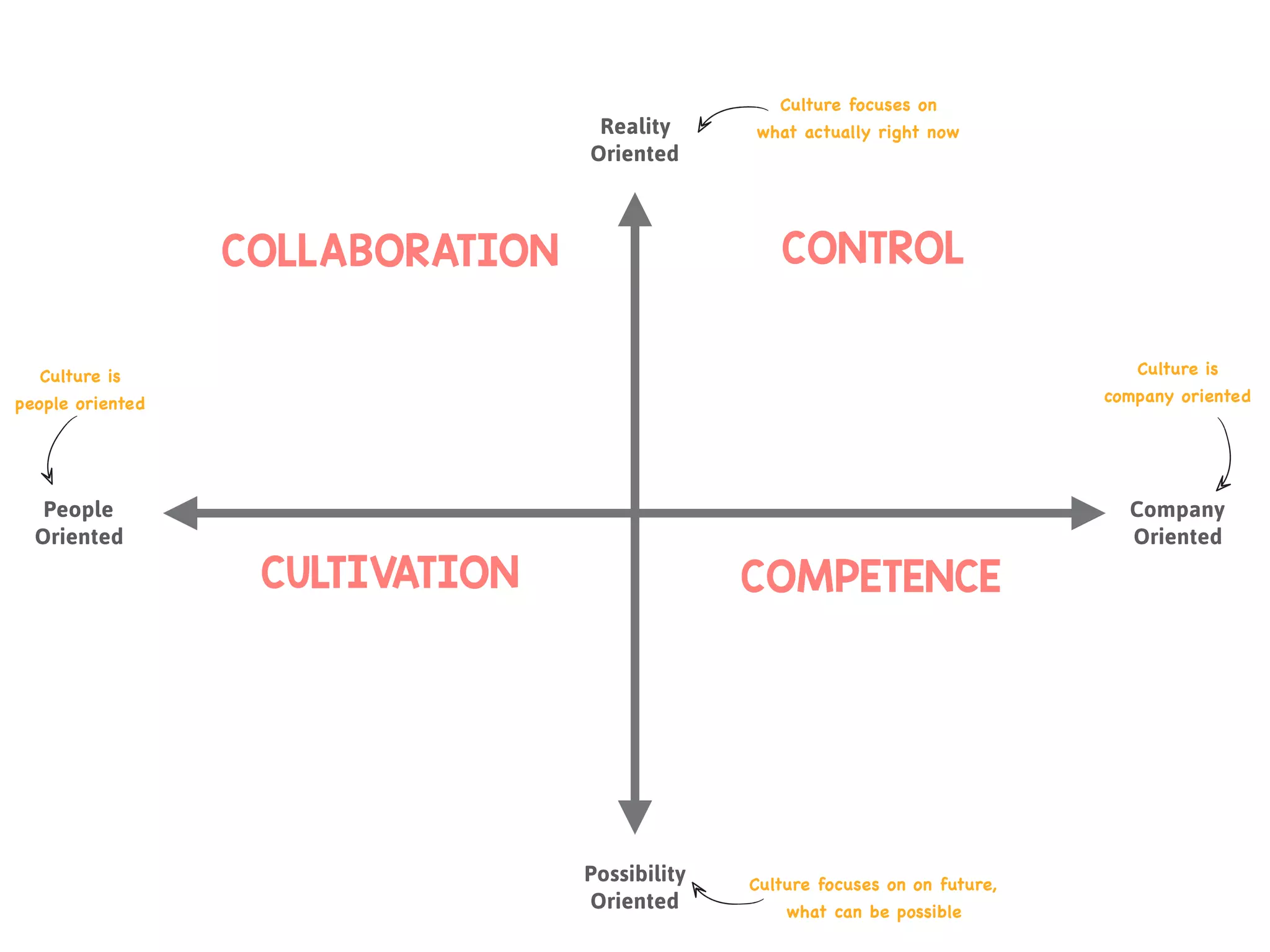
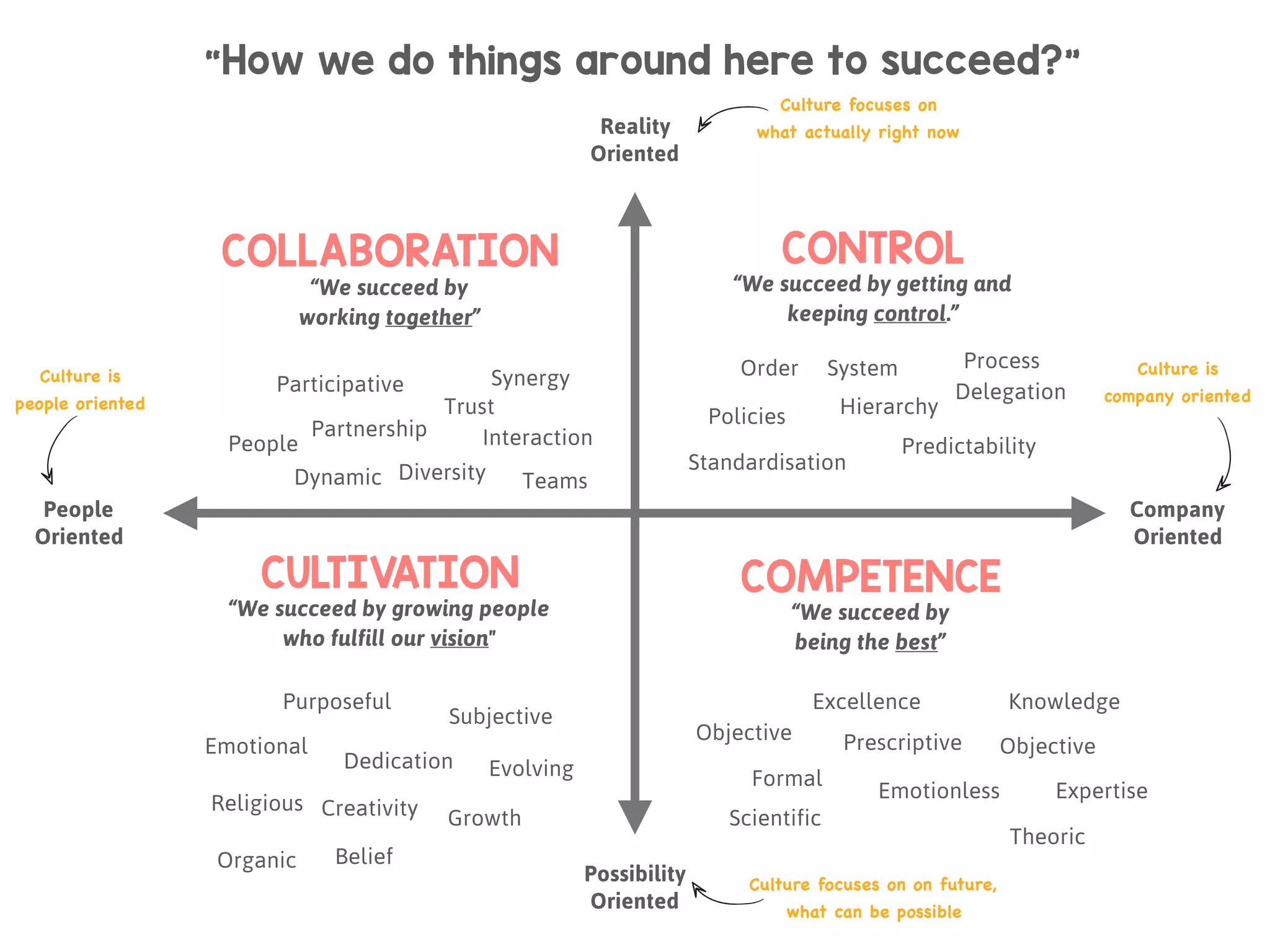
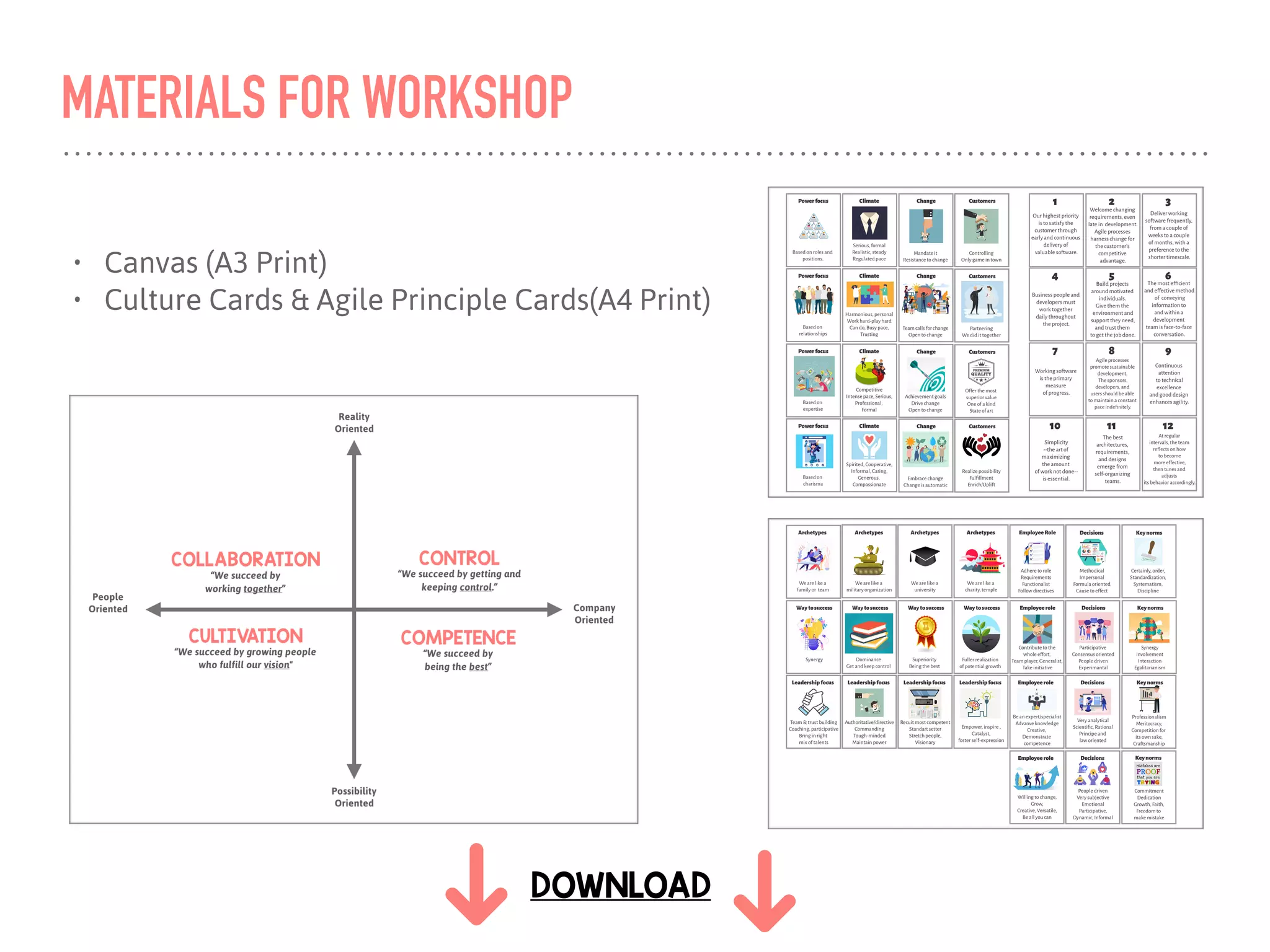
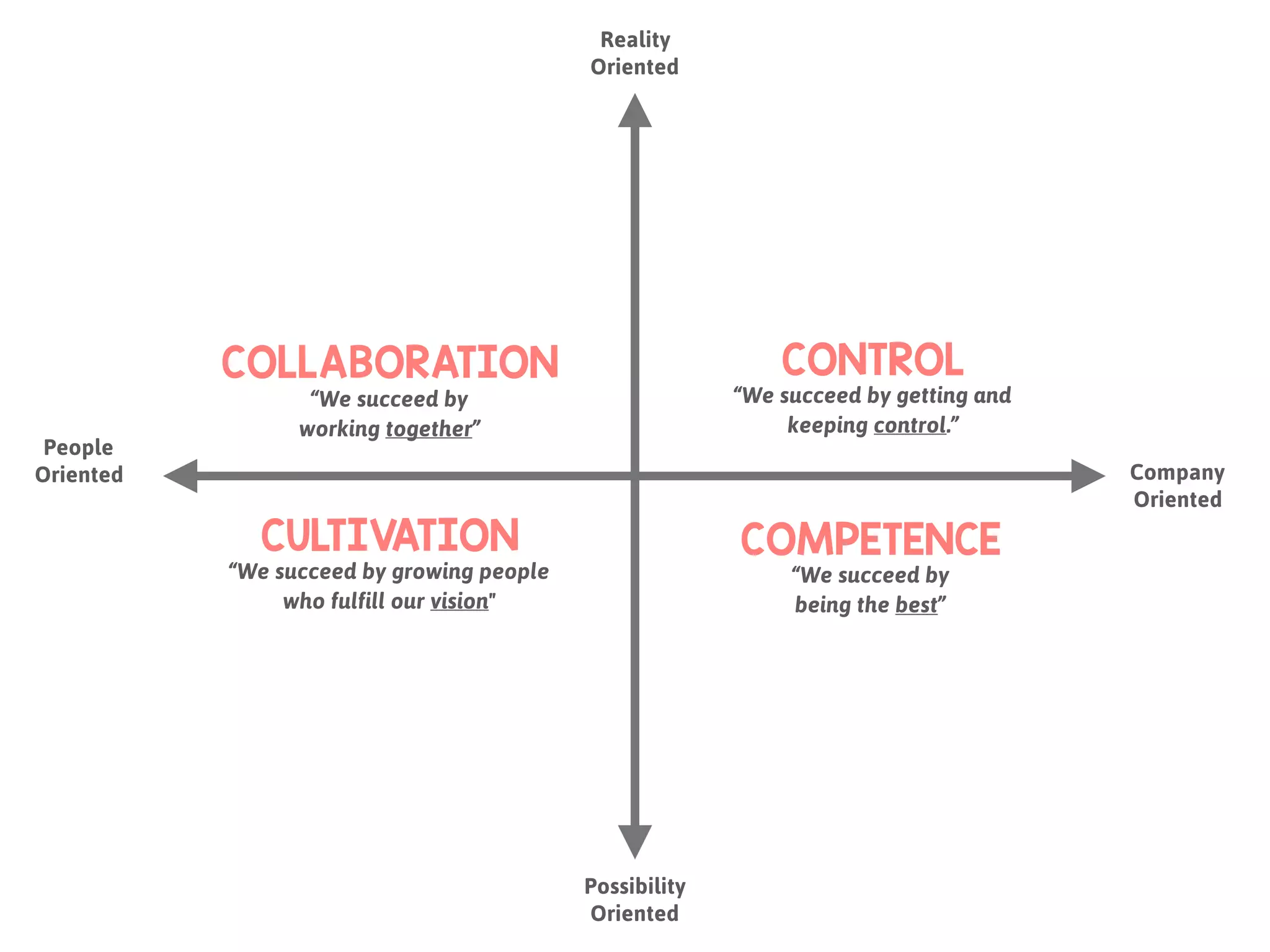
The document discusses the concept of culture within organizations, emphasizing its role in providing consistency, order, and communication patterns. It outlines William Schneider's culture model, which categorizes organizational culture into four types: control, collaboration, cultivation, and competence, each with distinct characteristics and best fit for different work environments. The document also includes a workshop format to help teams define their culture and explore strategies to develop an agile culture.