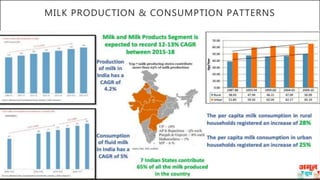
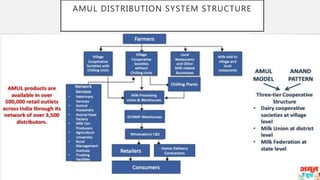
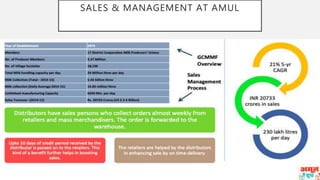
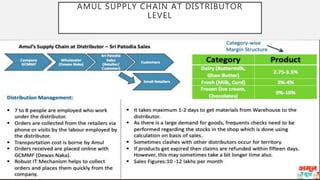
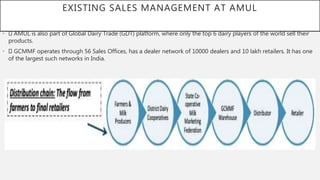
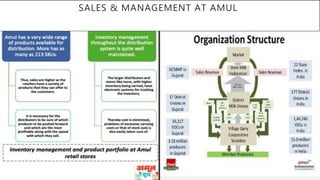
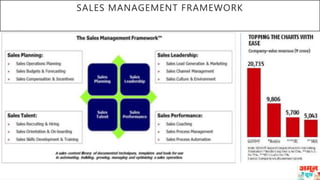
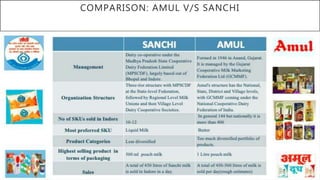
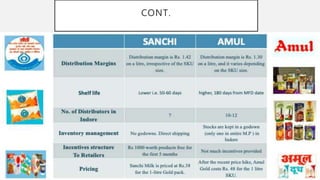
This document discusses Amul's cooperative business model for milk production and sales. It summarizes that Amul pays farmers based on both the quality and quantity of milk produced, and provides additional profits annually based on sales of value-added dairy products. It then outlines Amul's large distribution network of over 10,000 dealers and 1 million retailers across India. Finally, it provides recommendations for Amul to improve its operations and sales in Madhya Pradesh, such as increasing warehouses and distributors, improving demand forecasting, and promoting itself as a healthy brand.