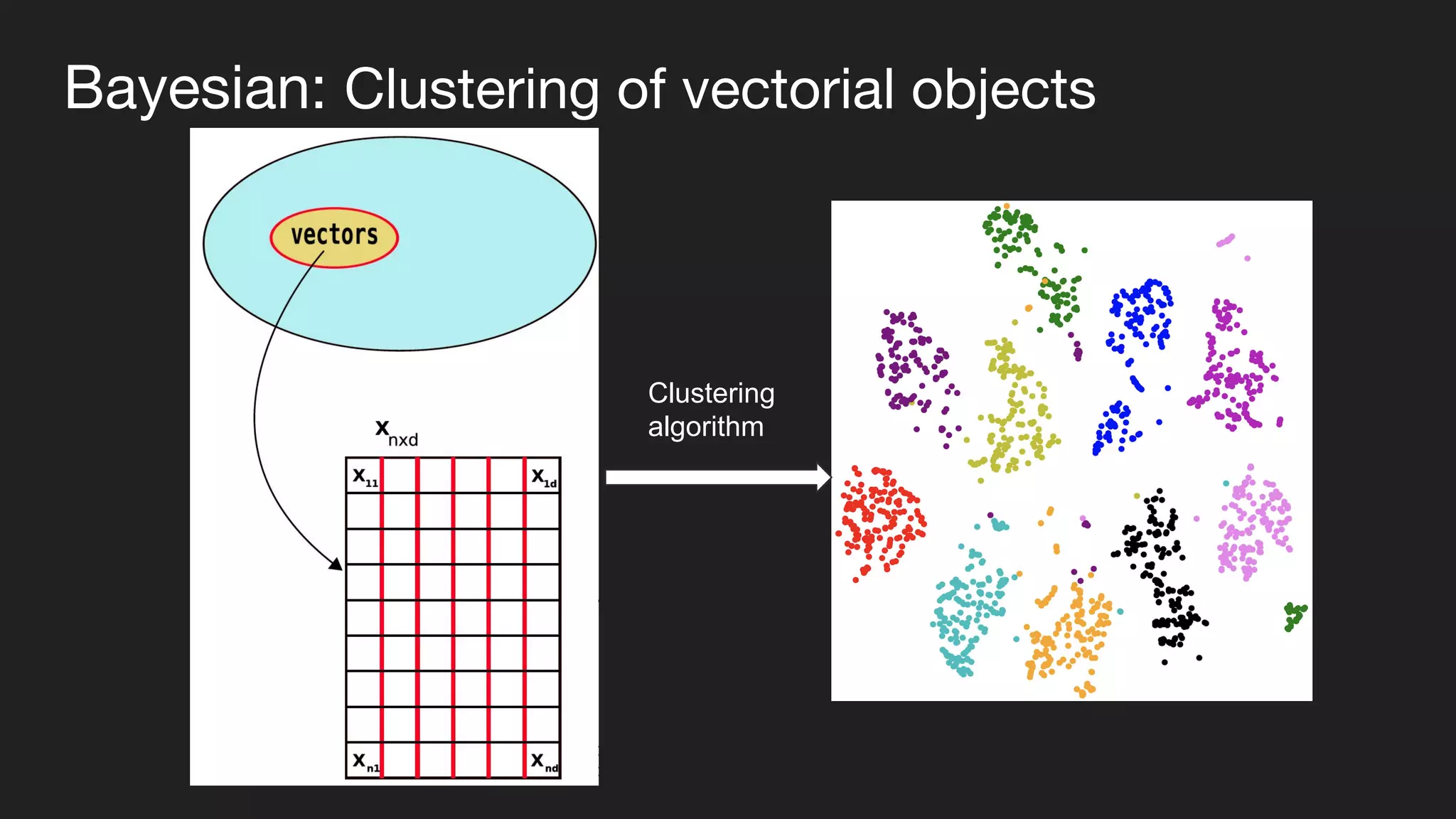
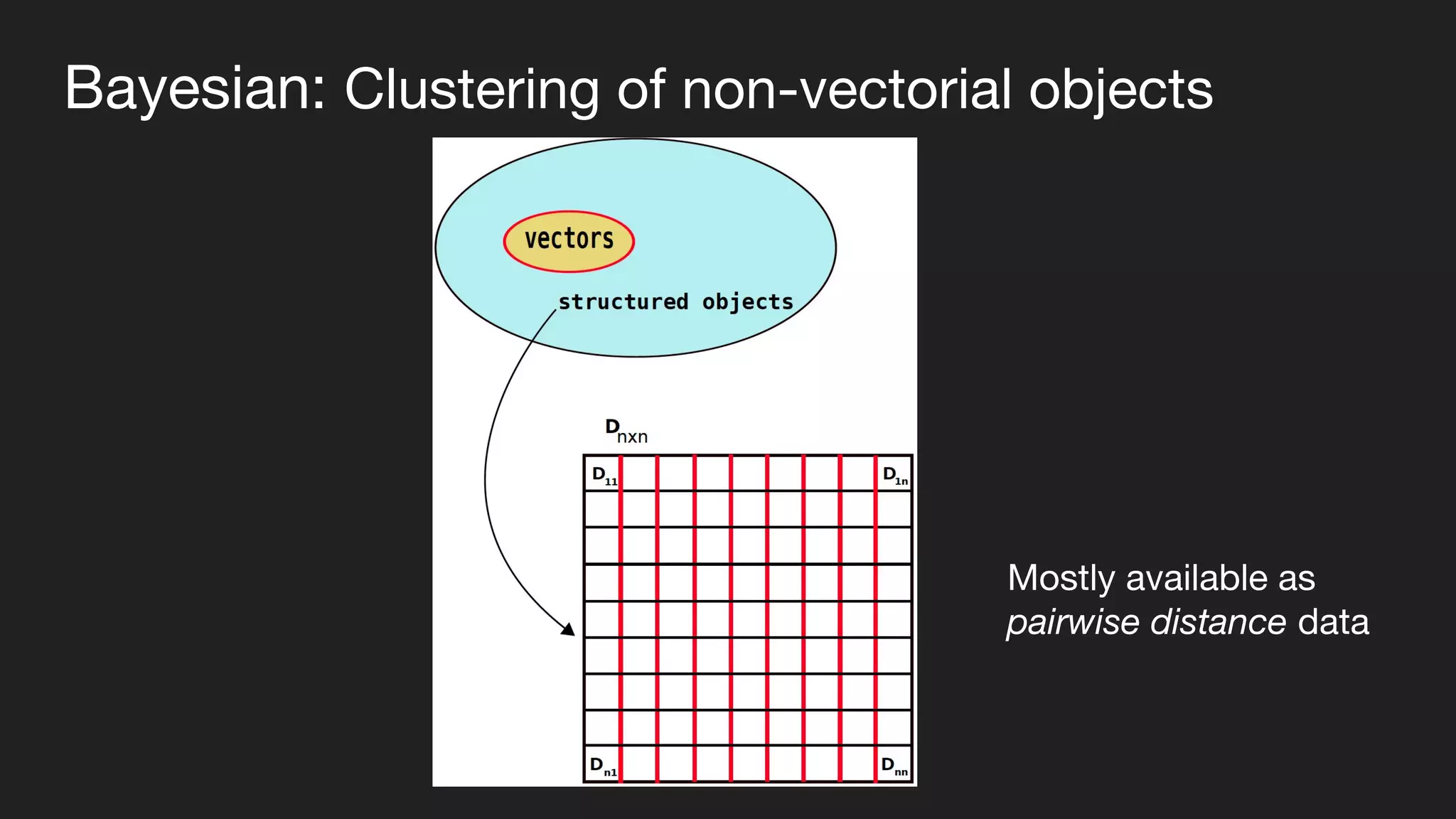
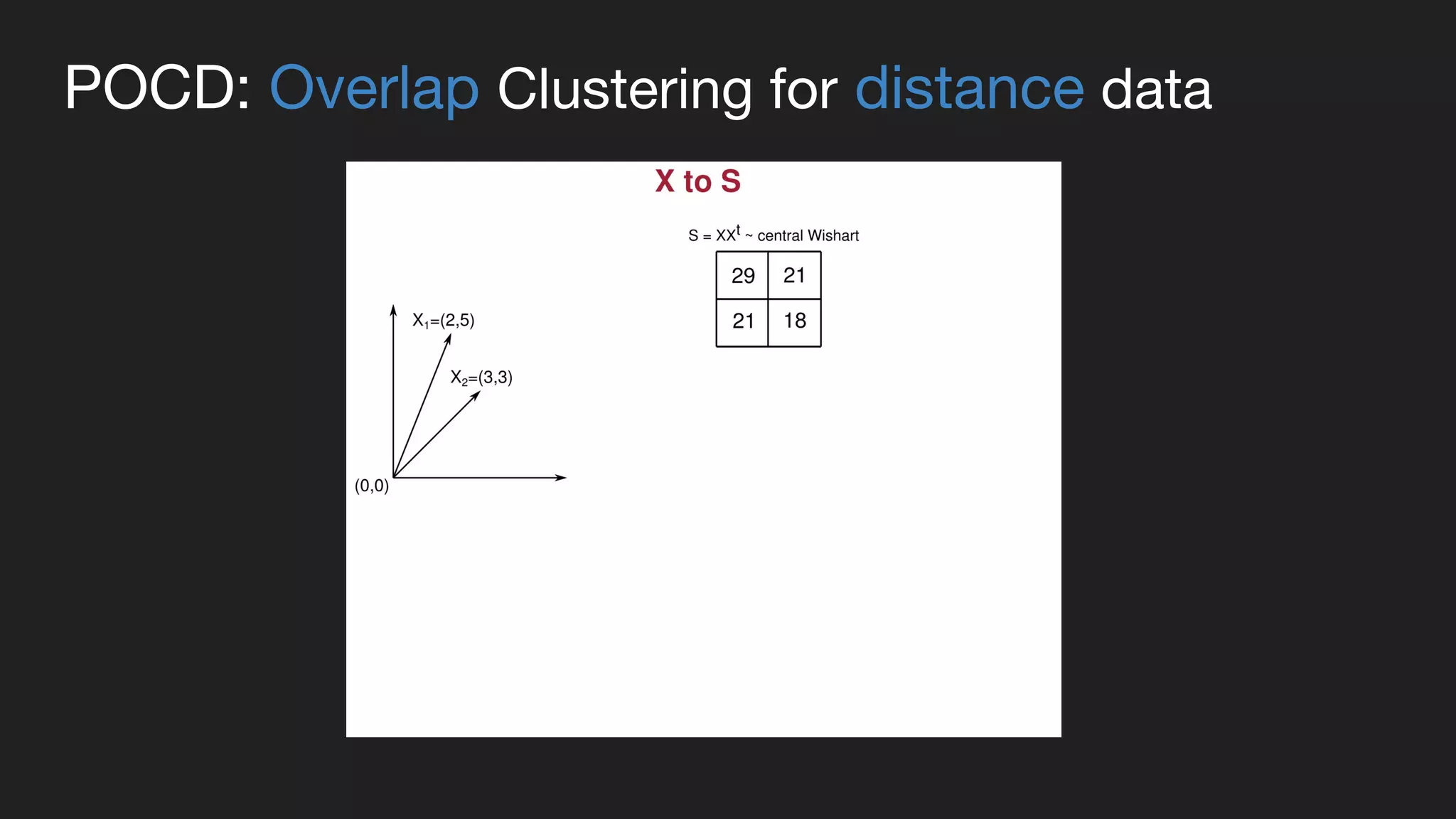
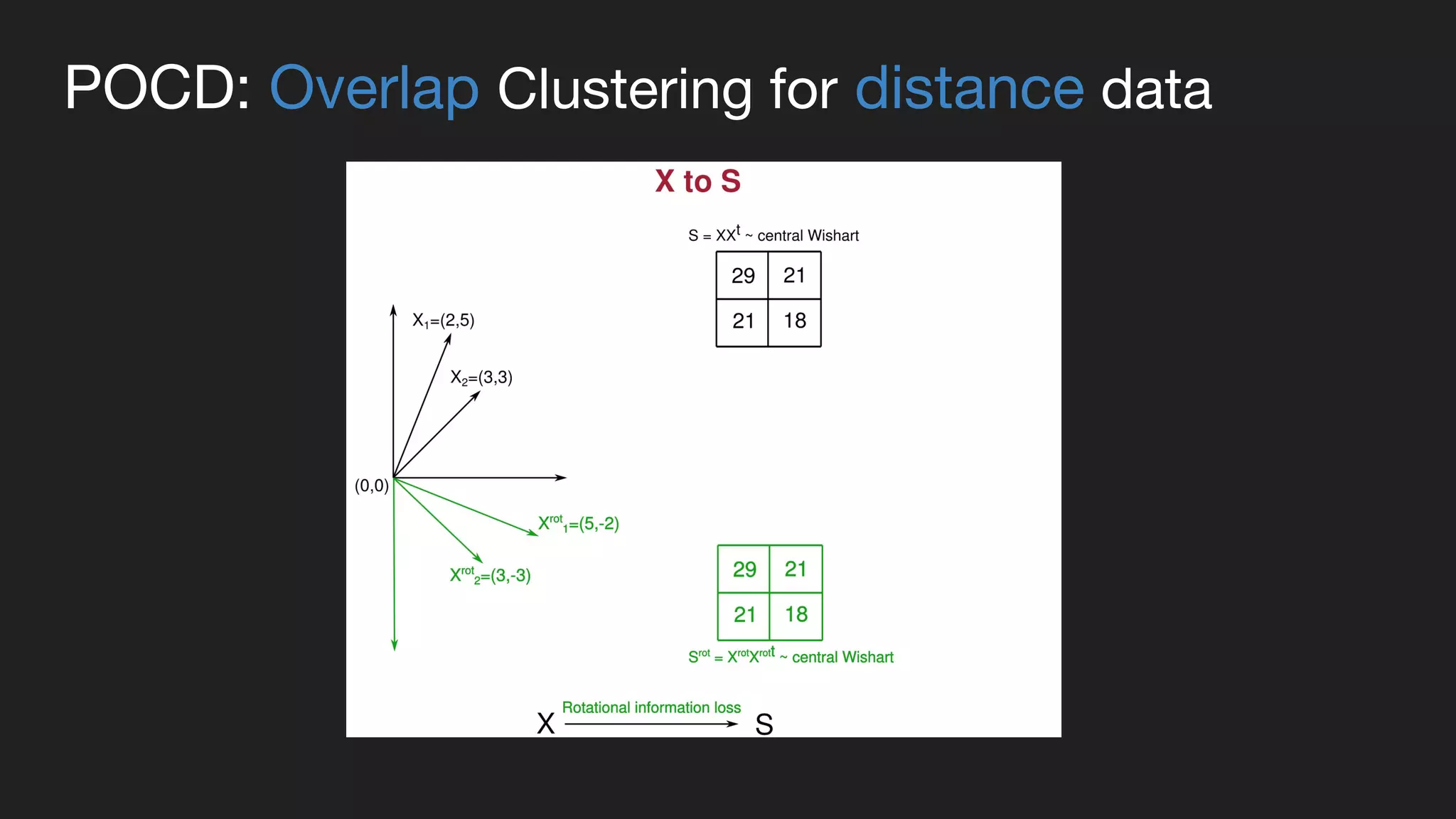
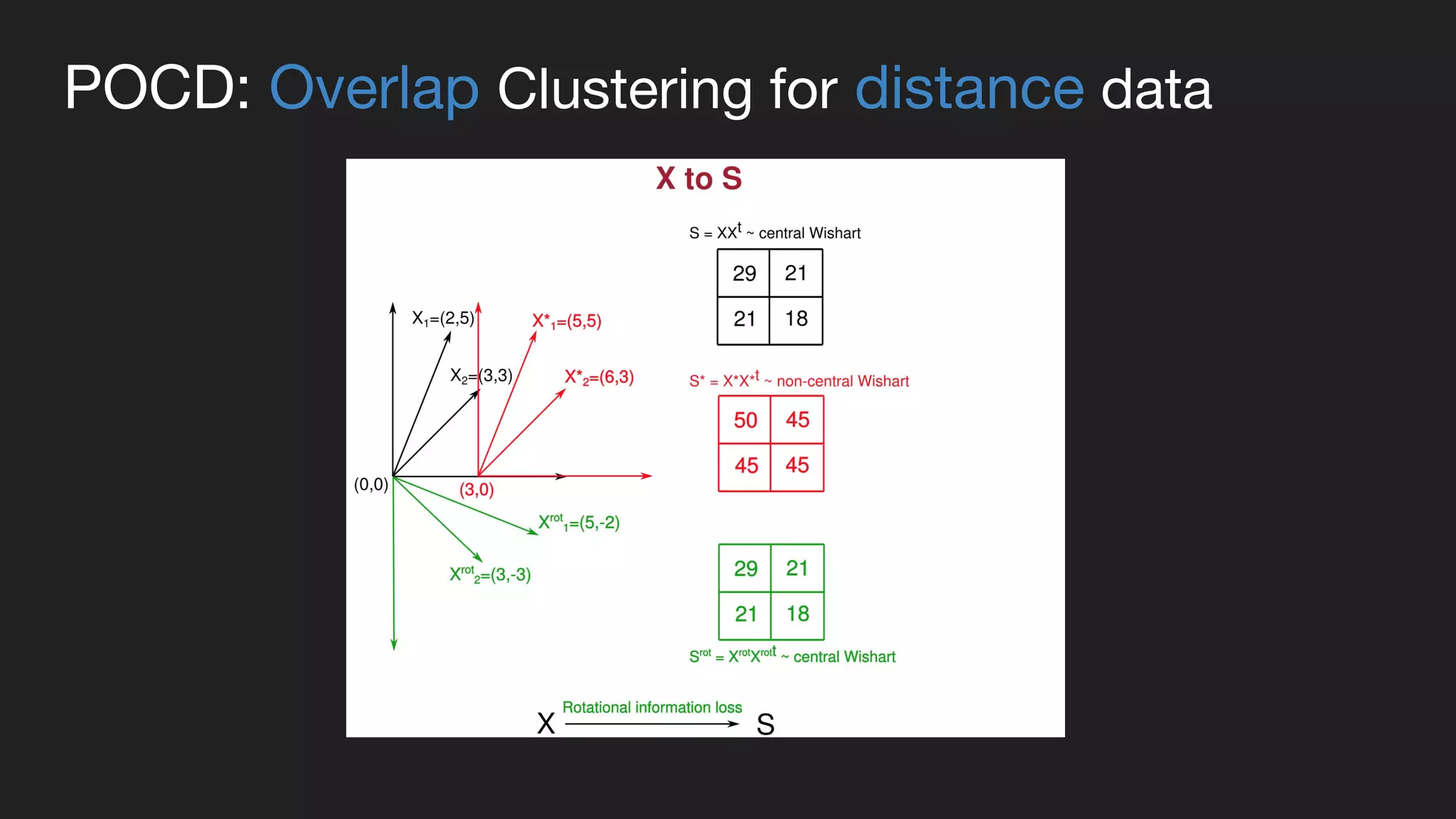
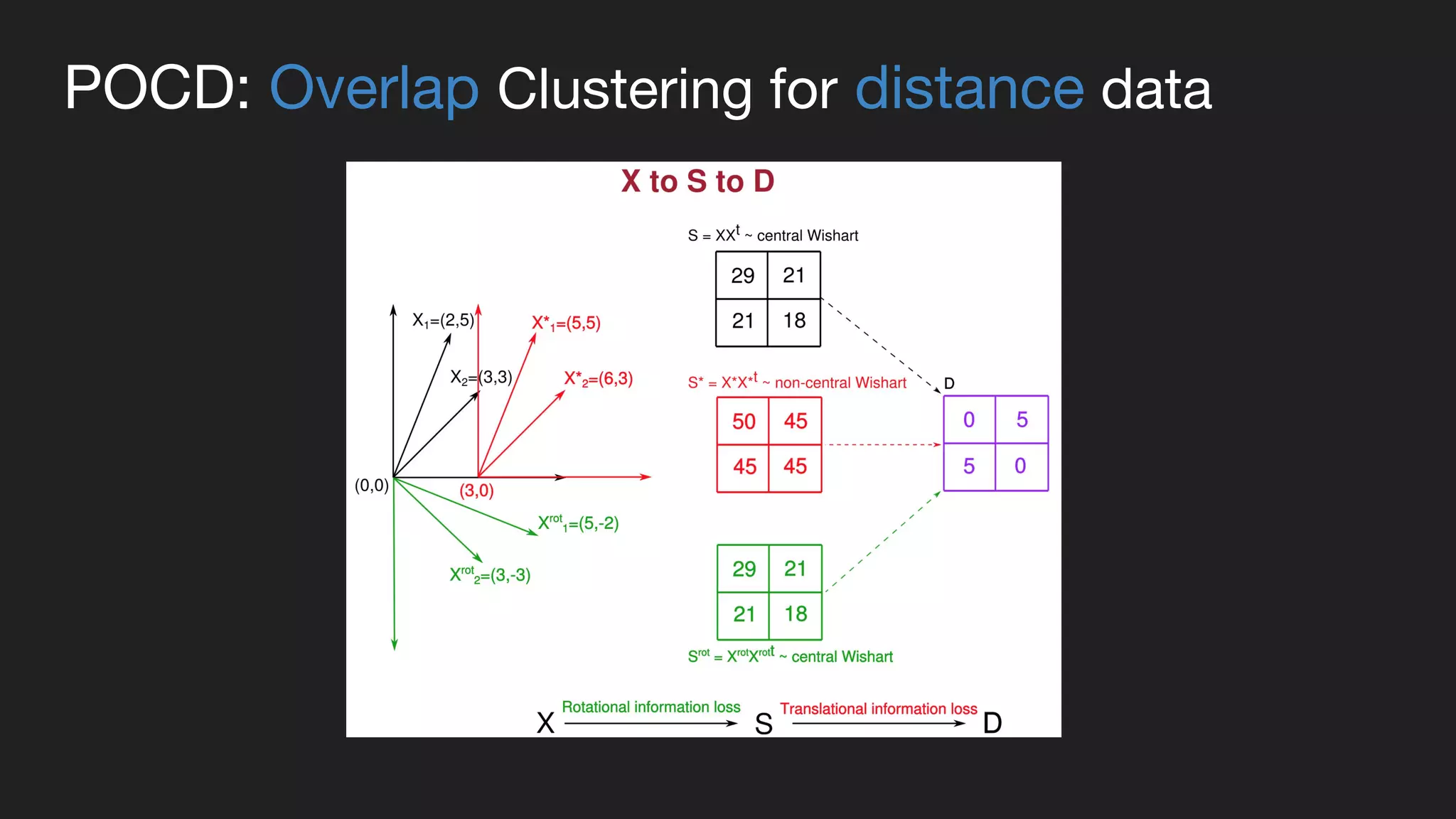
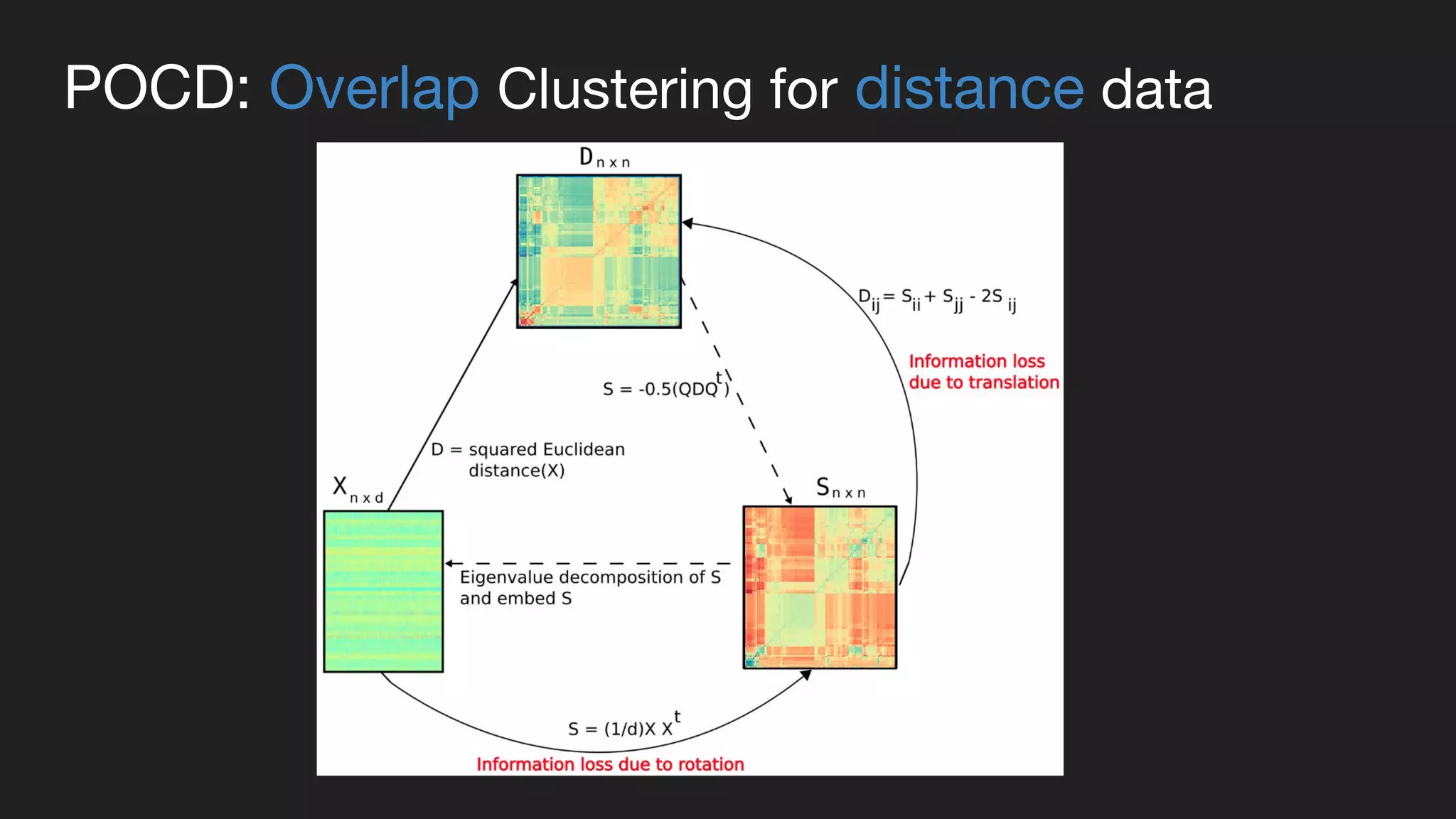
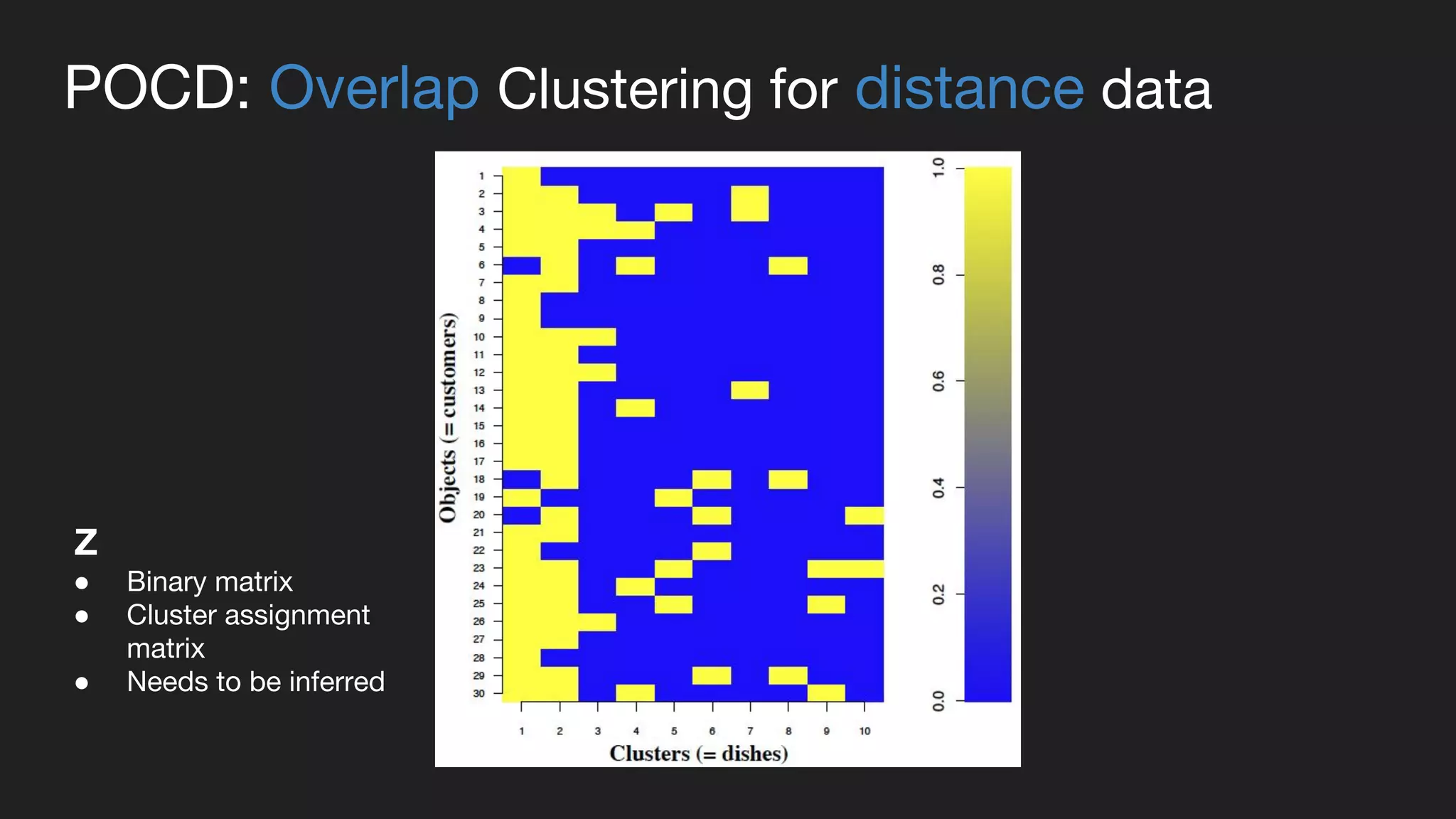
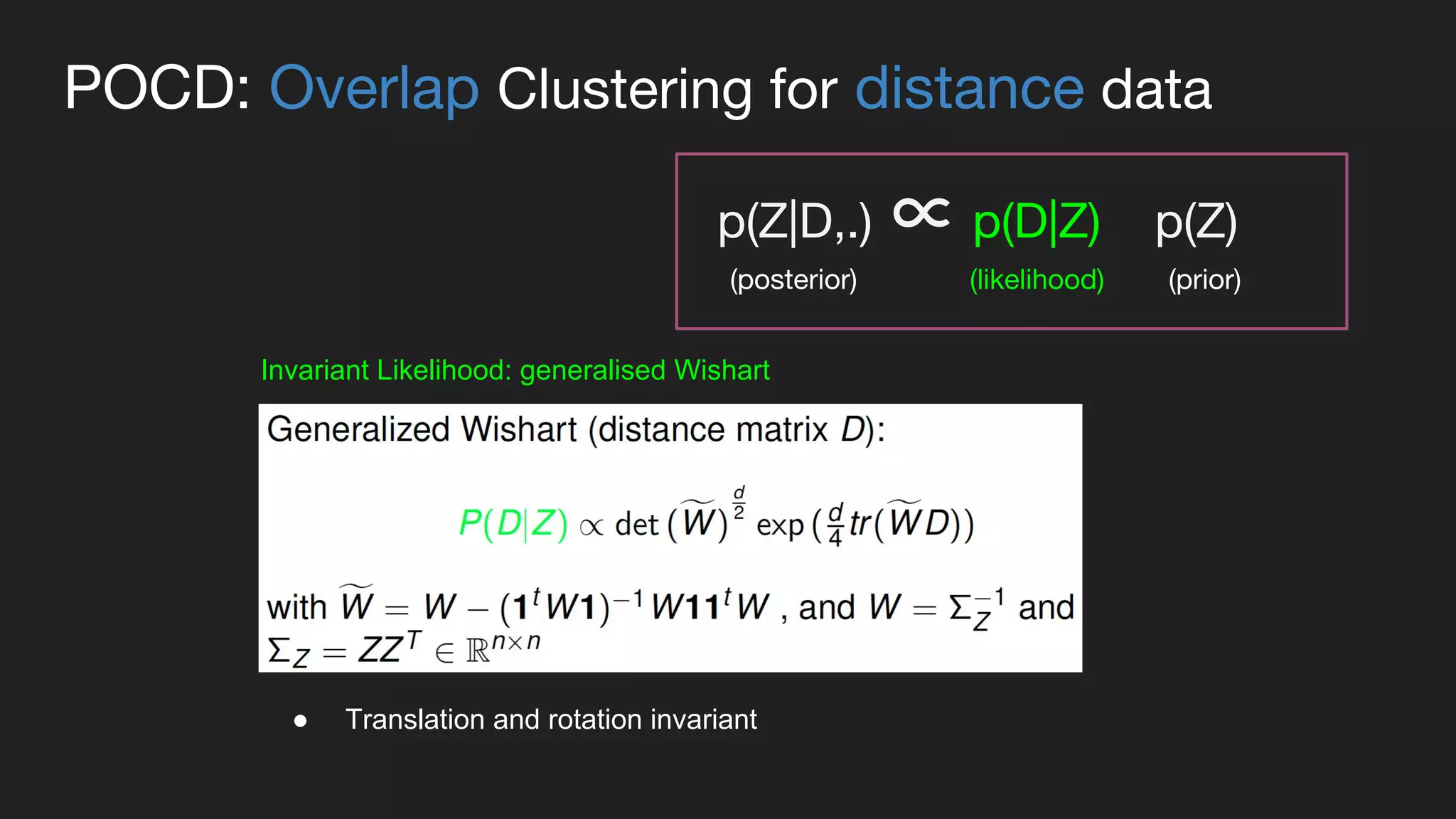
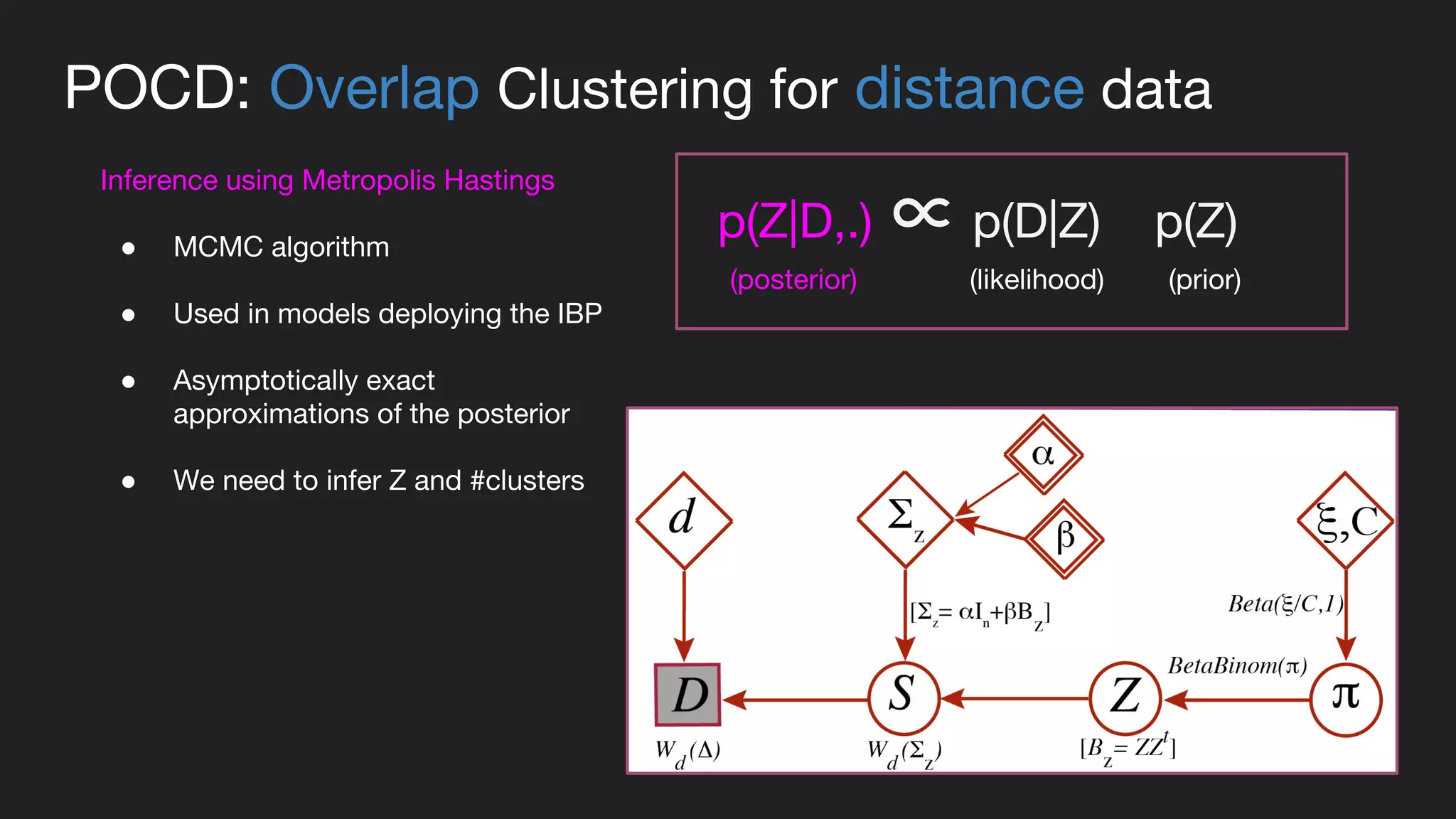
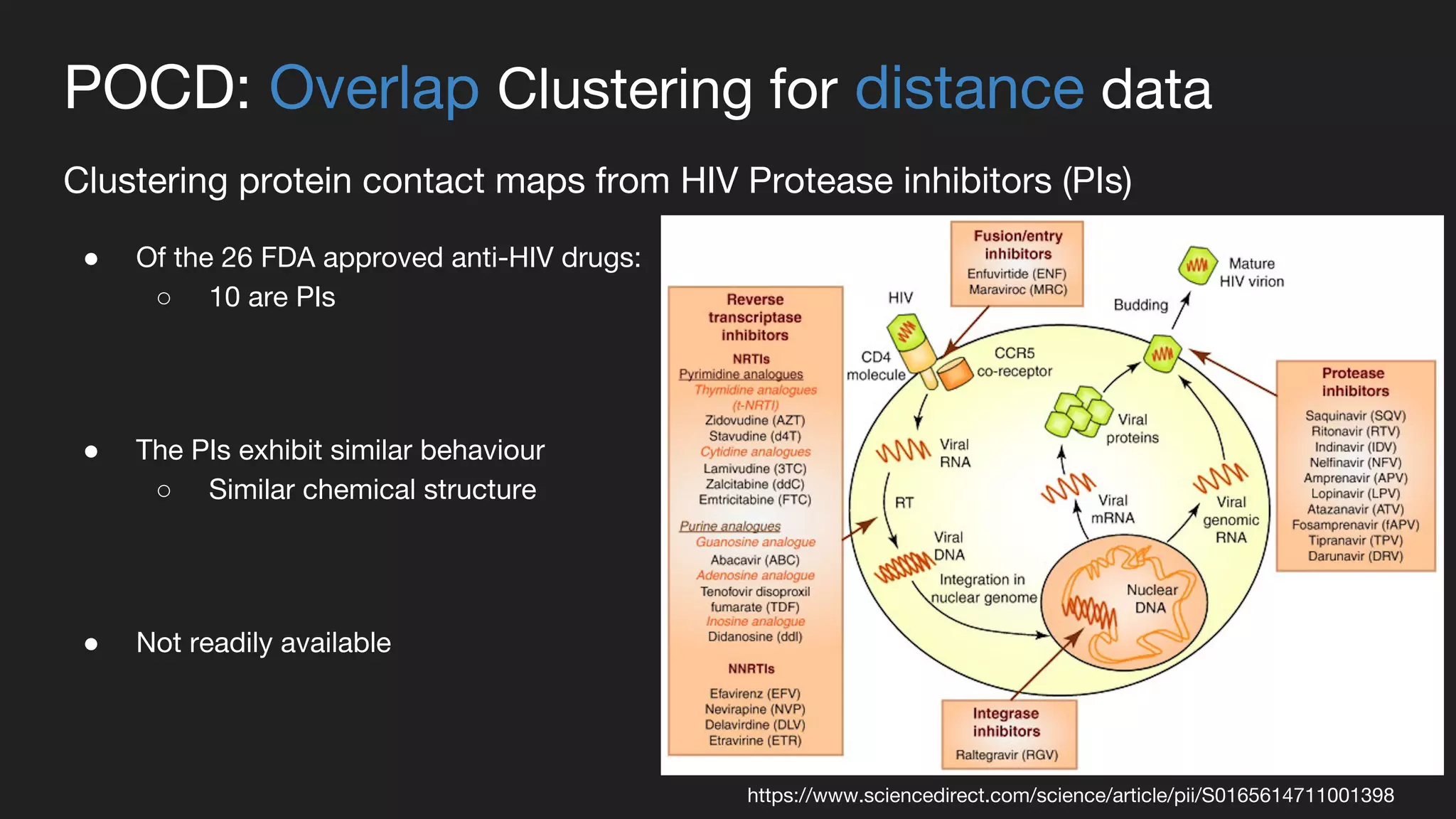
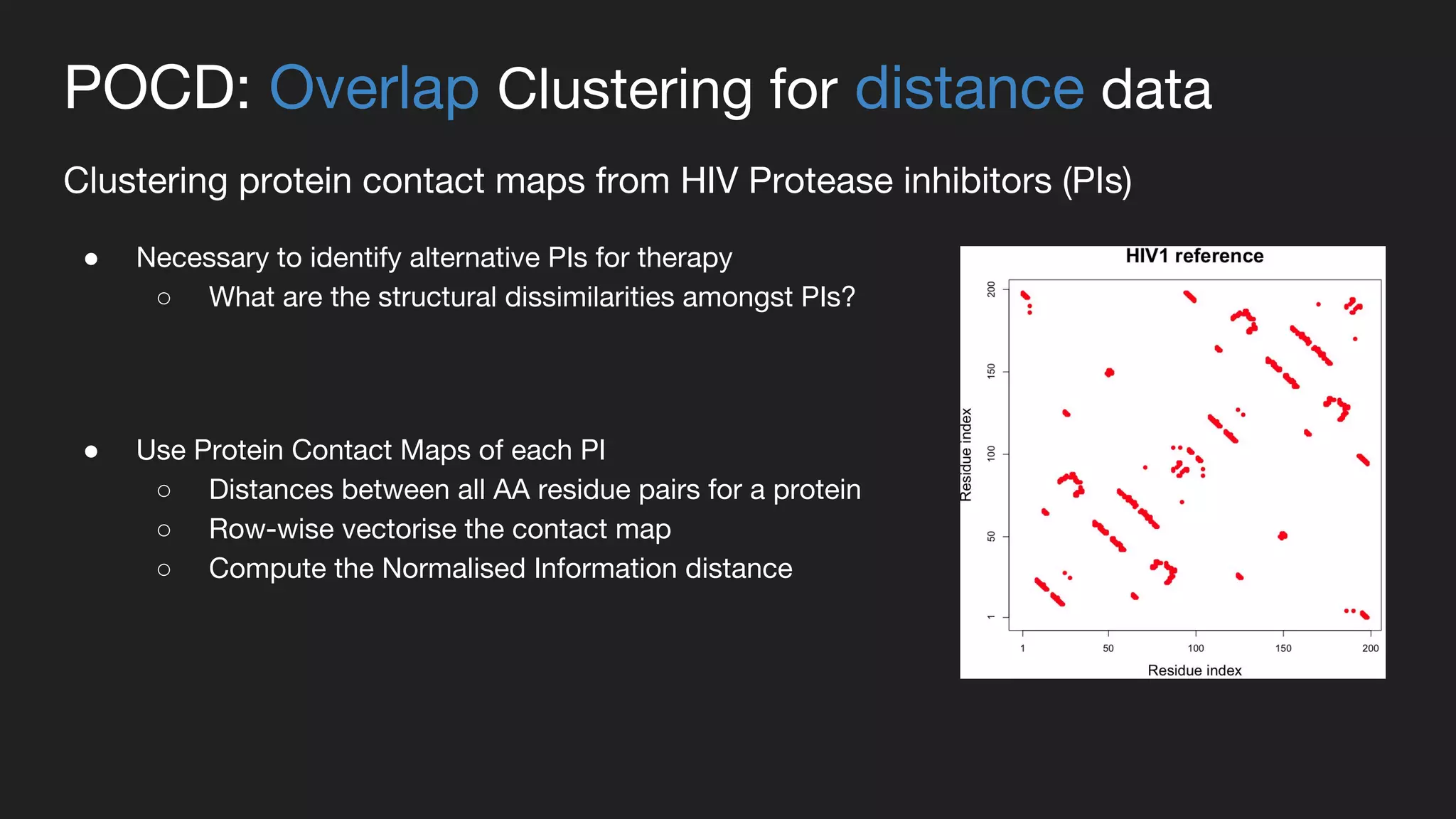
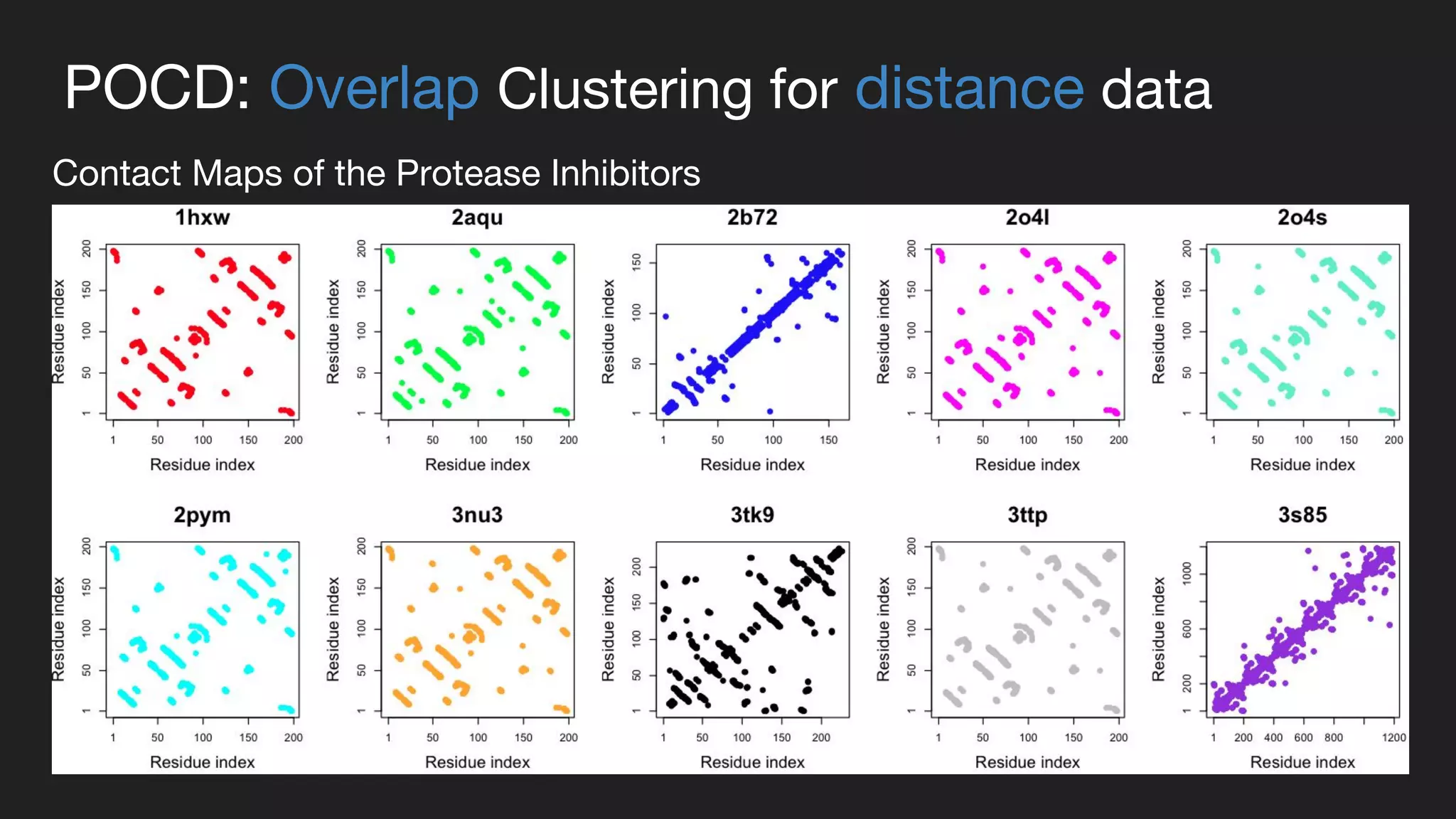
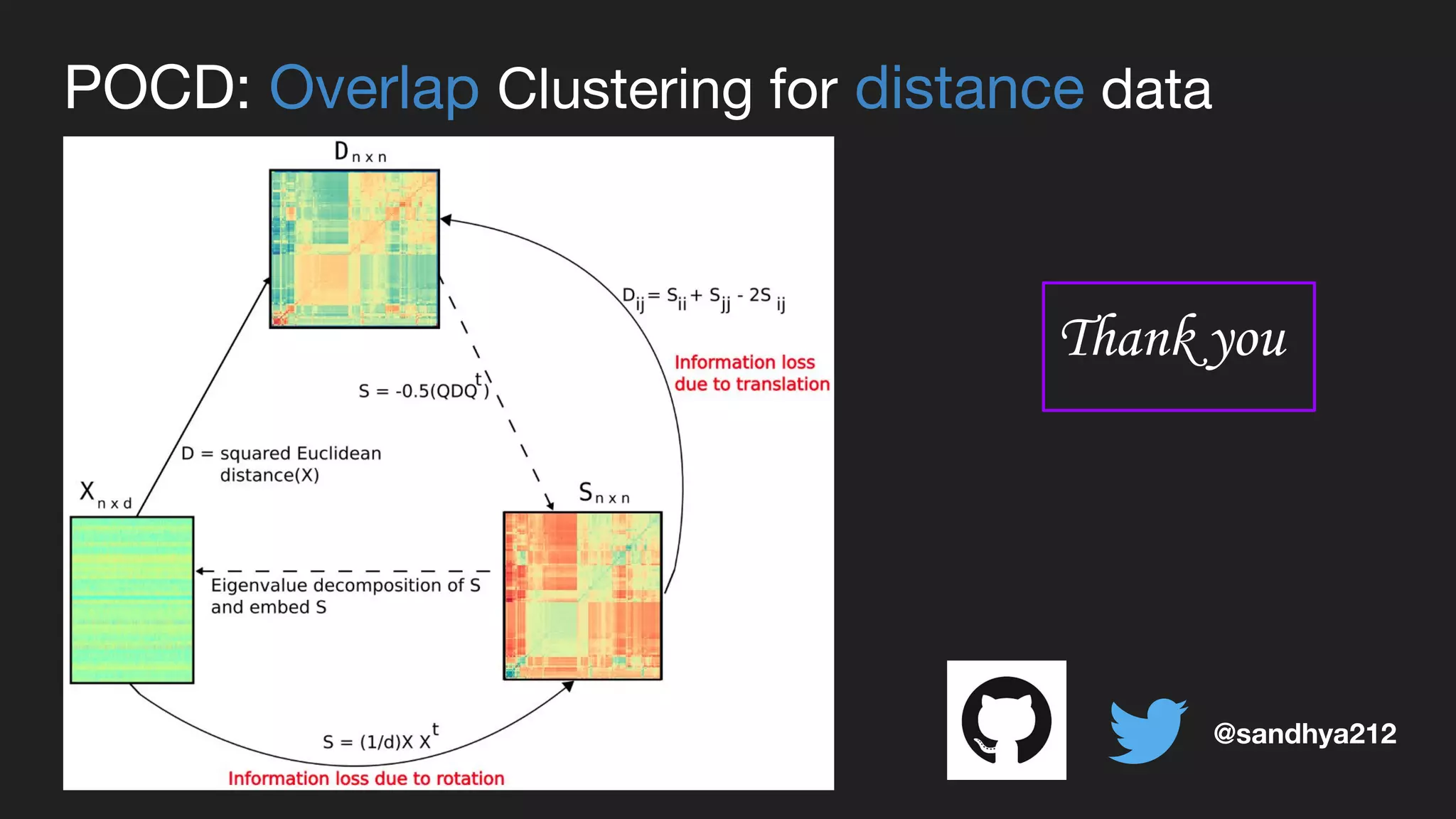
This document presents a Bayesian approach called POCD (Probabilistic Overlapping Clustering of Distance data) for clustering non-vectorial objects when only pairwise distance data is available. POCD models the cluster assignment using an Indian Buffet Process prior to allow for an unknown number of clusters. It then infers the cluster assignments using a generalized Wishart likelihood and Metropolis-Hastings sampling. The approach is demonstrated on clustering protein contact maps of HIV protease inhibitors using their normalized information distances, in order to identify structural similarities and differences between the inhibitors without vector representations.