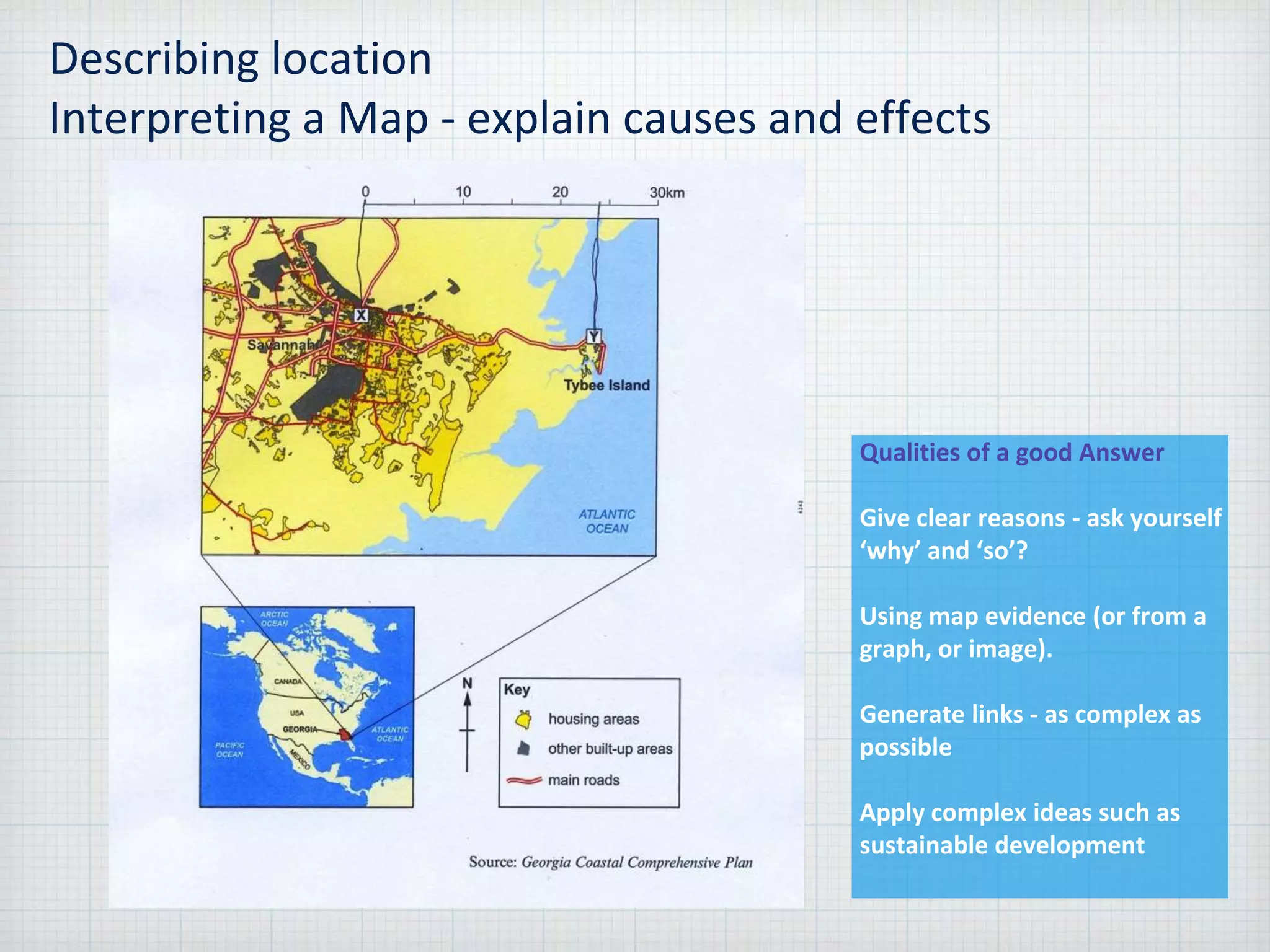
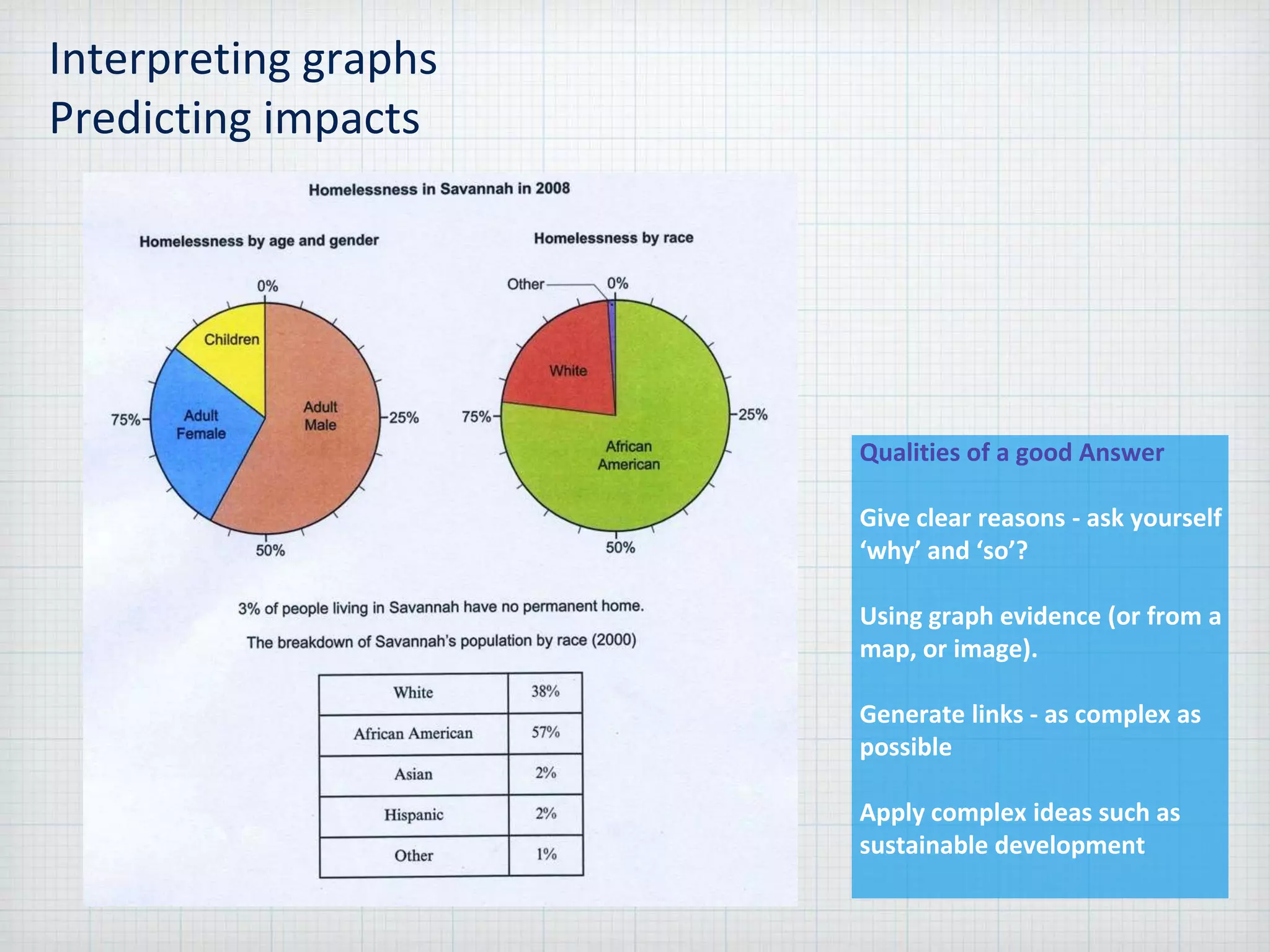
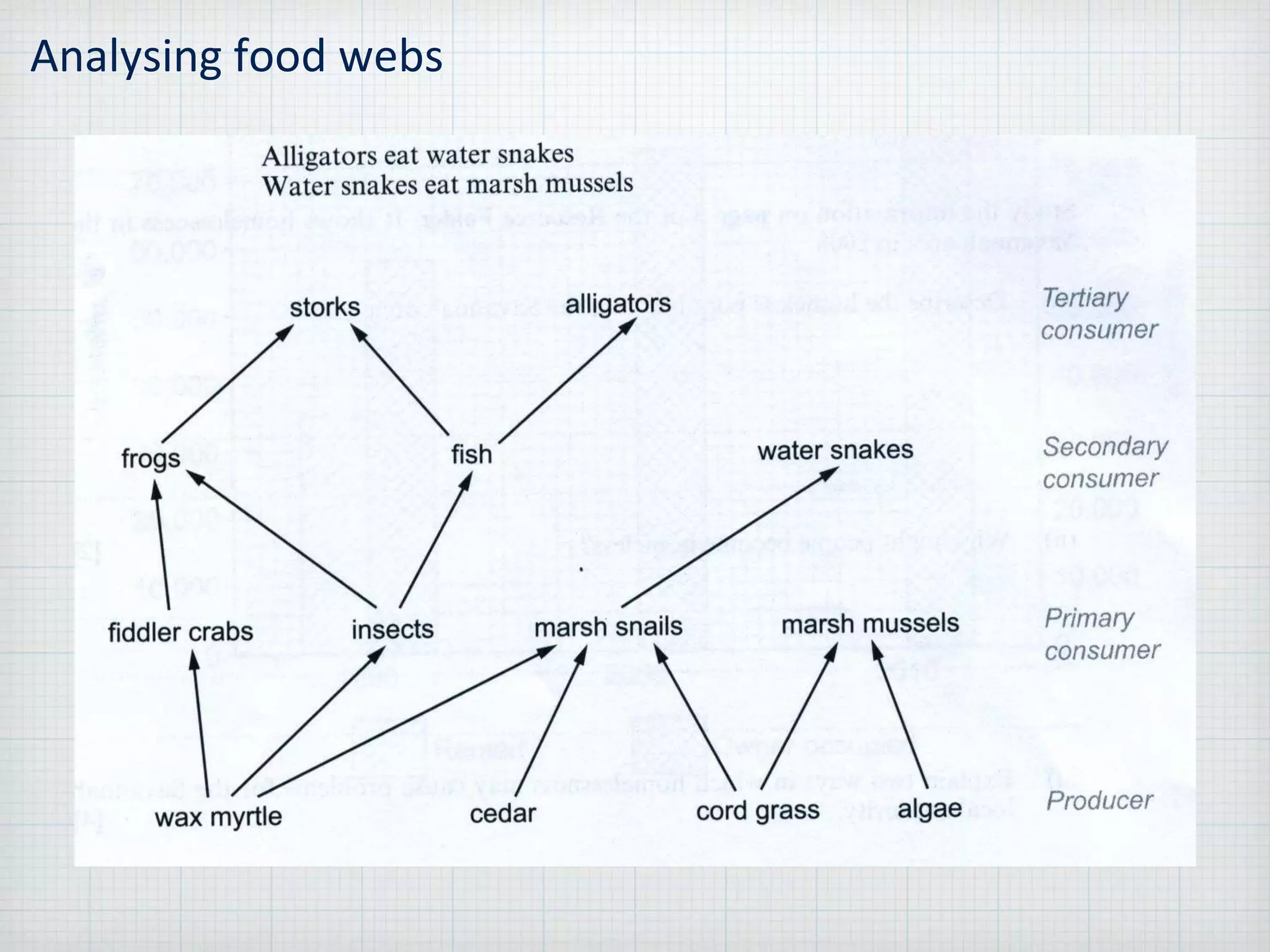
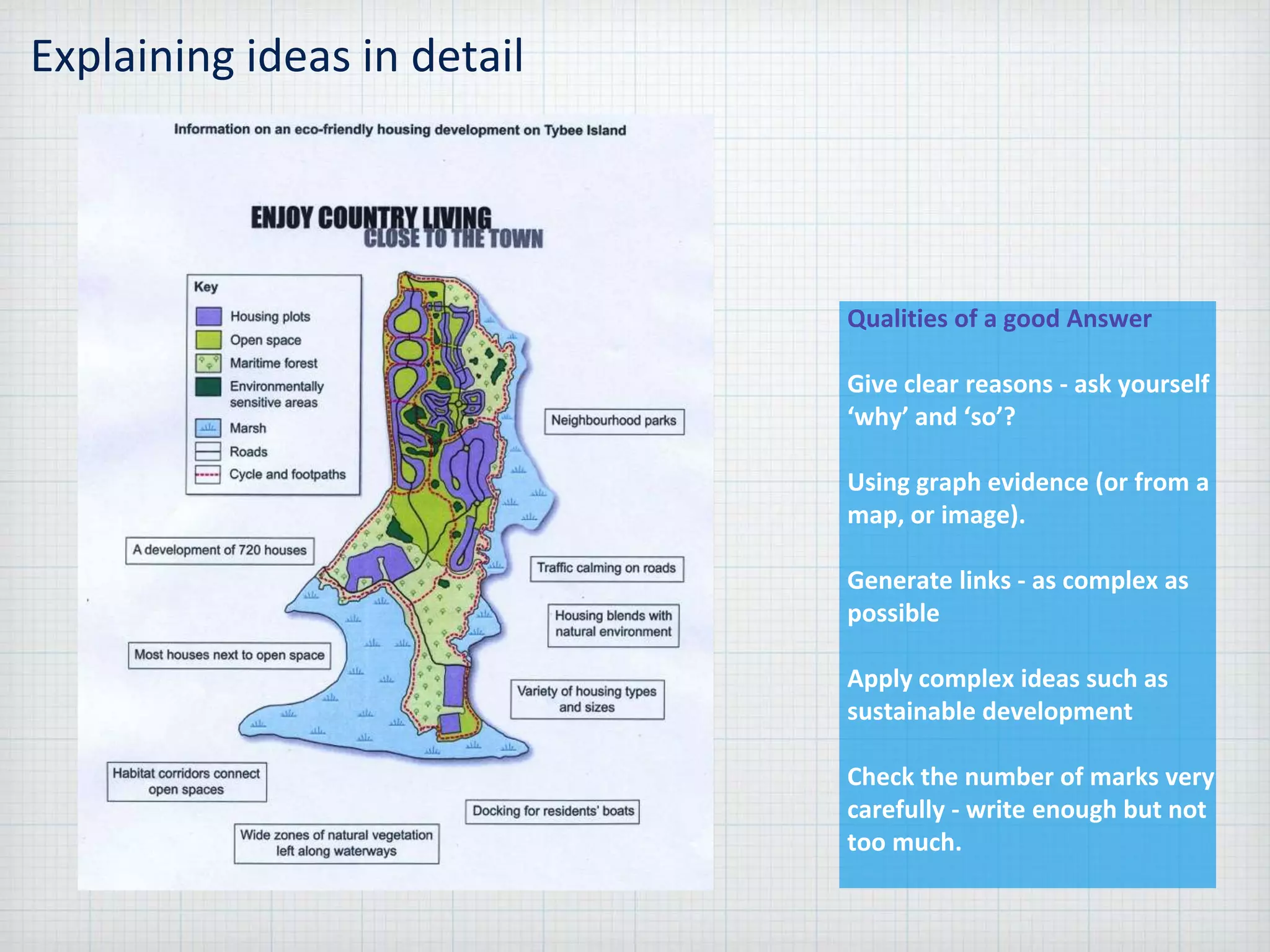
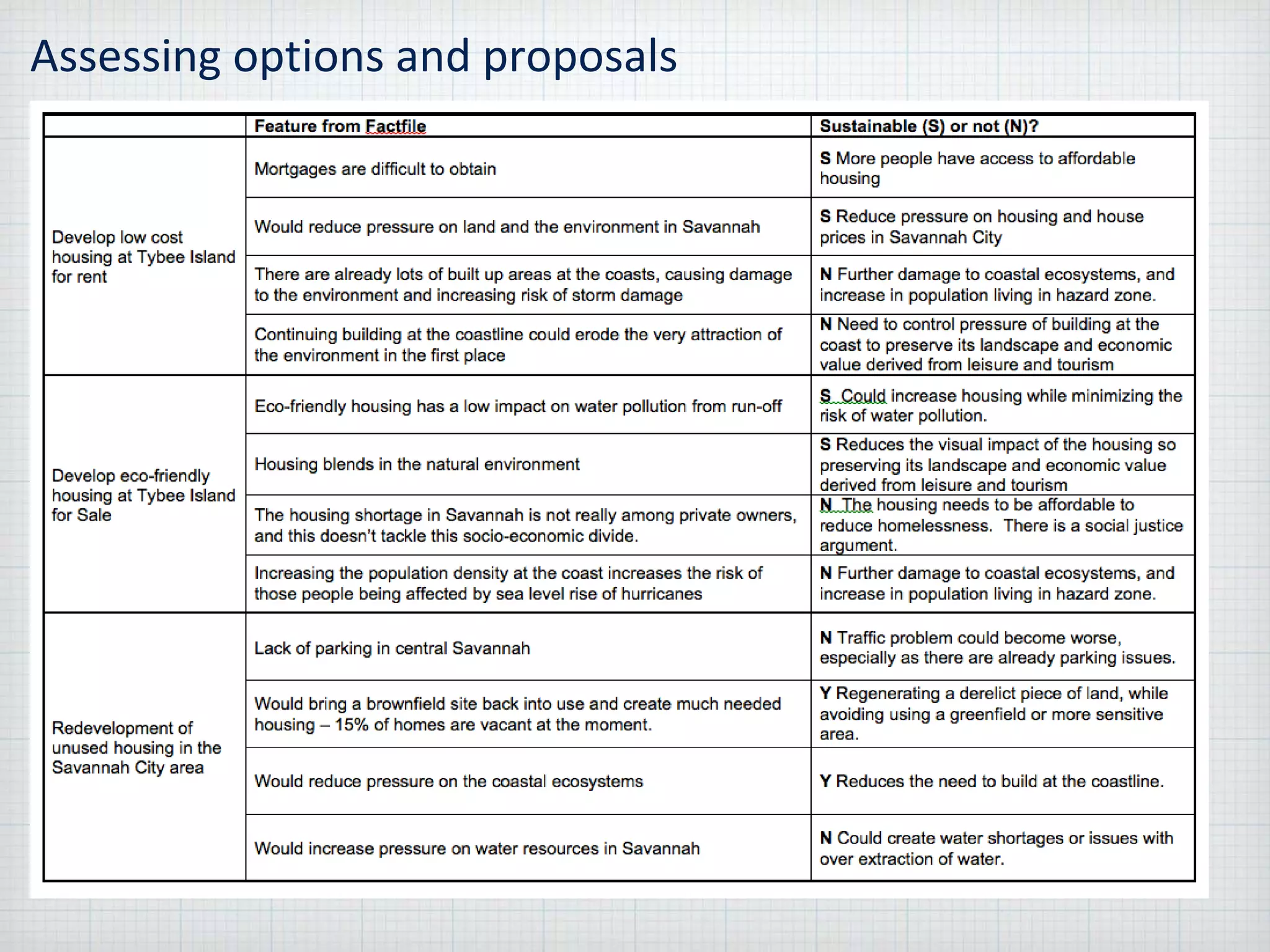
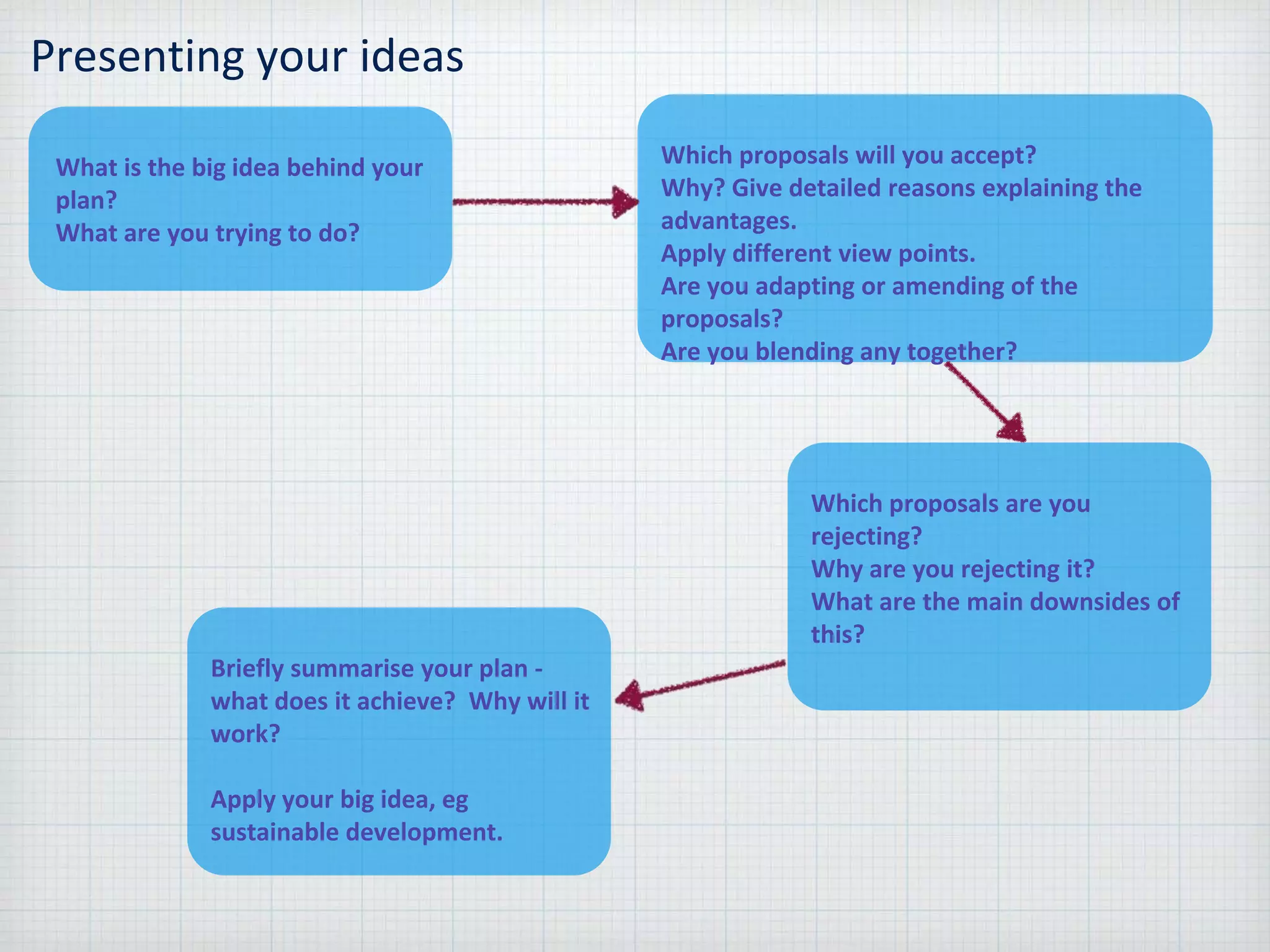
Sustainable development is meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, within the environmental limits of the planet. The document provides guidance for answering problem solving exercises, describing locations, interpreting maps and graphs, analyzing food webs, assessing options and proposals, and presenting ideas. It emphasizes giving clear reasons supported by evidence, generating complex links, and applying concepts like sustainable development.