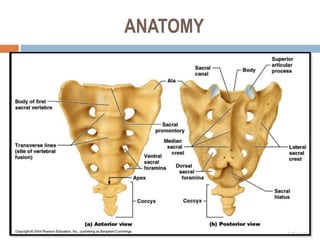
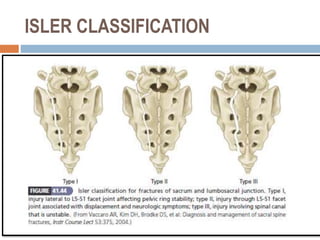
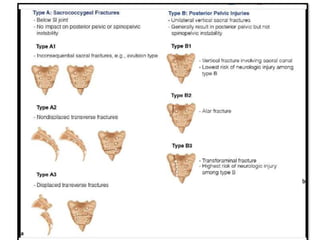
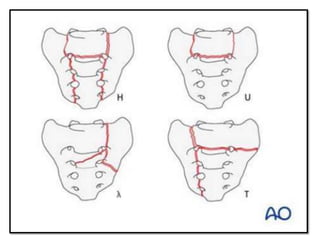
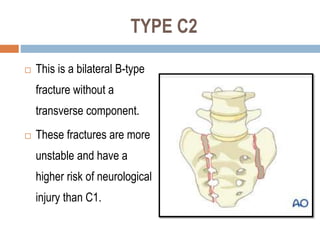
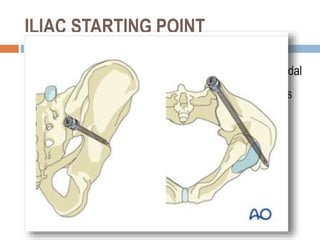
Sacral fractures involve the irregularly shaped sacrum bone made up of five fused vertebrae. It plays a central role in pelvic and spinal stability. Sacral fractures can injure the sacral nerve roots affecting bowel, bladder, and sexual function. Imaging like CT scans are needed to identify fracture type and involvement of neurologic structures. Several classification systems exist, with the AO system describing fracture morphology, neurologic status, and modifiers. Treatment depends on fracture type but may include conservative care, plating, or various fixation procedures like iliosacral screws.