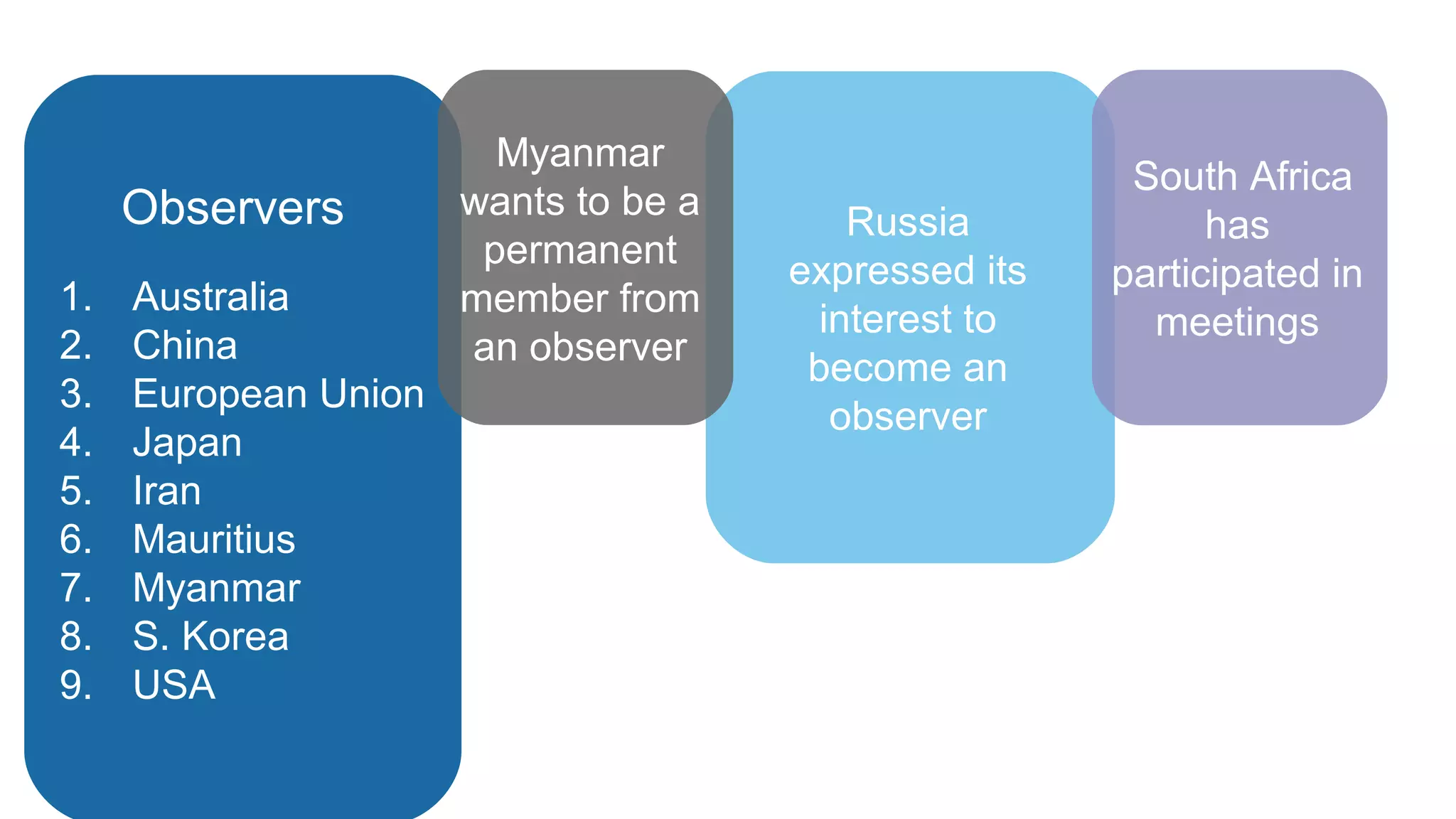
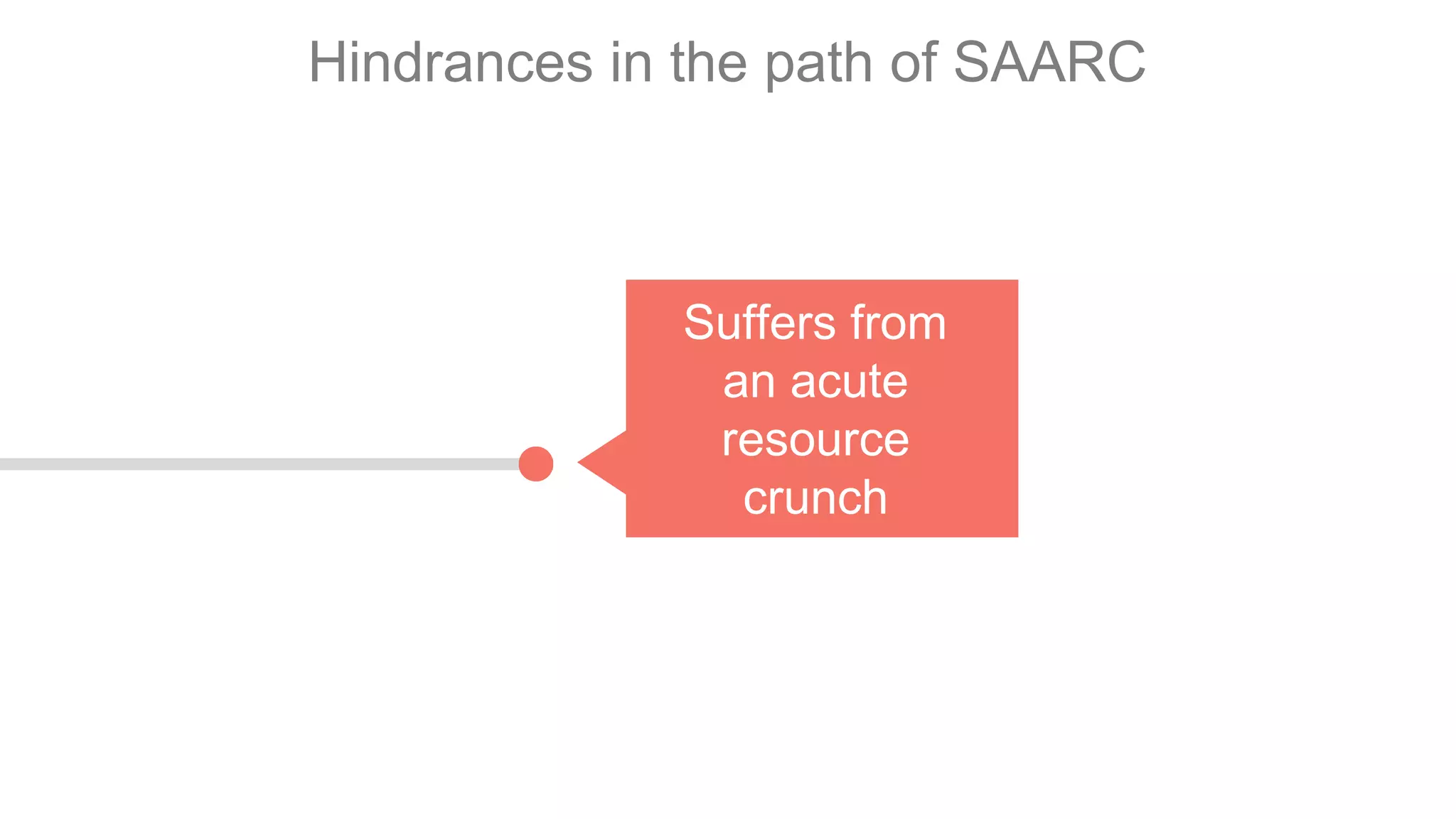
SAARC is an eco-political and intergovernmental organization in South Asia with 8 member states and 9 observer states, established for regional cooperation and development. It aims to promote economic growth and social progress among member nations but has faced challenges such as political rivalries, particularly between India and Pakistan, and internal conflicts that hinder its effectiveness compared to other regional associations like ASEAN. Key activities include the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) and cultural cooperation initiatives, though it struggles with resource constraints and differing political systems among its members.