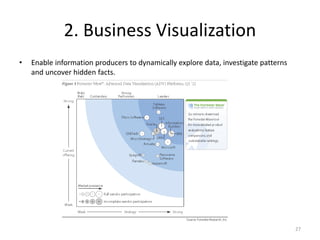
This document provides an overview of the Statistical Analysis System (SAS) software. It discusses SAS's history beginning in 1966 as a project to analyze agricultural data. SAS now has over 7,000 employees and provides software to 96 of the Fortune 100 companies. The document also describes SAS Enterprise BI Server, including its key features for business intelligence and a case study of its successful implementation at the US Department of Housing and Urban Development.