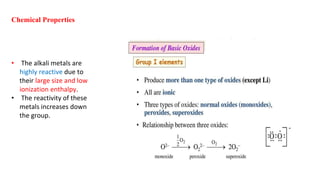
The document discusses several properties of alkali metals. It states that the hydration enthalpy of ions, which is the heat released when ions dissolve in water, is always negative and decreases with increasing ionic size from Li+ to Cs+. It also notes that density increases down the group, though K is lighter than Na. Different alkali metals and their salts impart different colors to flames due to electron excitation and emission. Detection methods include flame tests, flame photometry, and atomic absorption spectroscopy. Chemical reactivity increases down the group as ionization enthalpy decreases.