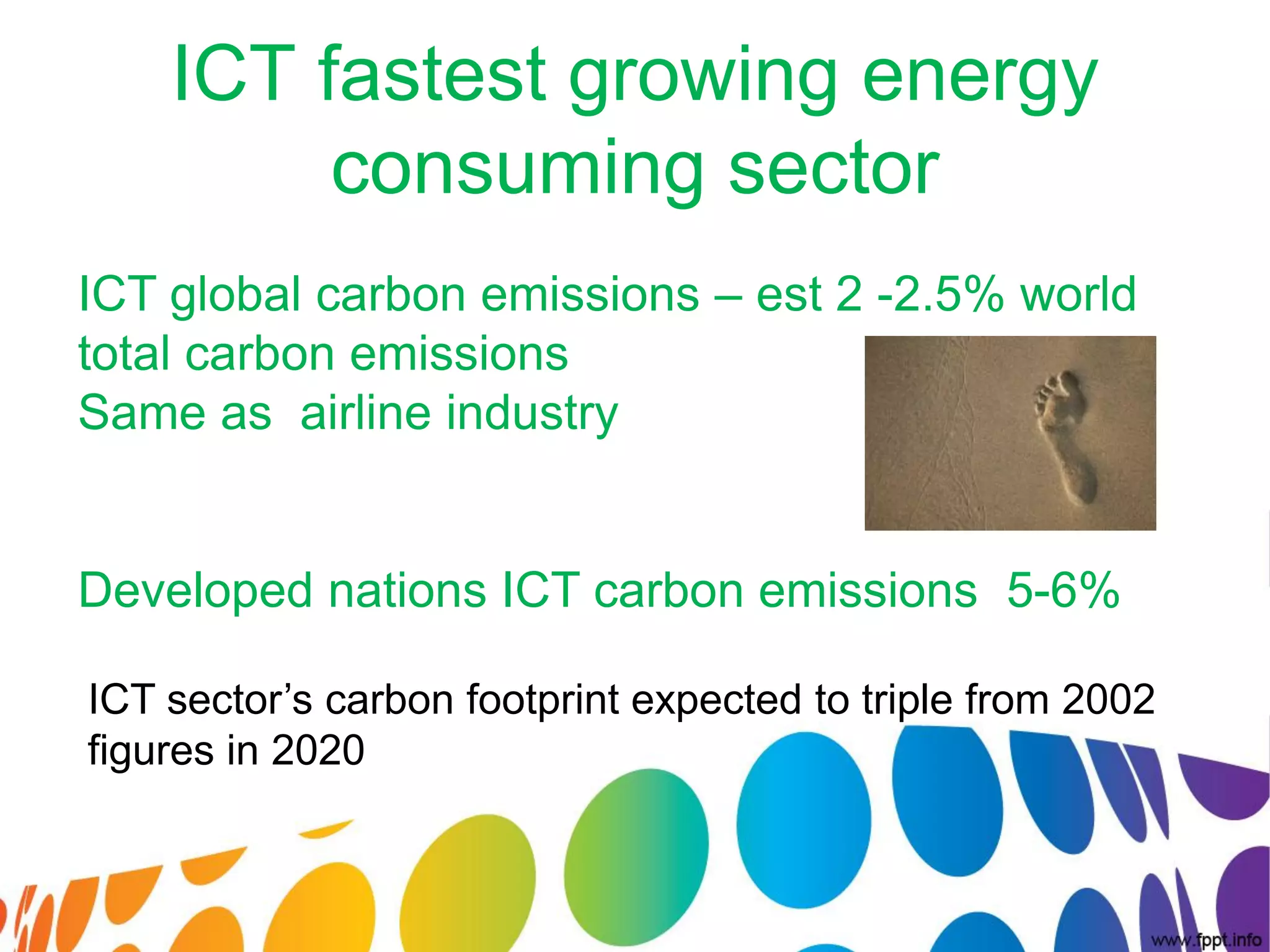
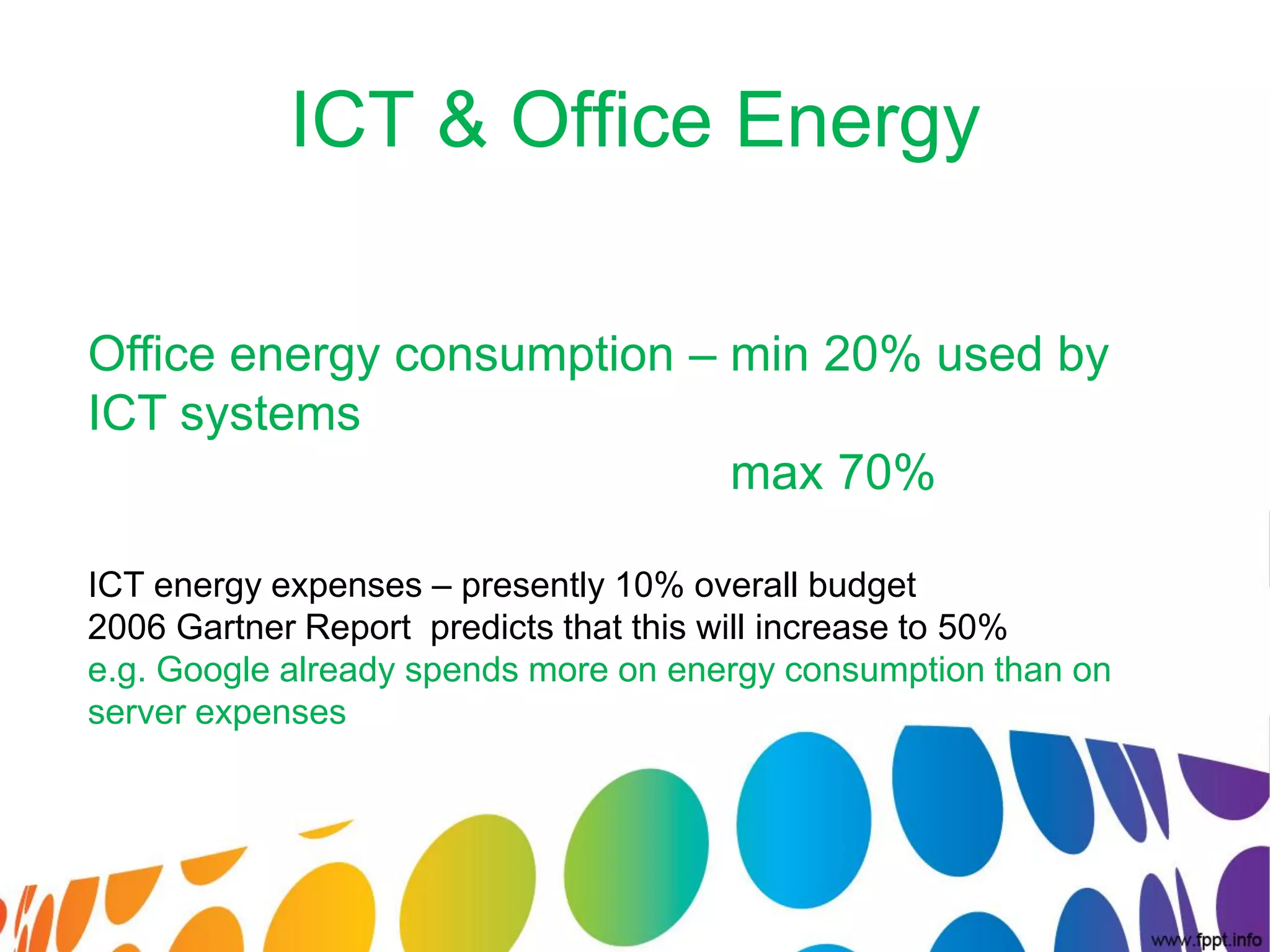
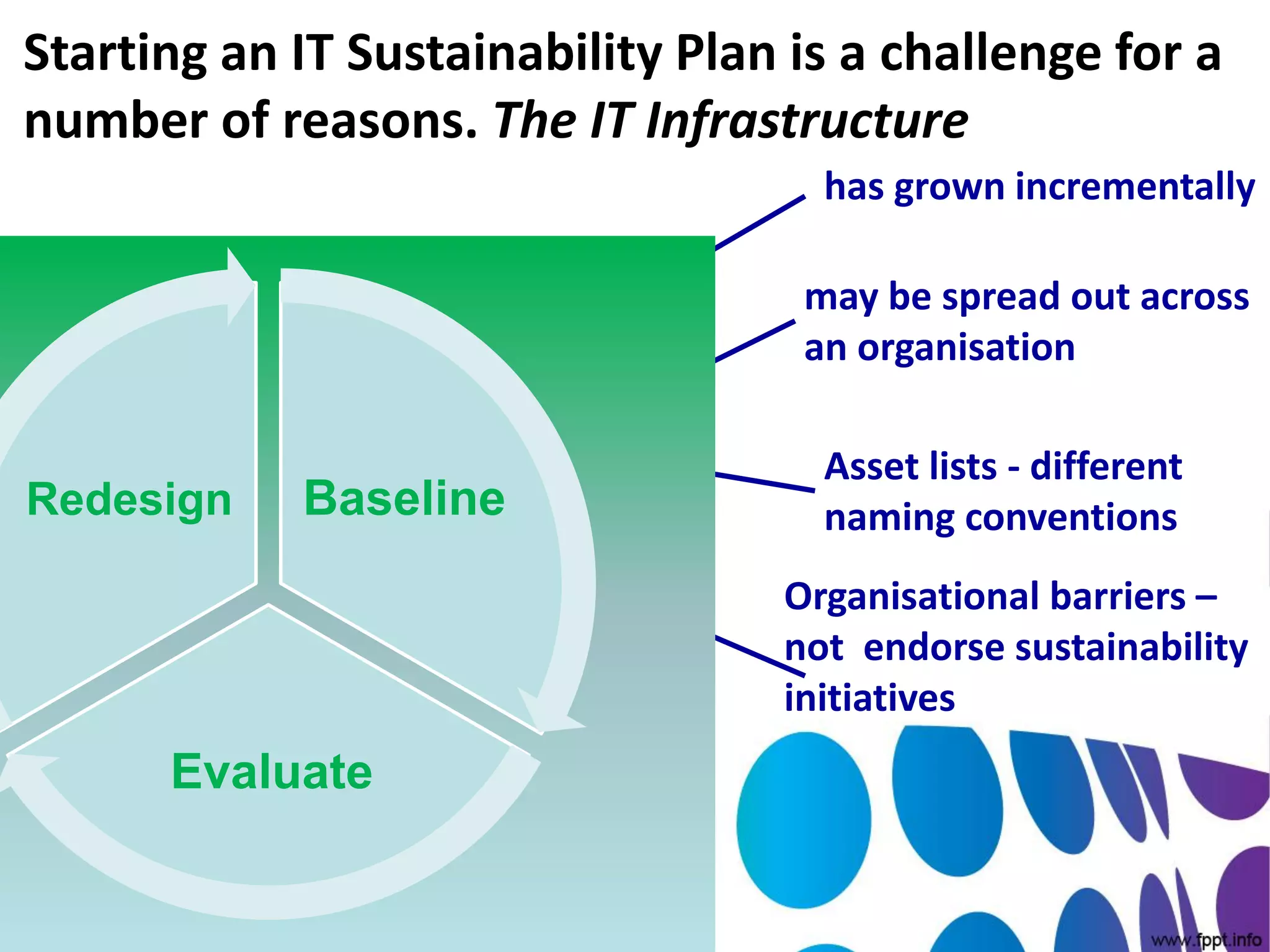
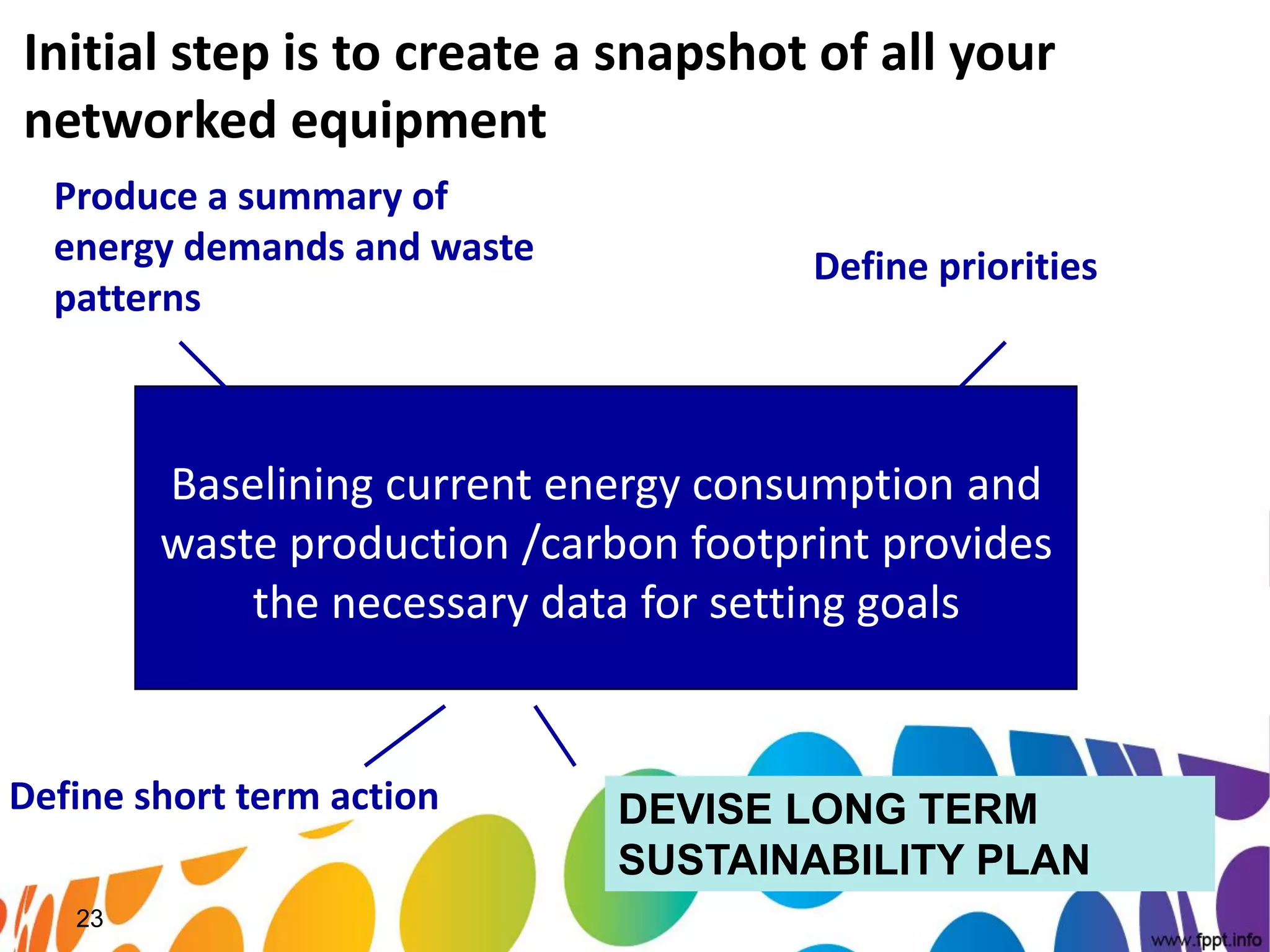
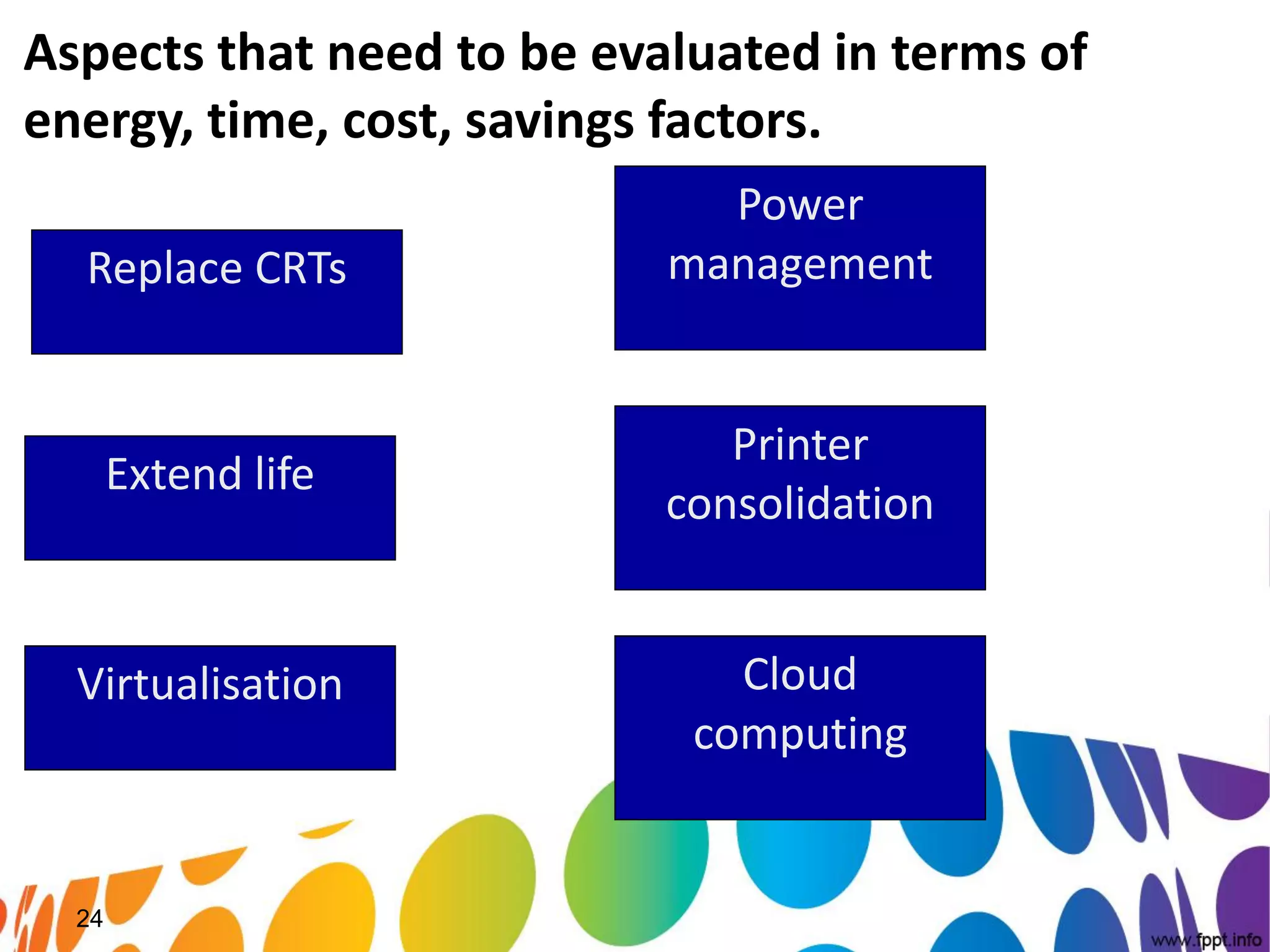
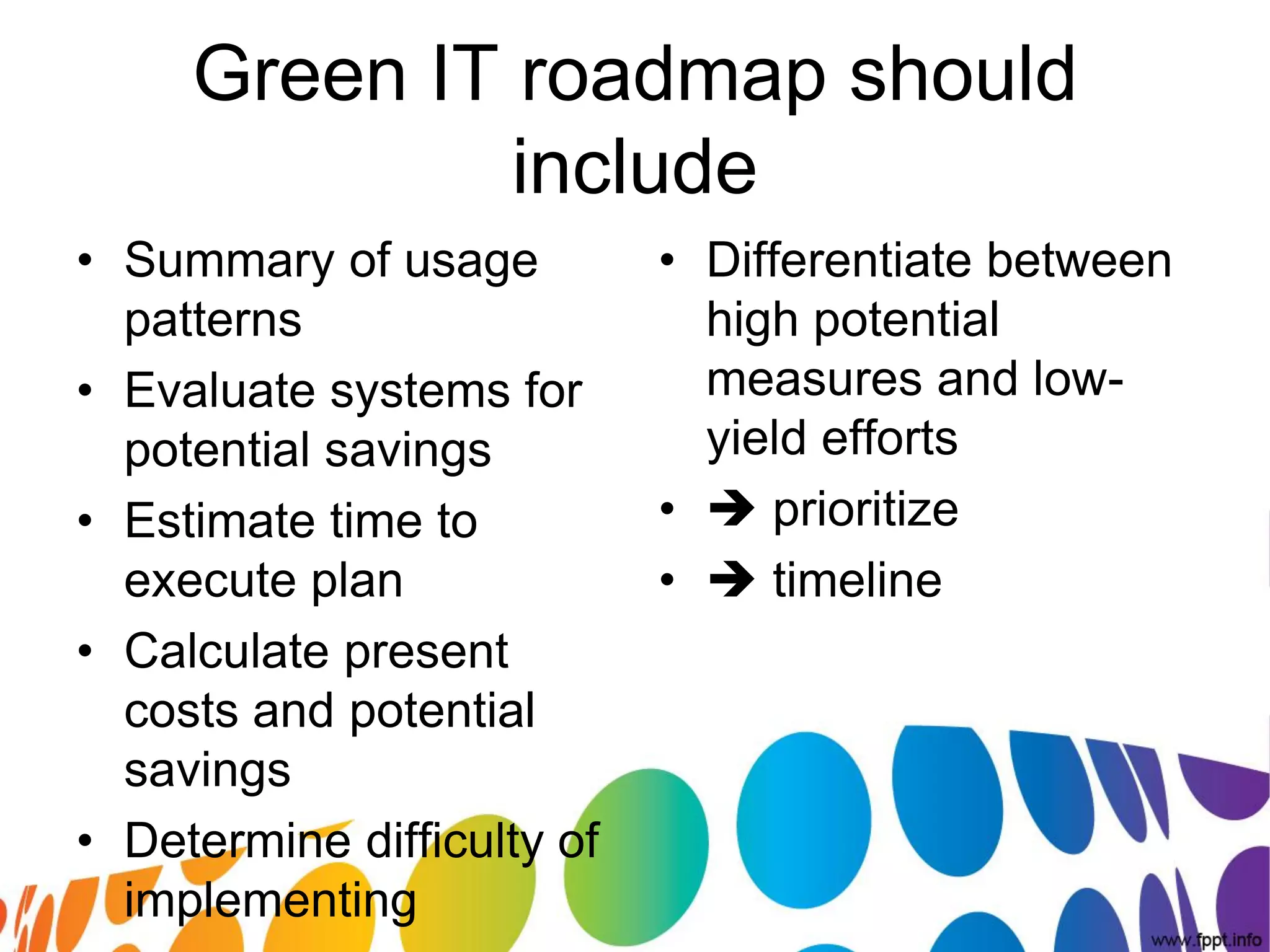
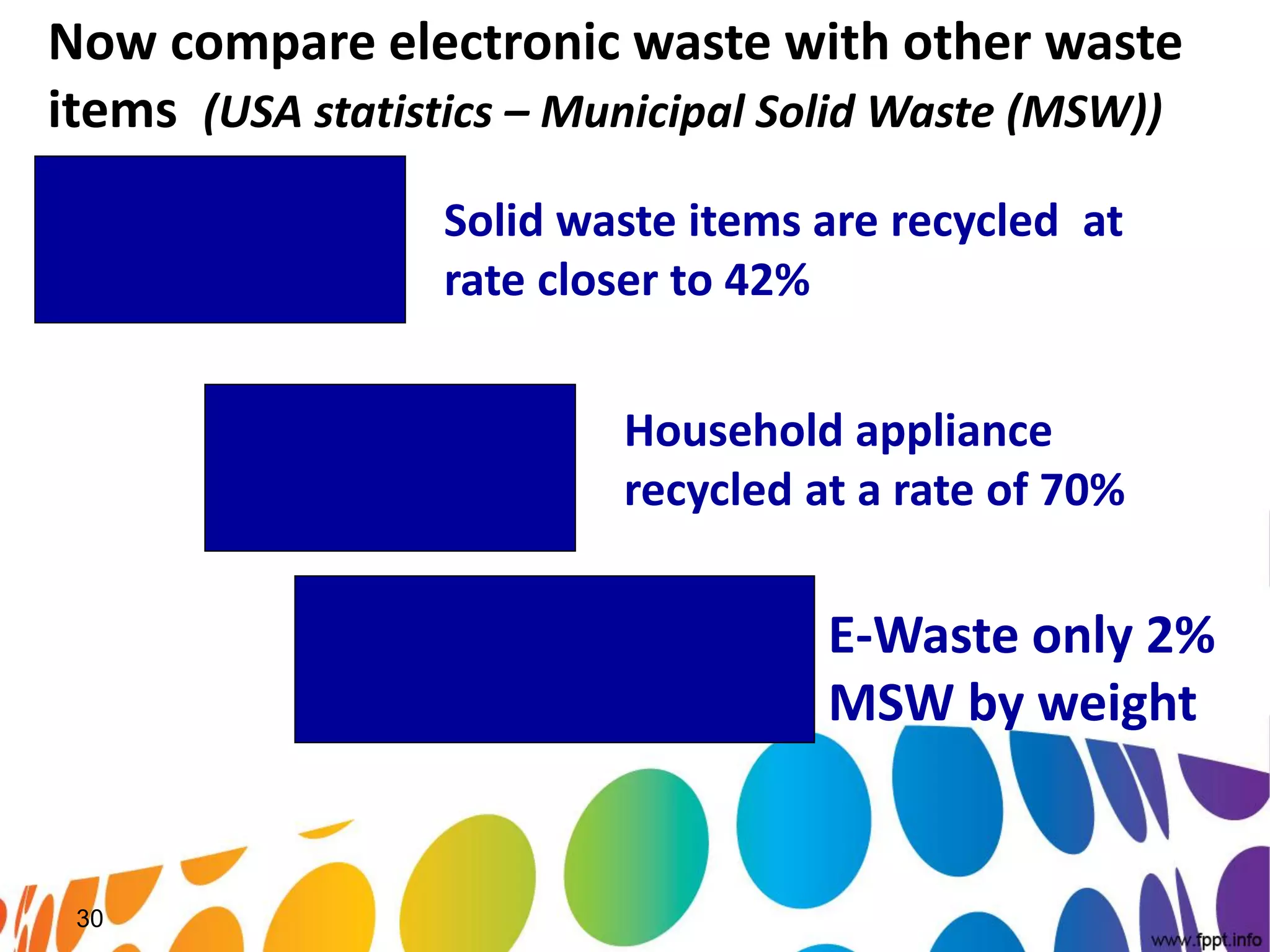
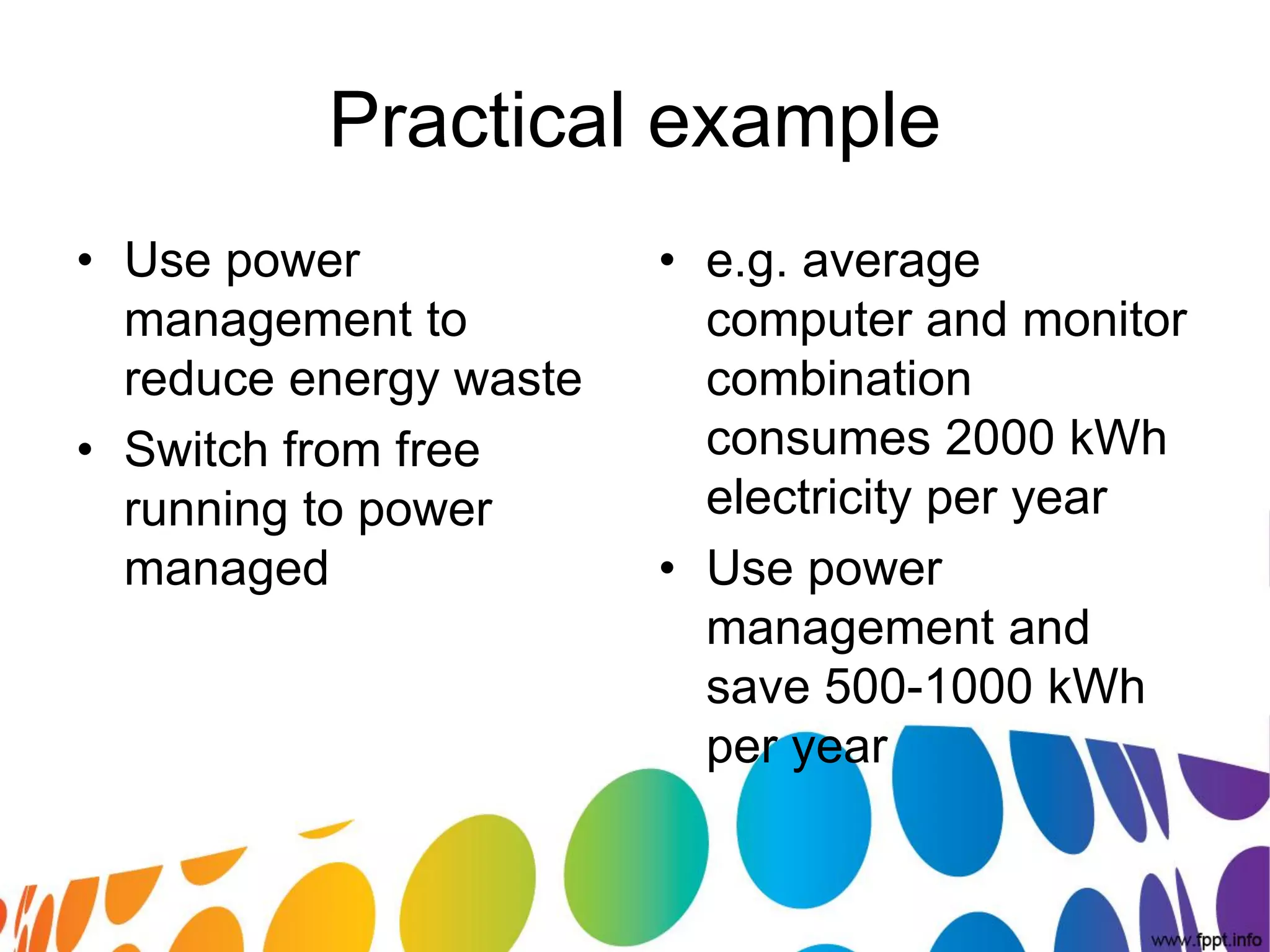
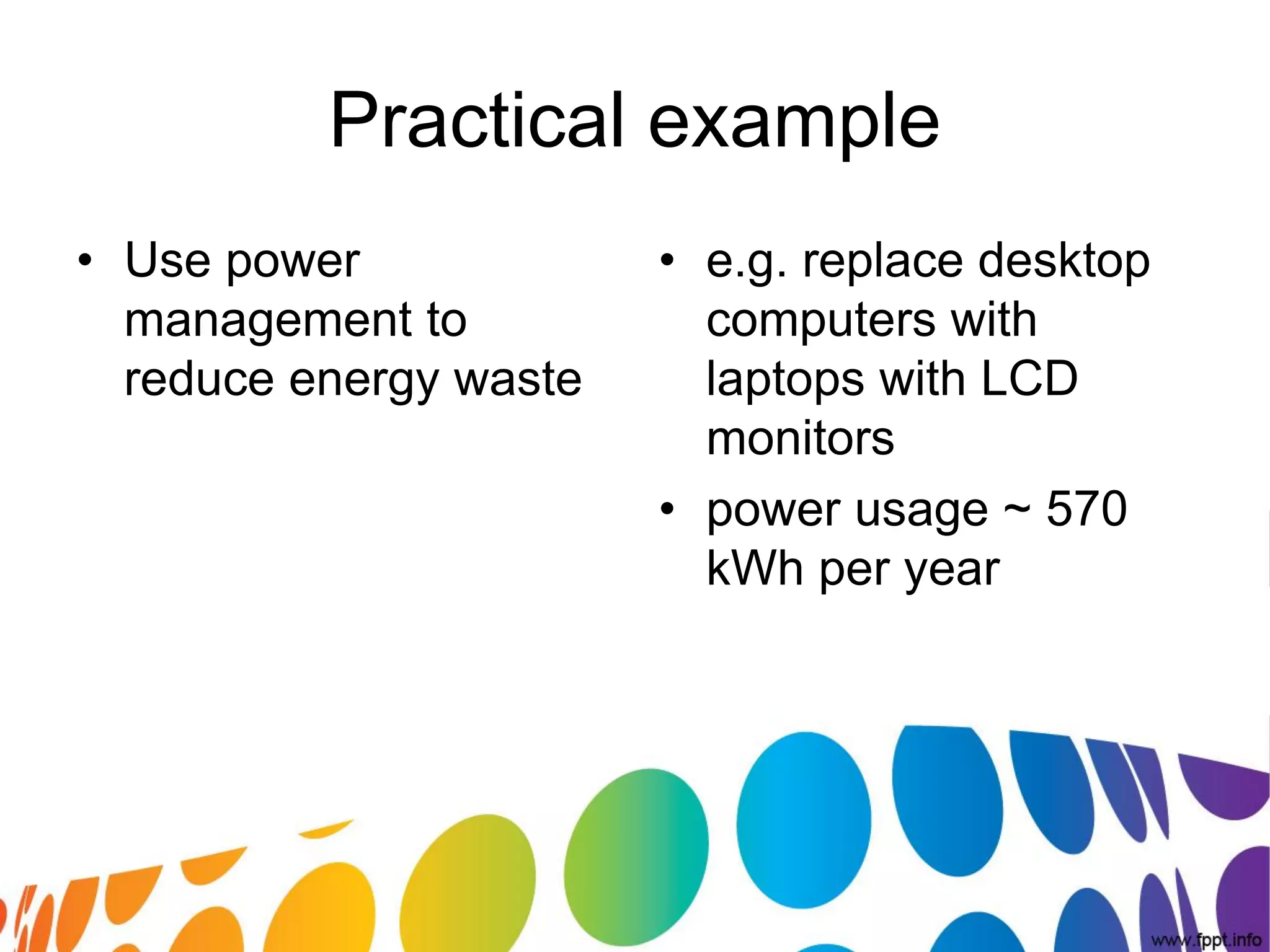
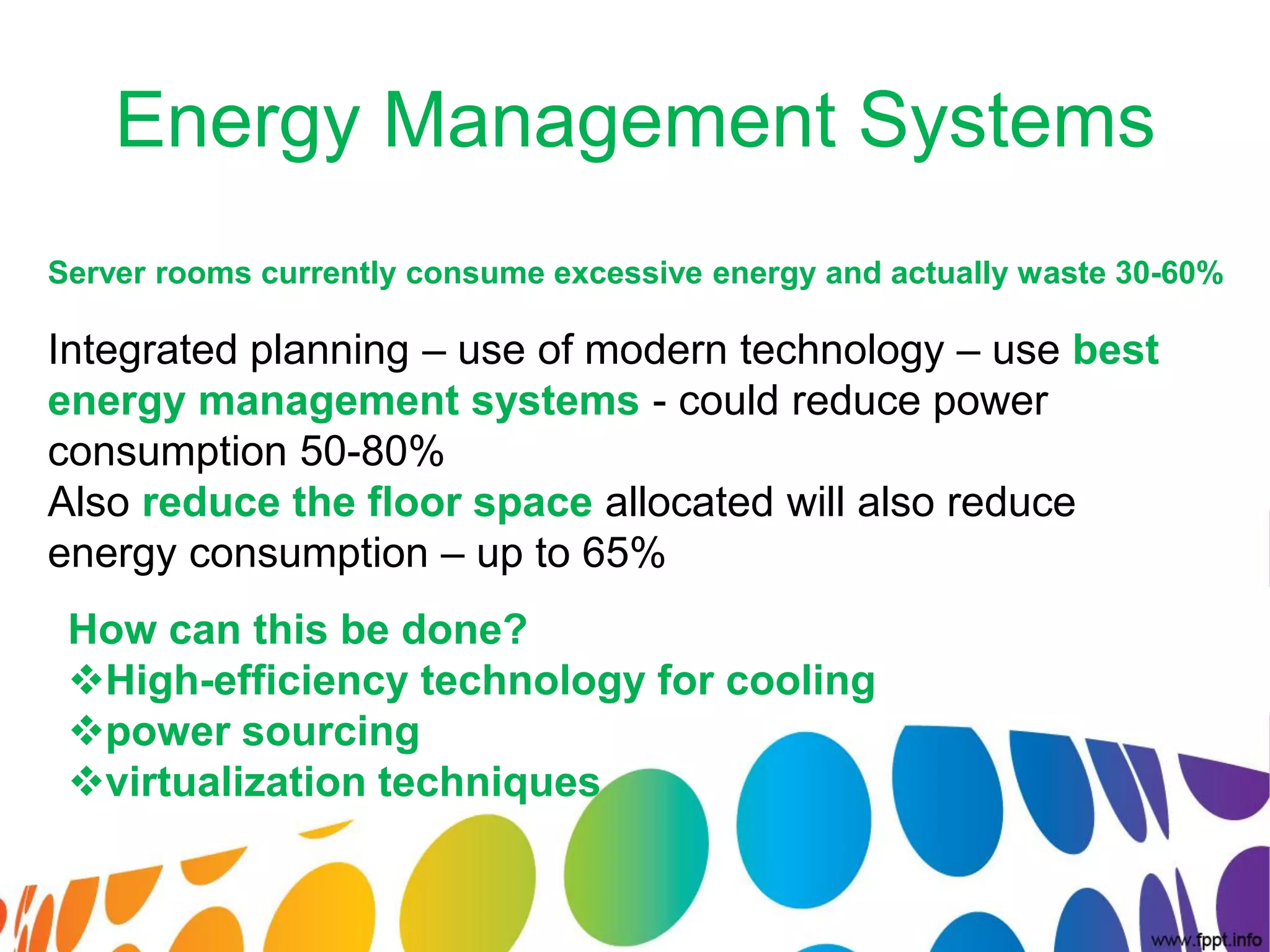
The document outlines a roadmap for implementing green IT practices. It discusses establishing a baseline of current energy usage and emissions. It then recommends short-term initiatives like power management and virtualization to reduce energy costs. Long-term, it suggests a strategic sustainability plan involving stakeholders to transition the organization to more eco-friendly IT through initiatives like green procurement, equipment refurbishing, and responsible e-waste recycling. The roadmap provides a framework for organizations to systematically improve their environmental performance through innovative technology solutions.