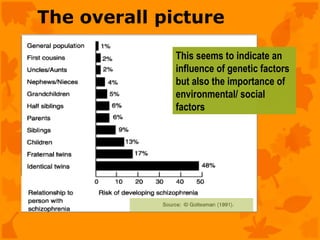
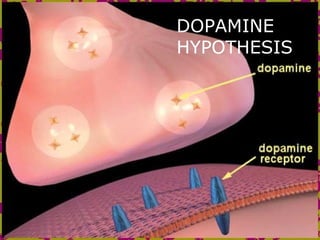
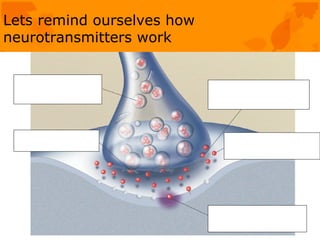
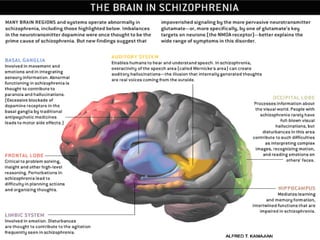
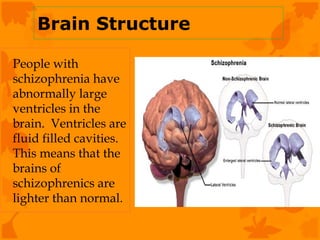
The document discusses several biological explanations for schizophrenia, including genetics, biochemistry, and neuroanatomy. It summarizes evidence from twin and adoption studies that support a genetic influence but also the role of environmental factors. The document then focuses on the dopamine hypothesis, explaining that schizophrenia may involve excessive dopamine activity in the brain. Evidence from drugs, post-mortem studies, and PET scans is presented to support this hypothesis, though it is noted that other neurotransmitters may also be involved. Alternative biological explanations discussed include brain structure abnormalities, brain damage, viral infections, and birth complications.