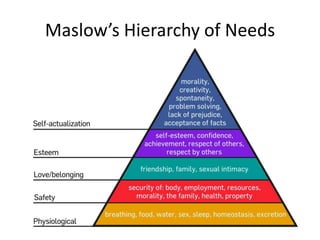
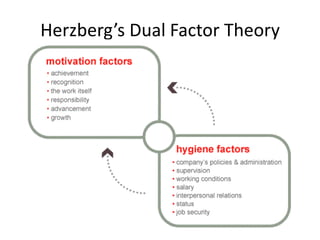
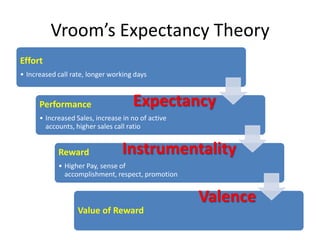
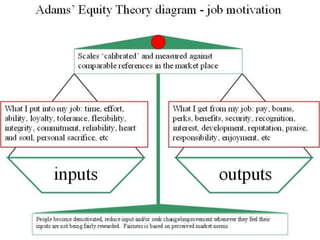
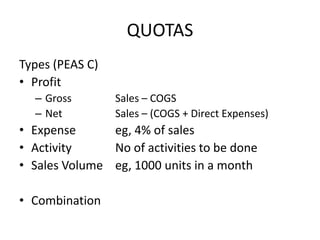
This document discusses sales management and the sales process. It covers topics like forecasting personnel needs, creating job descriptions, recruiting and selecting salespeople, training salespeople, setting quotas, and compensating the sales force. The key aspects of the sales process discussed include analyzing jobs, preparing job descriptions, identifying qualifications, recruiting through various sources, conducting interviews, making job offers, and onboarding new hires. It also examines theories of motivation like Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's dual factor theory, and Vroom's expectancy theory. The document provides details on training programs, content, methods, and evaluation. It outlines the buyer's decision process and the personal selling process. Finally, it discusses different types of compensation