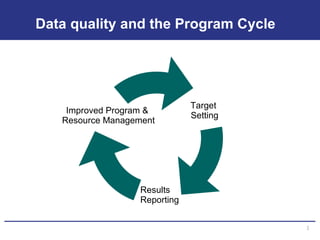
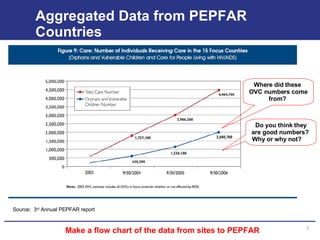
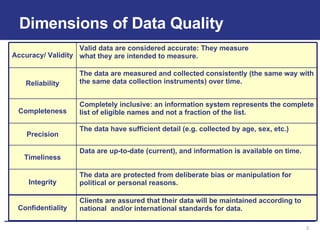
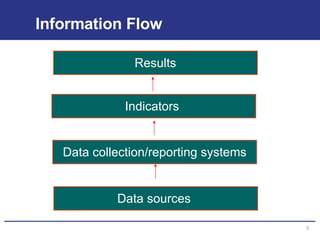
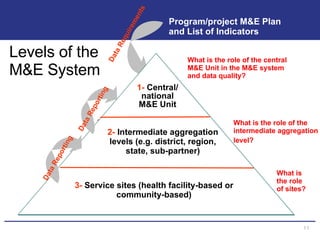
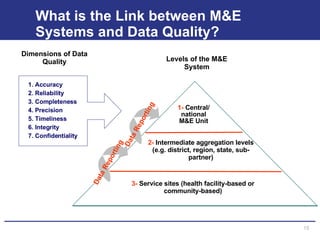
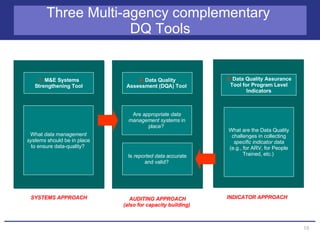
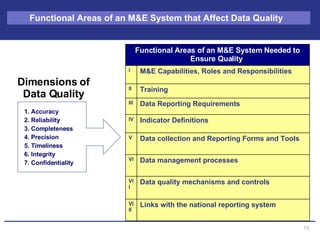
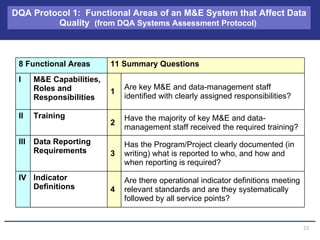
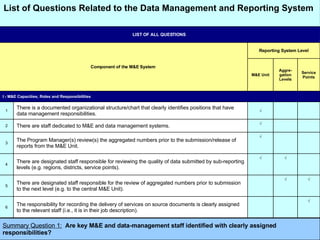
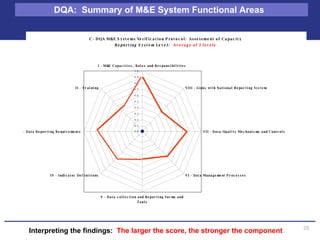
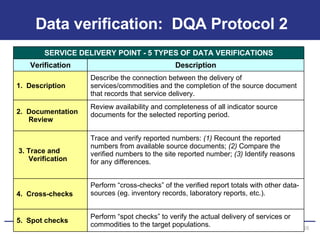
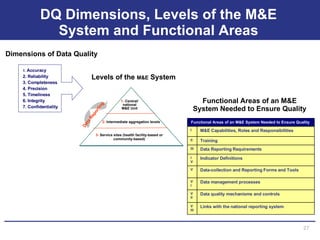
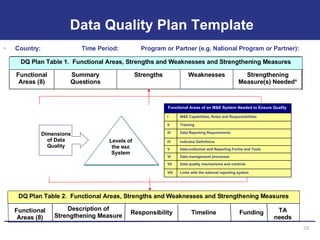
The document discusses the importance of data quality for monitoring and evaluation systems. It describes seven key dimensions of data quality - accuracy, reliability, completeness, precision, timeliness, integrity and confidentiality. It also outlines the different levels of an M&E system from service sites to national reporting and the roles and responsibilities needed at each level to ensure quality data collection, reporting and use. Tools are presented for strengthening M&E systems and assessing data quality.