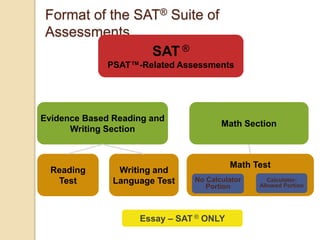
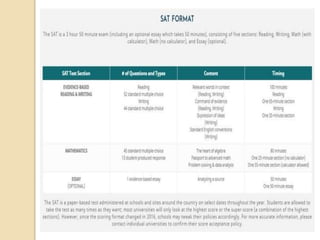
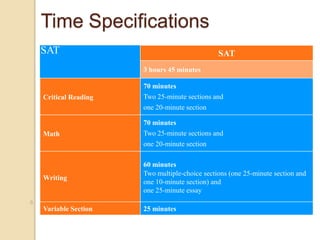
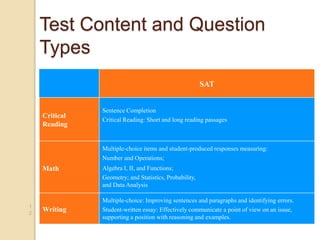
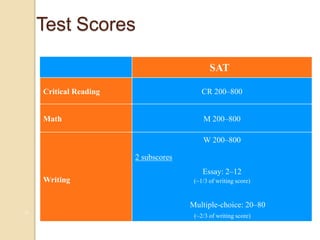
The SAT focuses on critical reading, mathematics, and writing skills that are important for college success. It measures students' ability to analyze and solve problems by applying what they have learned in school. Most students take the SAT after completing 3 years of math, so the test aligns with what students are learning. Field tests show that the length and difficulty of the test do not negatively impact student scores. The SAT consists of reading, writing and language, and math sections with various question types and takes about 3 hours and 45 minutes to complete. Students receive subscores in critical reading, math, and writing and an essay score. To prepare, students should take challenging courses, read and write extensively, and familiarize themselves with the SAT format