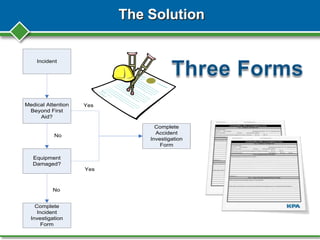
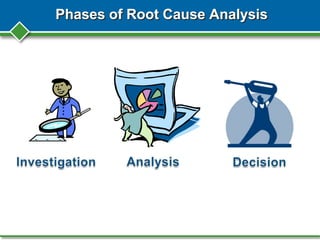
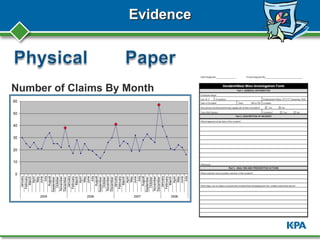
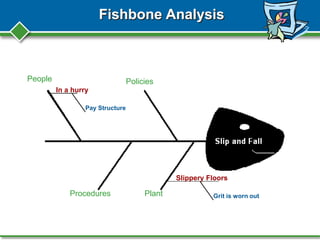
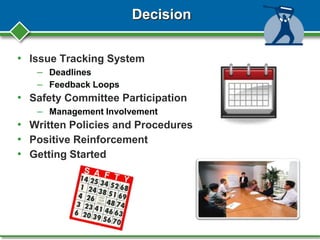
Peter Zaidel from KPA presented on root cause analysis for accident investigations. KPA is a nationwide compliance expert that provides services to over 3000 clients in areas like safety, environmental regulations, and human resources. The presentation covered why accident investigations and root cause analysis are important, how to conduct an investigation, potential causes of accidents, and methods for analyzing the root causes using tools like the 5 whys and fishbone diagrams. The goal of root cause analysis is to prevent future accidents by understanding the underlying reasons they occurred and guiding organizational changes.