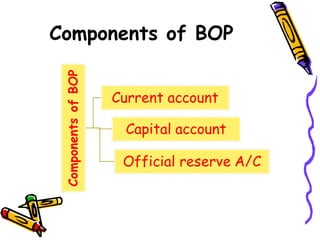
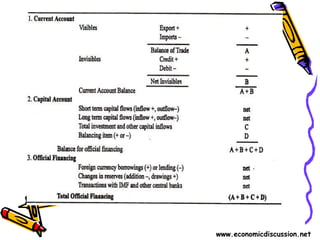
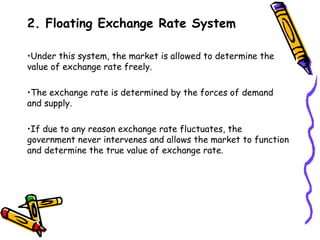
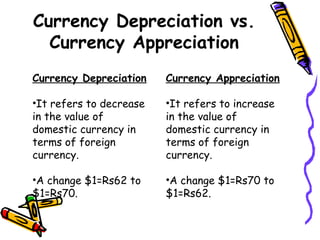
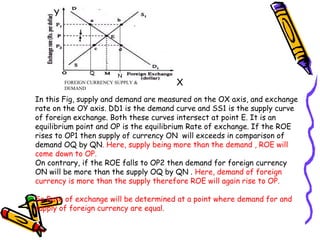
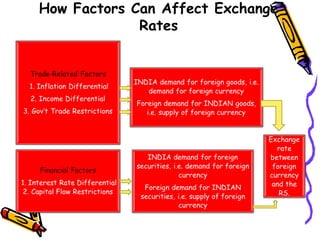
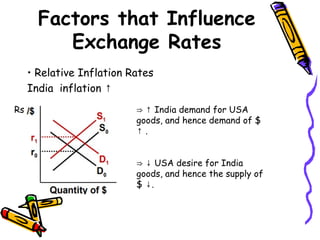
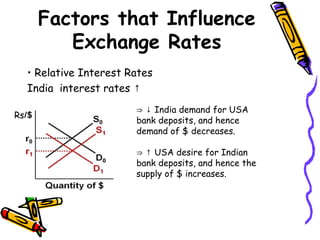
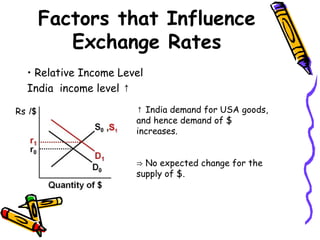
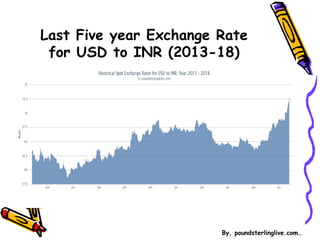
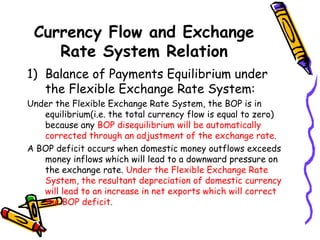
The document discusses currency flow, detailing its inflow and outflow between countries driven by international trade and transactions, and the role of balance of payments in recording these transactions. It also explains exchange rate determination, covering fixed versus floating exchange rate systems, currency depreciation and appreciation, and factors influencing exchange rates such as inflation and interest rates. Finally, the relationship between balance of payments and exchange rate systems is analyzed, highlighting how flexible and fixed systems address deficits differently.