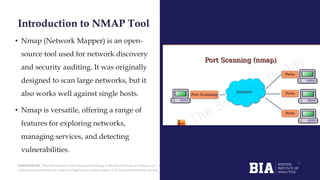
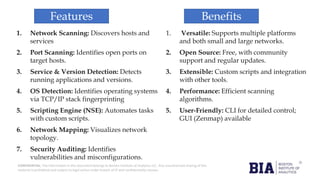
This document details a network security analysis for Modern Energy Rental Pvt. Ltd. using the nmap tool to identify open ports and associated security threats. It provides an overview of various network services, their functions, benefits, and the potential vulnerabilities related to their use. The document emphasizes the importance of identifying and mitigating risks tied to open ports to enhance overall cybersecurity.