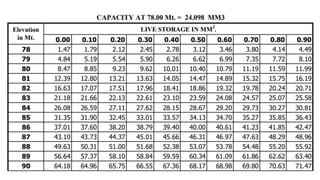
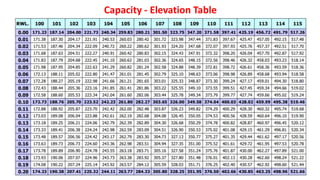
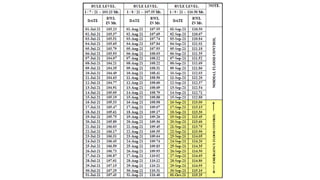
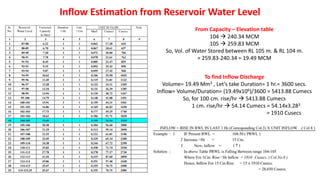
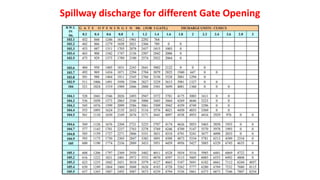
The document explains the various aspects of reservoir management, including definitions of dead storage, live storage, and gross storage, as well as the importance of rule levels for flood control and water regulation. It details the role of inflow data, water requirements, and past experiences in determining rule levels, in addition to flood routing and gate operation techniques for managing water discharge. Finally, it mentions graphical representations of storage capacity and area-elevation curves to aid in understanding reservoir dynamics.