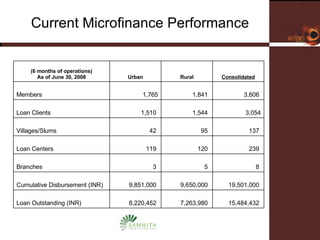
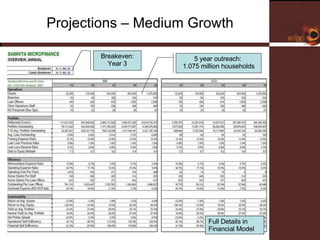
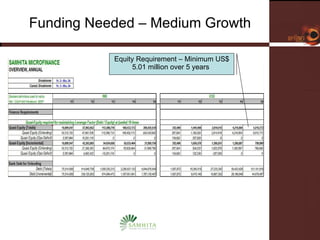
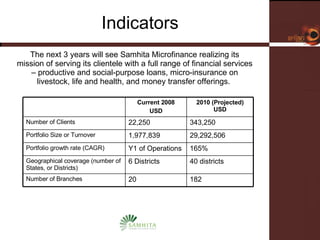
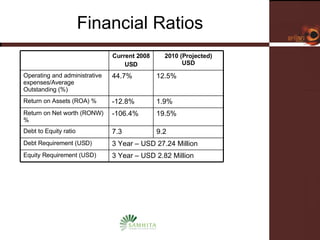
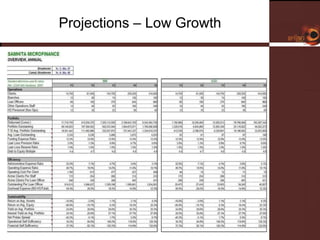
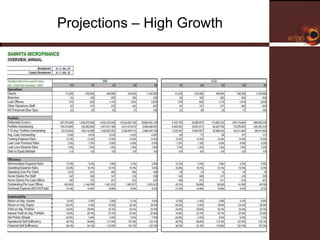
Samhita Microfinance is a startup microfinance institution operating in Madhya Pradesh, India. It provides microloans to low-income individuals, especially women, for productive purposes like livestock and small businesses. It has over 3,000 clients and a loan portfolio of $2 million after 6 months of operations. The founders have experience in microfinance and are seeking $5 million in equity funding over 5 years to expand operations and introduce additional financial and health services to better serve its clients.





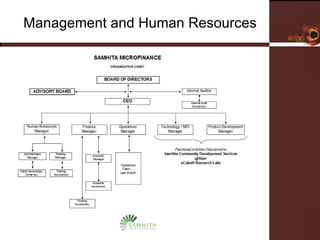
![Solution through Samhita Microfinance Samhita Microfinance is the microfinance initiative of its parent, Samhita Community Development Services [SCDS]. 3 Cornerstones of the SCDS broader strategy Common Appropriate Technology Platform Generate service efficiencies, cost reduction and product innovation through technology. In-house, live, responsive common solutions to multiple developmental needs. Network affiliate eCubeH Research Labs is the technology partner. Economic Initiatives Provision of capital for small enterprises Undertaking livelihood projects to further increase income from the small enterprises Primary Health Initiatives Begin with multimedia health education. Revenue-based self-managed health service network. Tele-medicine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-samhita-1216013879510812-9/85/Samhita-7-320.jpg)


![Microfinance Methodology Model Adaptation of Grameen / ASA models Joint Liability Groups Training Group Recognition Test Center Meetings Loan Proposals / Appraisals / Disbursement Loan Follow-ups Target Market Exclusive Targeting - Women of Poor Households Samhita Poverty Assessment Score [SPAS] mechanism More conservative than international USD1 PPP cutoff Factors housing quality, land and animal holdings, other assets, stability of income sources, family size, and access to basic services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-samhita-1216013879510812-9/85/Samhita-10-320.jpg)

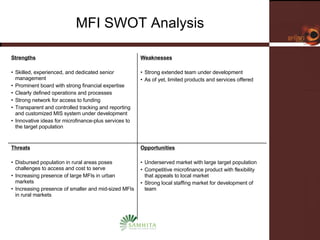
![Competition Competitors Large players expanding nationally (e.g., SKS, SHARE, Spandana) Downscaling banks and financial institutions (e.g., Fullerton) Smaller and mid-sized regional MFIs Government banks offering loans Retailers, Telecom service providers [potential] Competitive Assessment Scale of bigger competitors allows for Ease of access to capital and human resources Defined and scalable processes and operations Capacity to saturate new market rapidly Product offerings across competitors Limited differentiation on microfinance product offerings Some insurance services offered also with limited differentiation Little to no micro enterprise Service Little differentiation on customer service between market players (potential opportunity for differentiation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-samhita-1216013879510812-9/85/Samhita-14-320.jpg)











![Thank You Praseeda Kunam [email_address] Samhita Community Development Services 2/16/504, Nehru Nagar Rewa, MP 500026, India [email_address] Ph: (07662) 406101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-samhita-1216013879510812-9/85/Samhita-33-320.jpg)