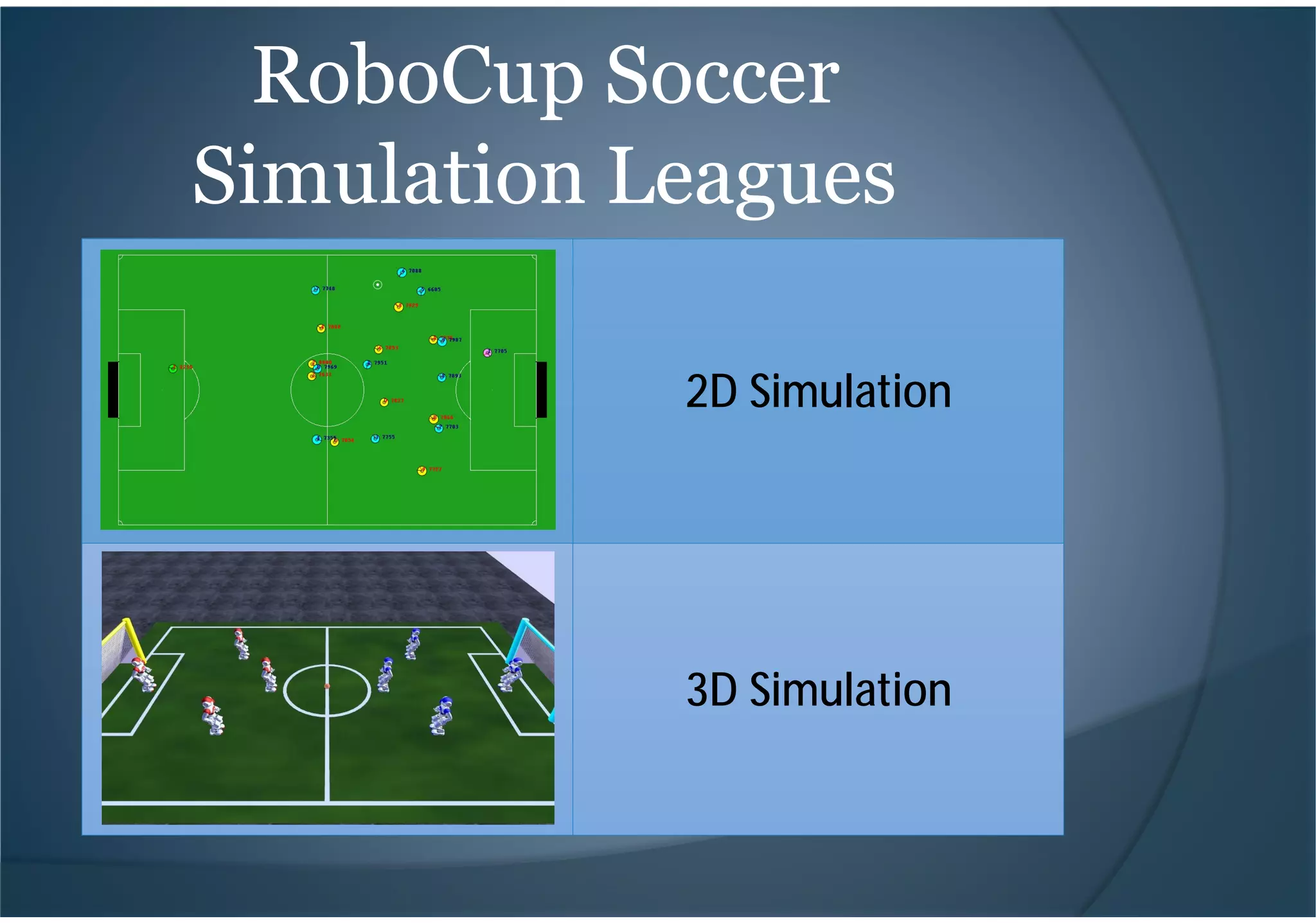
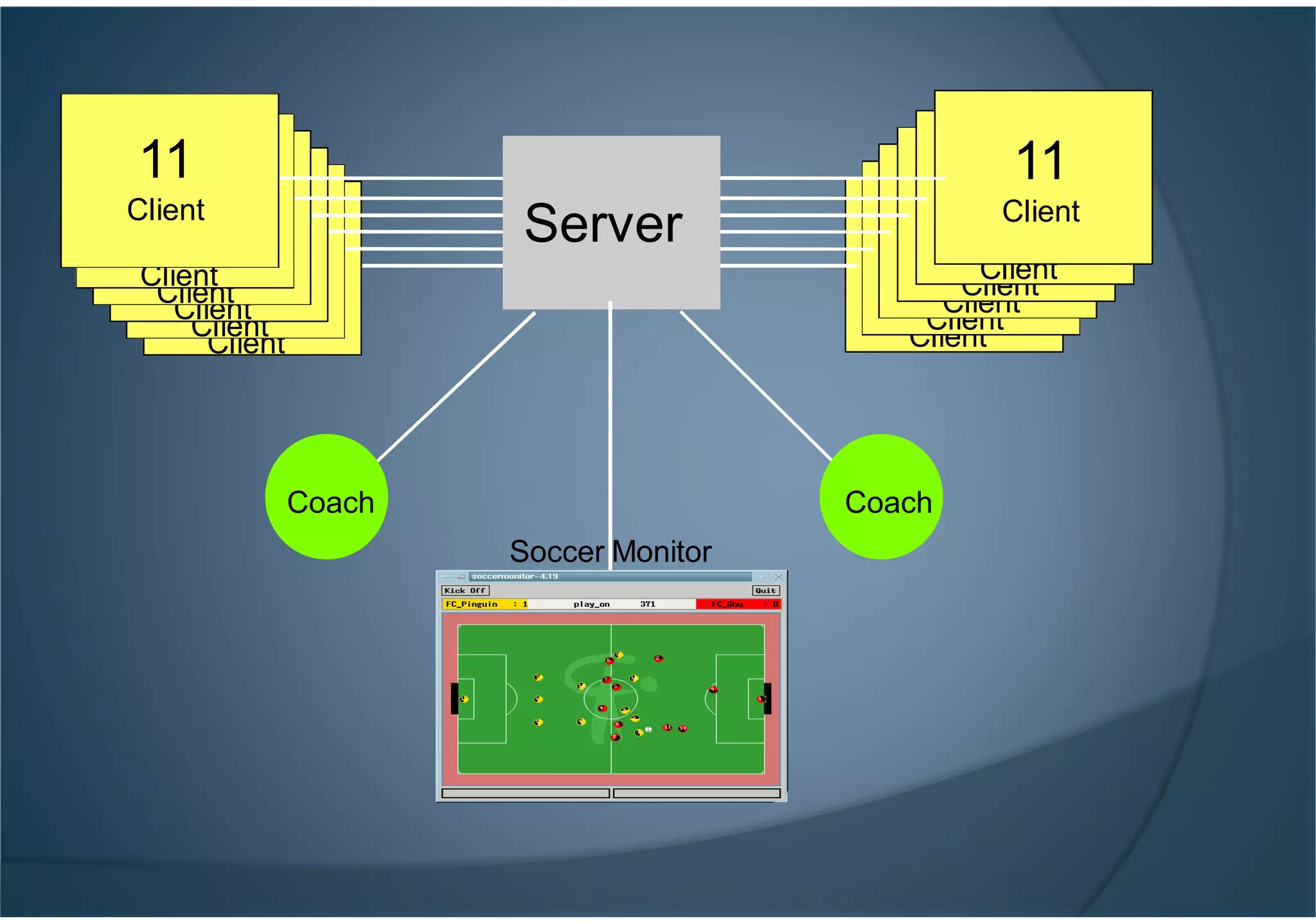
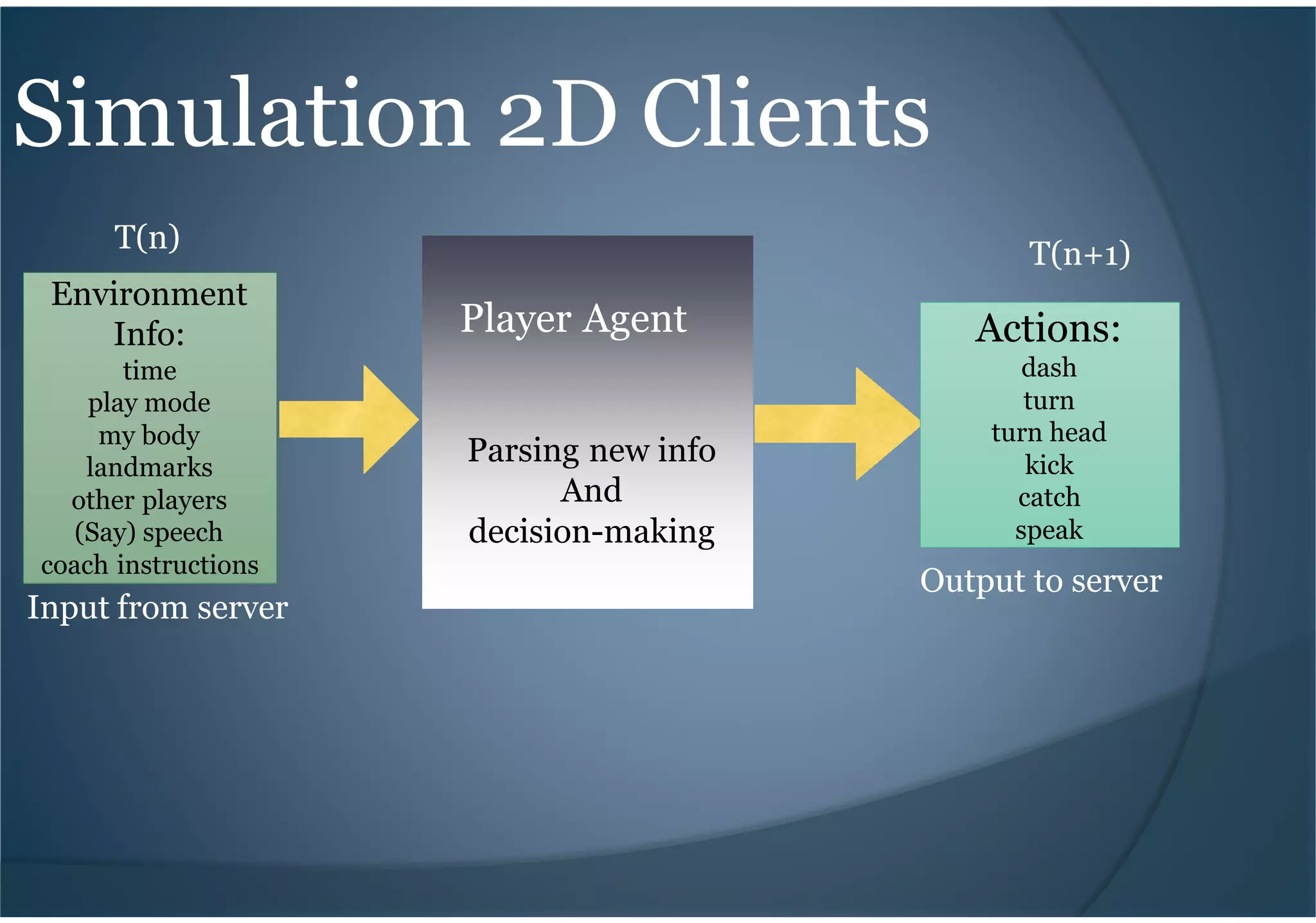
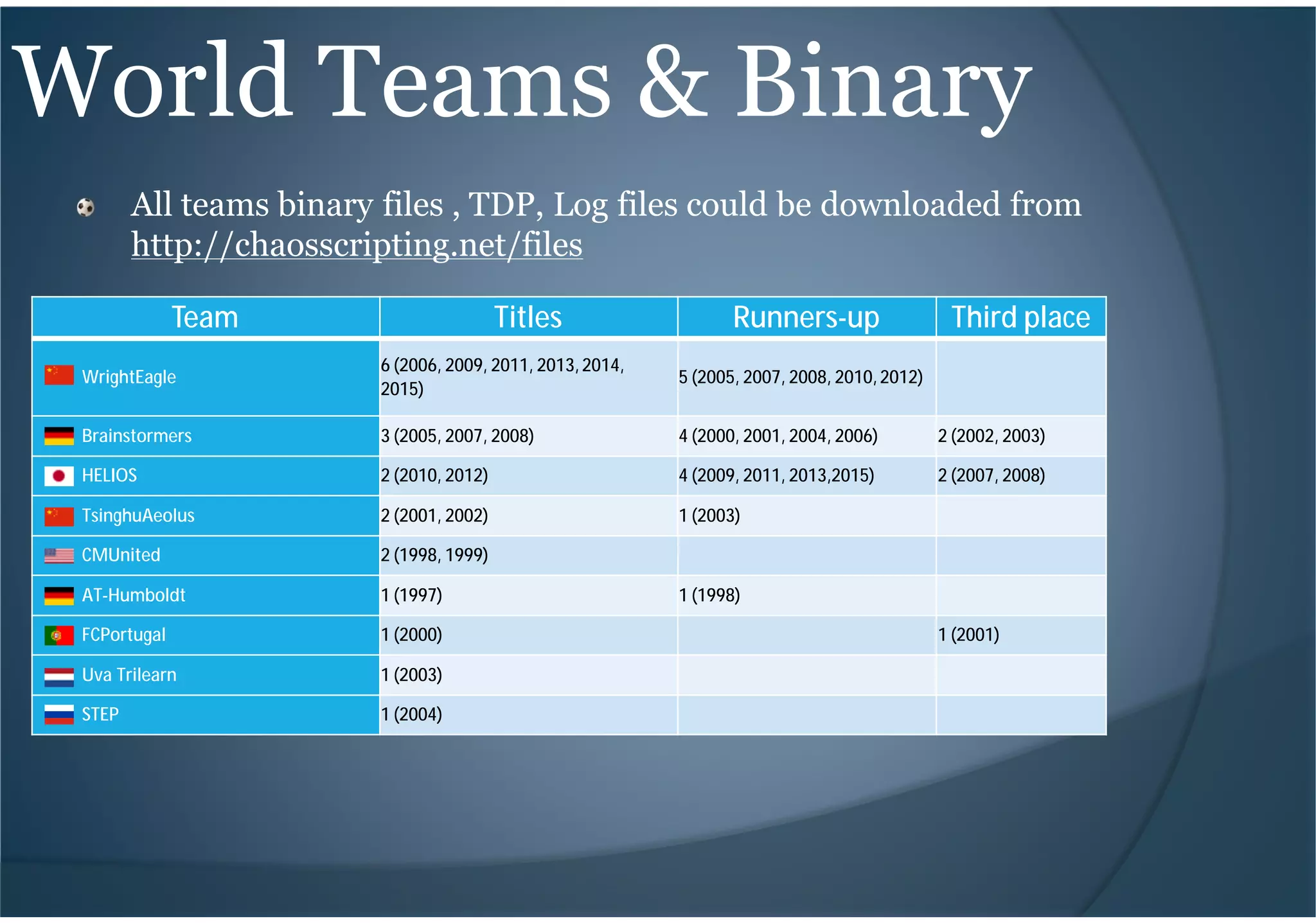
This document provides an introduction to RoboCup, a global robotics competition focused on developing autonomous humanoid robots that can play soccer. It discusses the goals of RoboCup to develop fully autonomous humanoid robots that can defeat the human world soccer champions by 2050. It describes the different RoboCup leagues including soccer simulation, where software agents play soccer in a simulated environment. It provides an overview of the soccer simulation setup, components like the server and clients, and how teams can install and start a simulated soccer game. It also briefly mentions some top performing teams in the soccer simulation league over the years.