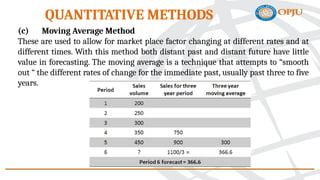
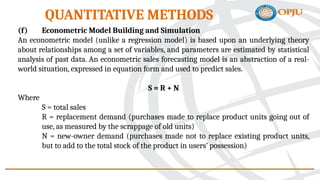
The document outlines various personal selling objectives and methods for sales forecasting, including analyzing market potential, sales potential, and sales forecasts. It details qualitative and quantitative methods for forecasting sales, such as the jury of executive opinion, Delphi technique, and regression analysis, emphasizing that no forecasting method is foolproof. Additionally, the document explains the differences between market potential and sales potential, highlighting factors that may cause sales forecasts to differ from potential sales.