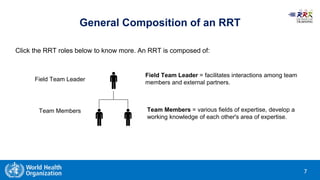
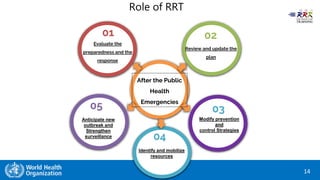
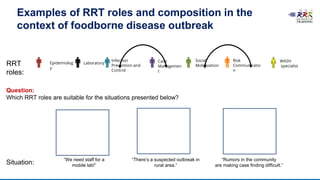
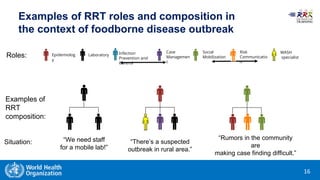
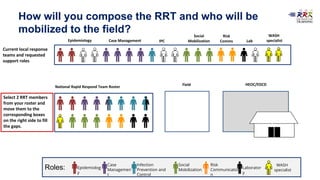
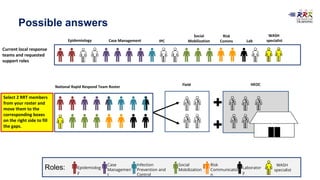
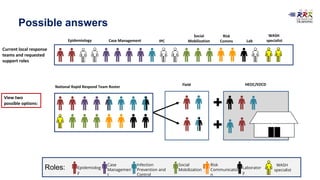
This document provides training materials on Rapid Response Teams (RRTs). It outlines the learning objectives, composition, roles, and operation of RRTs. The objectives are to explain what an RRT is and its characteristics, describe the composition and key activities of RRT members, list key partners during interventions, and describe how RRTs link to emergency response systems. An RRT is a multidisciplinary, adequately trained team that can rapidly mobilize as part of an emergency management structure. Key roles include a team leader, clinicians, epidemiologists, communicators, and logistics/support specialists. The document provides a scenario for trainees to practice composing an appropriate RRT based on local response needs.