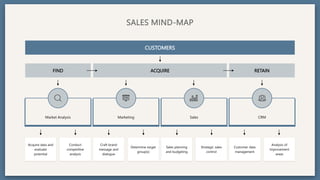
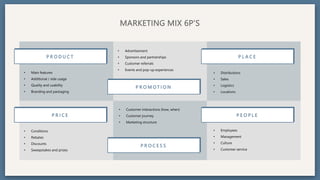
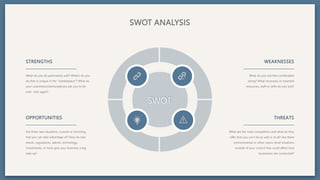
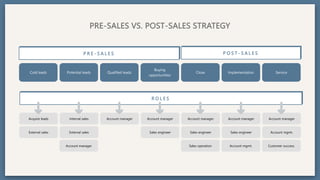
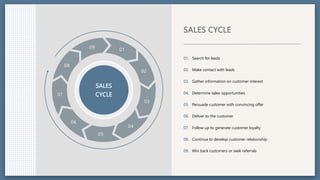
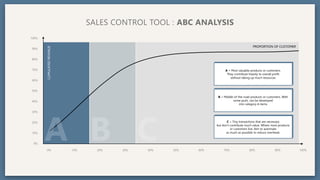
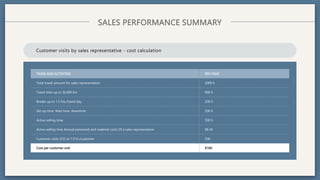
The document provides an overview of key concepts for developing an effective sales strategy, including conducting market analysis, crafting marketing messages, determining target customers, and analyzing competitive strengths and weaknesses. It also outlines the sales cycle from acquiring leads to developing customer loyalty, as well as tools for sales planning like ABC analysis and metrics for evaluating sales performance.