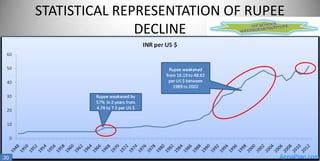
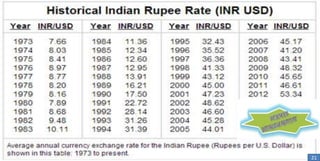
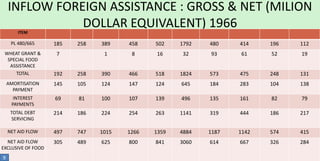
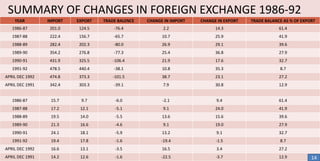
The document discusses India's exchange rate policies and crises since independence in 1947. It summarizes that India faced major financial crises and rupee devaluations in 1966 and 1991. In 1966, a war with Pakistan, drought, and reduced foreign aid necessitated devaluation despite trade restrictions. In 1991, high inflation, inconsistent trade deficits, and inadequate export incentives caused a crisis that led to economic liberalization. Foreign exchange reserves grew steadily from 2006-2012 except for a decline in 2008-2009 during the global financial crisis.



















![SUMMARY OF CHANGES IN FOREIGN EXCHANGE 2006-12
SL
NO.
YEAR
FOREIGN EXCHANGE
RESERVE AT END OF
FINANCIAL YEAR
TOTAL INCREASE/
DECREASE IN RESERVES
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
2006-07
199.2
+47.6
3
2007-08
309.7
+110.5
4
2008-09
252.0
-57.7
5
2009-10
279.1
+27.1
6
2010-11
304.8
+25.7
7
2011-12
311.5
+6.7
+36.6
[76.9%]
+92.2
[83.4%]
-20.1
[34.8%]
+13.4
[49.4%]
+13.1
[51.0%]
+5.7
[85.1%]
+11.0
[23.1%]
+18.3
[16.6%]
-37.6
[65.2]
+13.7
[50.6%]
+12.6
[49.0%]
+1.0
[14.9%]
18
INCREASE/DECREASE IN INCREASE/DEC
RESERVES ON BOP BASIS
REASE IN
RESERVES DUE
TO VALUATION
EFFECT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rupee-131201231838-phpapp01/85/Rupee-depreciation-22-320.jpg)