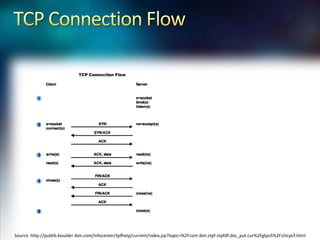
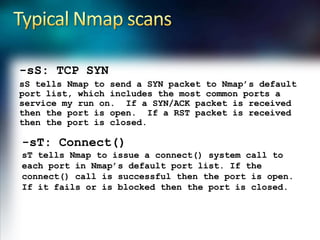
Using Nmap and Metasploit, the presenter demonstrates how to scan a target system using Nmap to identify open ports and operating system. Potential exploits are then searched for in CVE and executed using Metasploit, gaining shell access on the target. Alternatively, Nmap data can be imported into a Metasploit database to automatically attempt exploitation based on opened ports.